Highlight
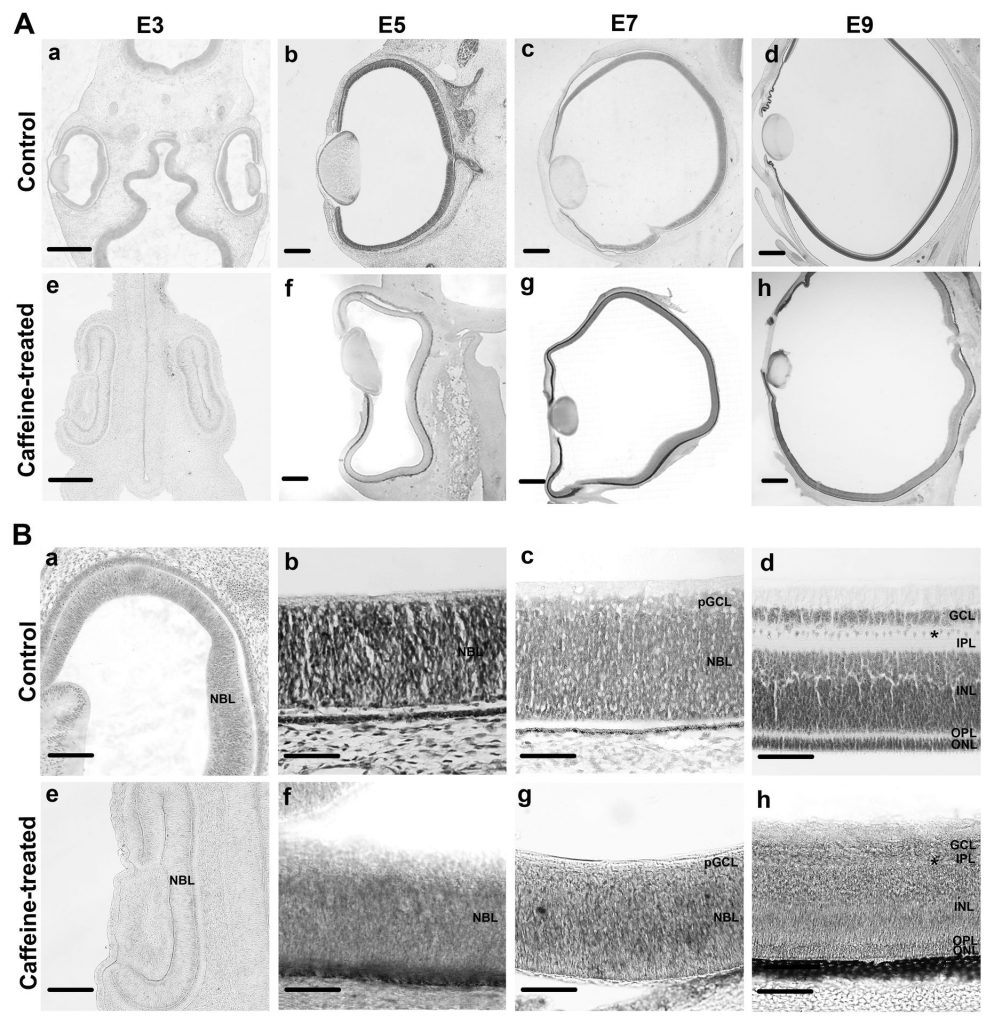
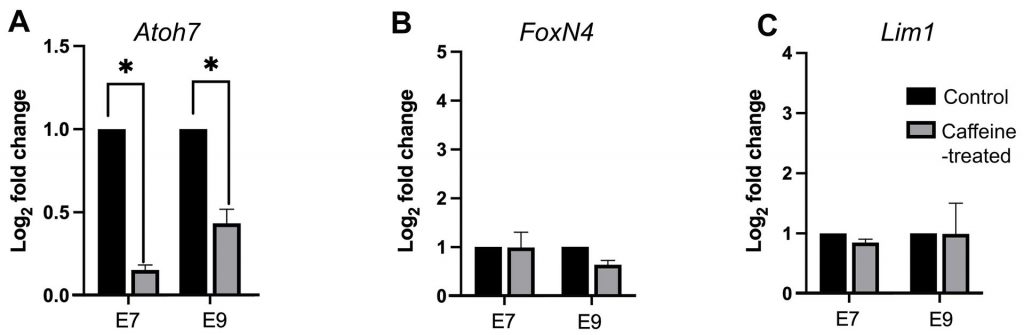
มีรายงานว่าการดื่มคาเฟอีนปริมาณมากในช่วงการตั้งครรภ์มีผลต่อการพัฒนาของเนื้อเยื่อประสาทระหว่างการเจริญเติบโตของตัวอ่อน ในการศึกษานี้มุ่งเน้นไปที่ผลของคาเฟอีนที่มีต่อการพัฒนาของชั้นเรตินา ซึ่งเป็นเนื้อเยื่อประสาทที่อ่อนไหวที่สุดในตัวอ่อนไก่ การติดตามการเปลี่ยนแปลงในเชิงโครงสร้างทั้งความหนาและการจัดเรียงตัวของเนื้อเยื่อประสาท โดยใช้การบ่งบอกของยีน 3 ตัว ได้แก่ Atoh7, FoxN4 และ Lim1 เมื่อให้คาเฟอีนที่ความเข้มข้น 15 ไมโครโมลาร์ เป็นโดสตั้งต้นและให้เพียงโดสเดียวที่ระยะตัวอ่อน E1เมื่อติดตามความหนาของชั้นเรตินาพบว่ามีการเปลี่ยนแปลงอย่างมากที่ตัวอ่อนระยะ E7และ E9 และยีนที่มีการแสดงออกเปลี่ยนแปลงอย่างเห็นได้ชัดคือ Atoh7 ในขณะที่ FoxN4 และ Lim1 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเพียงเล็กน้อยในการพัฒนาชั้นเรตินา เมื่อใช้การตรวจวัดปริมาณของยีนด้วยเทคนิค Quantitative polymerase chain reaction ผลการทดลองสนับสนุนว่าการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่เห็นชัดคือยีน Atoh7 ในขณะที่ FoxN4 และ Lim1 ไม่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง โดยเฉพาะในตัวอ่อนระยะ E7 ผลของคาเฟอีนที่มีต่ออวัยวะอื่นๆ ในระหว่างการพัฒนาของตัวอ่อนควรมีการศึกษามากขึ้น และต้องมีการกระตุ้นให้ตระหนักในการดื่มคาเฟอีนปริมาณมาก
ชื่องานวิจัยภาษาไทย
ผลของคาเฟอีนที่มีต่อการแสดงออกของยีนในการพัฒนาชั้นเรตินาในตัวอ่อนไก่
Abstract
It has been reported that overconsumption of caffeine during pregnancy leads to a deleterious effect within the nervous tissues during embryonic development. In this study, we further extrapolated the effect of caffeine in the developing retinas, which is known to be one of the most sensitive tissues in chick embryos. Morphological changes of retinal thickness and organization of neuroretinal epithelium were monitored using