Highlight
การศึกษาปุ่มกระดูกซิฟอยด์ (xiphoid process) พบว่ากระดูกอ่อนเป็นส่วนประกอบปกติที่พบใน 85% ของตัวอย่าง โดยจัดแบ่งปุ่มกระดูกซิฟอยด์ได้เป็น 4 ประเภทตามสัดส่วนของกระดูกและกระดูกอ่อน การทำความเข้าใจนี้ช่วยลดข้อผิดพลาดในการวินิจฉัยและเพิ่มความแม่นยำทางคลินิก
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
ปุ่มกระดูกซิฟอยด์ (xiphoid process) เป็นส่วนที่เล็กที่สุดและมีความหลากหลายมากที่สุดของกระดูกหน้าอก (sternum) ซึ่งประกอบด้วยกระดูกและกระดูกอ่อน โดยในมนุษย์ กระดูกอ่อนบริเวณปุ่มกระดูกซิฟอยด์ถูกมองว่าเป็นความแปรผันทางกายวิภาค การศึกษานี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อสำรวจลักษณะทางกายวิภาคของปุ่มกระดูกซิฟอยด์ผ่านการตัดและตรวจด้วยกล้องจุลทรรศน์ พบว่ารูปแบบของปุ่มกระดูกซิฟอยด์สามารถจัดแบ่งได้เป็น 4 แบบตามสัดส่วนของกระดูกและกระดูกอ่อน ซึ่ง 85% ของปุ่มกระดูกซิฟอยด์มีส่วนประกอบของกระดูกและกระดูกอ่อน การศึกษานี้เน้นให้เห็นความสำคัญของการพิจารณากระดูกอ่อนเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของลักษณะทางกายวิภาคปกติ
Abstract
Background
The xiphoid process (XP) in animals such as sheep and rats are well known to have cartilage called xiphoidal cartilage (XC). In humans, the cartilage in the xiphoid process is considered an anatomical variant and is not well understood. The aim of this study was to investigate the morphology of the XP.
Methods
A total of twenty embalmed European descendant cadaveric sterna (aged 52 to 98 years) were used. Transilluminated XPs and midsagittal sections of XPs were used to examine the bone and cartilage. Subsequently, a sagittally-sectioned XP was harvested for histology and stained with Masson’s trichrome. The results of the transillumination and histological examinations were compared qualitatively.
Results
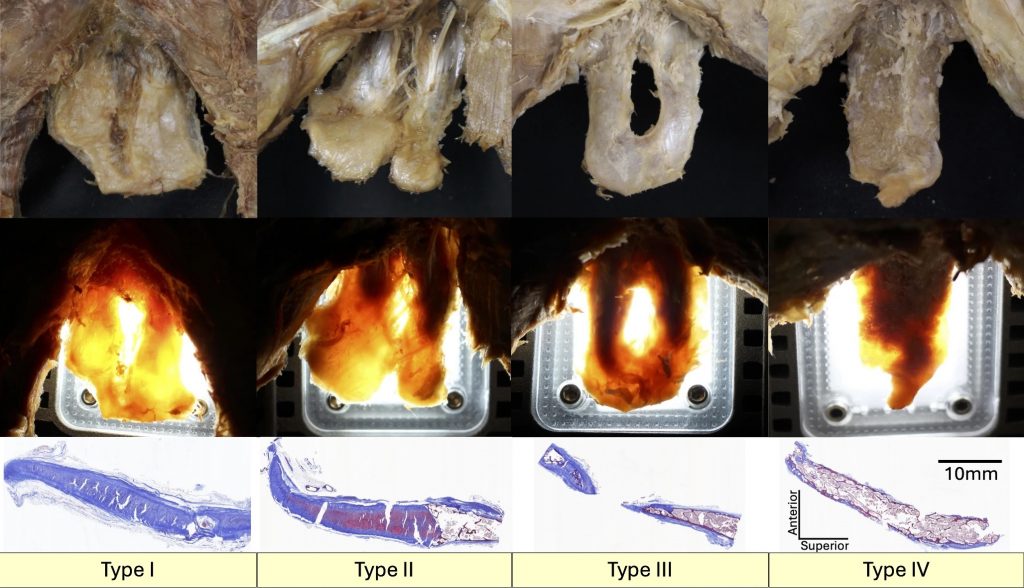
The dark area visible in transilluminated XPs was consistent with the bony part in the midsagittal XP sections, which contained bone marrow; the bright area was consistent with the cartilage part in the midsagittal XP sections. This was all demonstrated histologically. Most of the XPs (85%) had some portion of cartilage. The XP was classified into four types based on its proportions of bone and cartilage: Type I, no ossification (< 1/3 ossification) 45%; Type II, minor ossification (1/3 − 1/2 ossification) 20%; Type III, major ossification (1/2–2/3 ossification) 20%; Type IV, complete ossification (> 2/3 ossification) 15%. Most of the XPs (85%) had bone and cartilage, which could have been overlooked in studies using skeletons or CT.
Conclusion
Previous studies probably underestimated or overestimated the size of the XP. The XC needs to be considered as normal anatomy.
KEYWORDS: Bone, Cadaver, Cartilage, Sternum, Xiphoid process
Citation: Iwanaga, J., Samrid, R., Shelvin, K. B., Cardona, J. J., Kikuchi, K., Chaiyamoon, A., Suwannakhan, A., & Tubbs, R. S. (2024). Revisiting morphology of xiphoid process of the sternum in human: A comprehensive anatomical study. Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy, 46, 1687-1692.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-024-03463-1
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
Credit ภาพ: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
Webmaster: ว่าที่ ร.อ. นเรศ จันทรังสิกุล
Tags: Bone, Cadaver, Cartilage, Sternum, Xiphoid process
