ฤทธิ์ในการฟื้นฟูระบบประสาทของสาร 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran จากปลิงทะเลขาว ผ่านกระบวนการต้านความเครียดและลดความเป็นพิษในแบบจำลองโรคพาร์กินสันของหนอน C. elegans ที่ถูกชักนำด้วยสาร 6-OHDA
Highlight
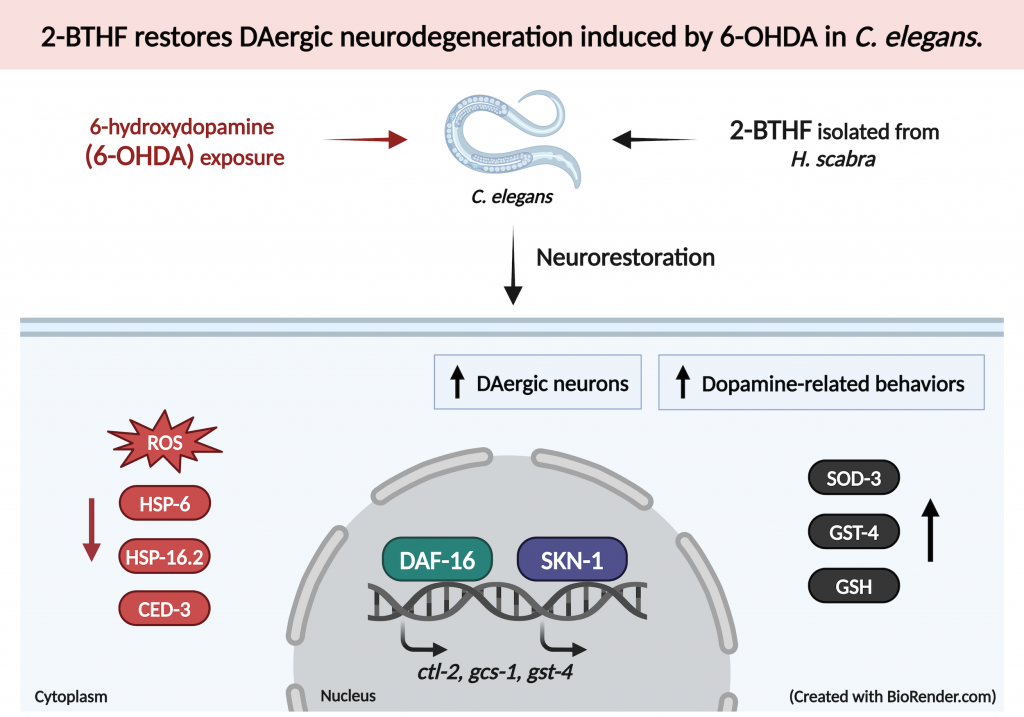
สารสกัด 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran (2-BTHF) จากปลิงทะเลขาว Holothuria scabra ช่วยปกป้องเซลล์ประสาทโดปามีน ฟื้นฟูการเคลื่อนไหวในหนอน C. elegans ที่จำลองโรคพาร์กินสัน ลดความเครียดออกซิเดชัน ฟื้นฟูการทำงานของไมโตคอนเดรีย และกระตุ้นกลไกต้านความเครียดและการลดความเป็นพิษ โดยมีศักยภาพในการพัฒนาเป็นสารป้องกันความเสื่อมของระบบประสาท
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
ปลิงทะเลมีฤทธิ์ป้องกันโรคความเสื่อมของระบบประสาทและฟื้นฟูเซลล์ประสาทจากการถูกทำลาย โดยมีสารออกฤทธิ์ที่สำคัญคือ 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran (2-BTHF) โดยสามารถลดการเกาะกลุ่มและความเป็นพิษของ amyloid-beta และ alpha-synuclein ในโรคความเสื่อมระบบประสาทได้ การศึกษาวิจัยนี้จึงได้ศึกษาการออกฤทธิ์ของ 2-BTHF ต่อโรคพาร์กินสันที่เกิดจากการทำลายเซลล์ประสาทโดปามีน
Abstract
Holothuria scabra (H. scabra), a marine organism traditionally known for its health benefits, has been utilized in both food and medicine. Our previous studies indicated that 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran (2-BTHF), which is isolated from H. scabra, possesses the potential to alleviate amyloid-β and α-synuclein accumulations associated with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases (AD and PD), respectively. However, the mechanisms through which 2-BTHF mitigates PD-related neurotoxicity remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the effects of 2-BTHF on a 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) model. Our results demonstrated that 2-BTHF recovered dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons from degeneration and restored dopamine-related behaviors. Furthermore, 2-BTHF reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, preserved mitochondrial fluorescence, and decreased both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic unfolded protein responses (UPRmt and UPRcyto) activation. Transcriptome sequencing analysis revealed the critical roles of various systems, including the immune system, nervous system, glutathione (GSH) metabolism, xenobiotics, terpenoids, energy metabolism, cell growth and death, and aging-related longevity pathways. Additionally, 2-BTHF showed potential interactions with stress resistance and detoxification transcription factors, promoting the nuclear translocation of DAF-16 and SKN-1, which in turn activated their targets, including SOD-3, CTL-2, GCS-1, and GST-4. Moreover, 2-BTHF increased total GSH levels and reduced the ced-3-related cascade. This study demonstrates that 2-BTHF holds promise as a therapeutic agent for treating 6-OHDA-induced DAergic neurodegeneration in the C. elegans model.
KEYWORDS: Holothuria scabra, 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran, 6-OHDA, Stress resistance, Detoxification, Caenorhabditis elegans
Citation: Promtang S, Sanguanphun T, Chalorak P, Rodma D, Sunan R, Pe LS, Niamnont N, Chompoopong S, Sobhon P, Meemon K*. Neurorestorative properties of 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran from Holothuria scabra via activation of stress resistance and detoxification in a 6-OHDA-induced C. elegans model of Parkinson’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 May 16;188:118158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118158
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Sukrit Promtang
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: ทุนยุทธศาสตร์มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล ประเภท Rising
ภาพถ่าย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
Tags: 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran, 6-OHDA, Caenorhabditis elegans, Detoxification, Holothuria scabra, Stress resistance