three gene markers, Atoh7, FoxN4, and Lim1. Upon treating with a single dose of caffeine (15 µmol at embryonic day 1 [E1]), relative thicknesses of developing retinas (particularly of E7 and E9) were significantly altered. Among the three genes studied, the expression pattern of Atoh7 was notably altered while those of FoxN4, and Lim1 mRNA showed only a slight change in these developing retinas. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction results supported the most notable changes of Atoh7 but not FoxN4, and Lim1 gene in the developing retinas, particularly at E7. The effect of caffeine towards other organs during development should be extrapolated and the awareness of its intensive consumption should be raised.
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
การบริโภคคาเฟอีนที่มากเกินไปมีผลต่อการพัฒนาของตัวอ่อนโดยเฉพาะเนื้อเยื่อประสาทเรตินา
KEYWORDS: Caffeine, Chick embryo, Retina, Epithelium, Retinal ganglion cells
Citation:
Lekchaoum T, Buddawong A, Ahi S, Chandee N, Weerachatyanukul W, Asuvapongpatana S*. Effect of caffeine on genes expressions of developing retinas in the chick model. Anatomy & Cell Biology 2022, 55(3):311-319. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.22.034
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.สมลักษณ์ อสุวพงษ์พัฒนา
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.วัฒนา วีรชาติยานุกูล, รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.สมลักษณ์ อสุวพงษ์พัฒนา
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Thanyarat Lekchaoum
ภาพถ่าย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.วัฒนา วีรชาติยานุกูล, รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.สมลักษณ์ อสุวพงษ์พัฒนา
Tags: Caffeine, Chick embryo, Epithelium, Retina, Retinal ganglion cells
