Highlight
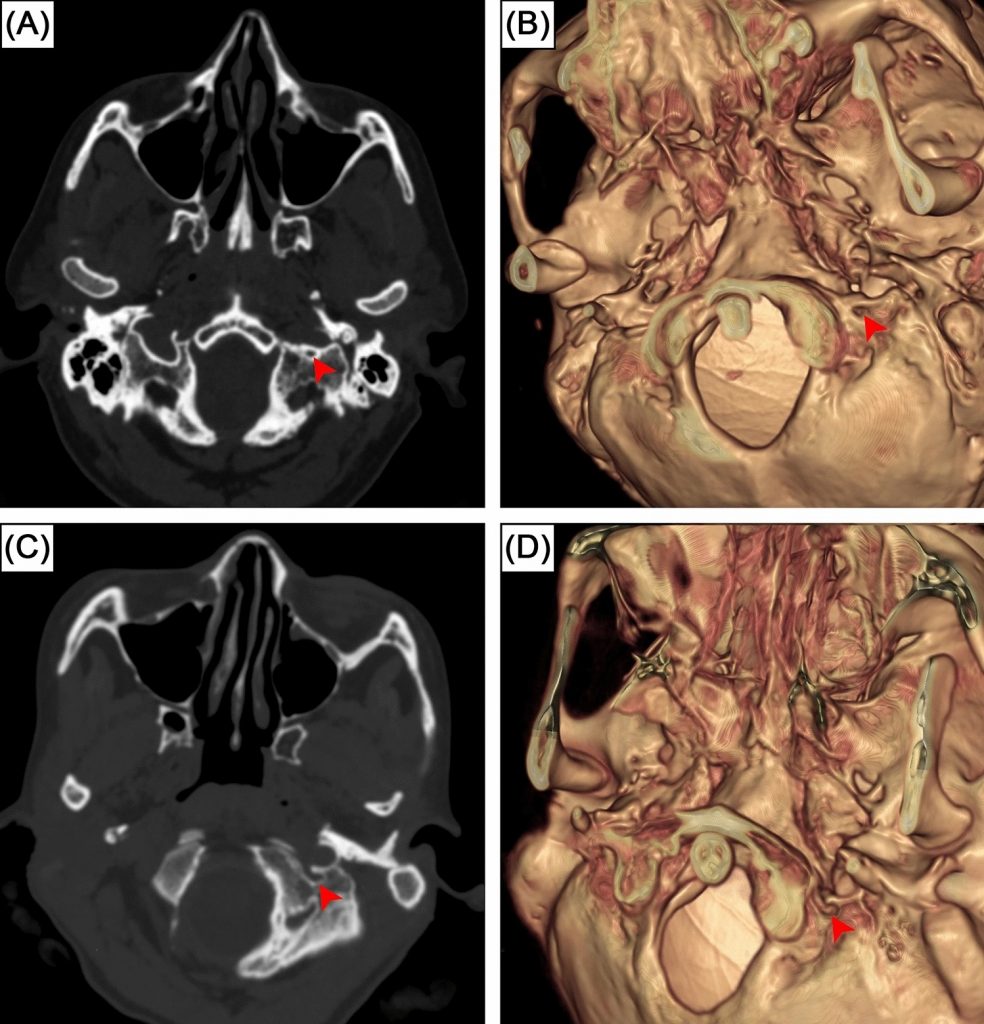
การศึกษานี้เป็นการตรวจสอบช่องว่างกลางคอนดิลาร์ในฐานกะโหลกศีรษะด้วยภาพเอกซเรย์คอมพิวเตอร์ พบการมีอยู่ของช่องดังกล่าวในร้อยละ 10.5 ของผู้ตรวจและร้อยละ 6 ของด้านกะโหลก ซึ่งช่วยให้แพทย์และศัลยแพทย์คุ้นเคยกับความแปรผันของกายวิภาคเพื่อวางแผนการผ่าตัดอย่างปลอดภัย
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
ช่องว่างกลางคอนดิลาร์ (intermediate condylar canal) เป็นช่องเล็ก ๆ บนฐานกะโหลกศีรษะที่อยู่ใน fossa condyloid ด้านข้างของ condyle หลังศีรษะและด้านหลัง–ด้านกลางของ foramen jugulare โครงสร้างนี้มีการกล่าวถึงในตำราน้อยมากและยังไม่มีการศึกษาทางรังสีอย่างละเอียดมาก่อน งานวิจัยนี้จึงตรวจสอบการมีอยู่ของช่องว่างกลางคอนดิลาร์ในชุดข้อมูลการสแกนด้วยเอกซเรย์คอมพิวเตอร์จากอาสาสมัครชาวอินเดียจำนวน 490 ราย (820 ด้าน) พบช่องนี้ในร้อยละ 10.5 ของผู้ตรวจและร้อยละ 6 ของด้านกะโหลก พร้อมทั้งพบอุบัติการณ์แบบสองข้างและหนึ่งข้าง ซึ่งมีความสำคัญต่อศัลยแพทย์ฐานกะโหลกศีรษะเนื่องจากเป็นบริเวณที่เชื่อมต่อกับแนวทางผ่าตัดหลายแนว งานนี้เป็นการศึกษาพื้นฐานด้านรังสีวิทยาที่เปิดทางให้มีการศึกษาต่อในตัวอย่างกะโหลกจริงจากประชากรต่างเชื้อชาติได้ในอนาคต
Abstract
Intermediate condylar canal is a skull base canal in the condyloid fossa, located laterally to the occipital condyles and posteromedially to the jugular foramen. Despite its presence in the human skull base, this structure is rarely mentioned in textbooks and has not previously been examined radiologically. This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of intermediate condylar canal in CQ500 dataset, an open-access computed tomography scans of Indian population. A total of 490 head and neck computed tomography scans were thoroughly investigated. The presence of the intermediate condylar canal was investigated by two observers. Our results indicated the intermediate condylar canal was found in 10.5% of subjects (43 out of 410 individuals) or 6% of sides (49 out of 820 sides). Bilateral prevalence and unilateral prevalence were 1.5% (6 subjects) and 9% (37 subjects), respectively. No significant difference was found between sides. The width of these canals was 2.0 ± 0.5 mm (1.1–3.5 mm range). It is important to surgeons to be aware and familiar of intermediate condylar canal as it is located at the crucial crossroad of various surgical skull base approaches. This study serves as the fundamental research and further studies could include the investigation of intermediate condylar canal in skeletal specimens of various ethnic origins and imaging study to examine the content of the canals.
KEYWORDS: Intermediate condylar canal, Skull base, Anatomical variation, Computed tomography, Condyloid fossa
Citation: Pitaksinagorn, W., Pongruengkiat, W., Iwanaga, J., Tubbs, R. S., Sangchay, N., Yurasakpong, L., Taradolpisut, N., Triantafyllou, G., & Suwannakhan, A. (2025). Radiological study of the intermediate condylar canal. Bratislava Medical Journal, 126, 3349–3353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44411-025-00378-0
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ลภัสรดา ยุรศักดิ์พงศ์
ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: นางสาวนภาวรรณ ธราดลพิศุทธ์
Credit ภาพ: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
Webmaster: ว่าที่ ร.อ. นเรศ จันทรังสิกุล
Tags: anatomical variation, computed tomography, Condyloid fossa, Intermediate condylar canal, Skull base
