ชื่องานวิจัยภาษาไทย
ฤทธิ์ของสารสกัด decanoic acid จากปลิงทะเลดำในการป้องกันเซลล์ประสาทและต้านโรคพาร์กินสันในสัตว์ทดลอง C. elegans
Highlight
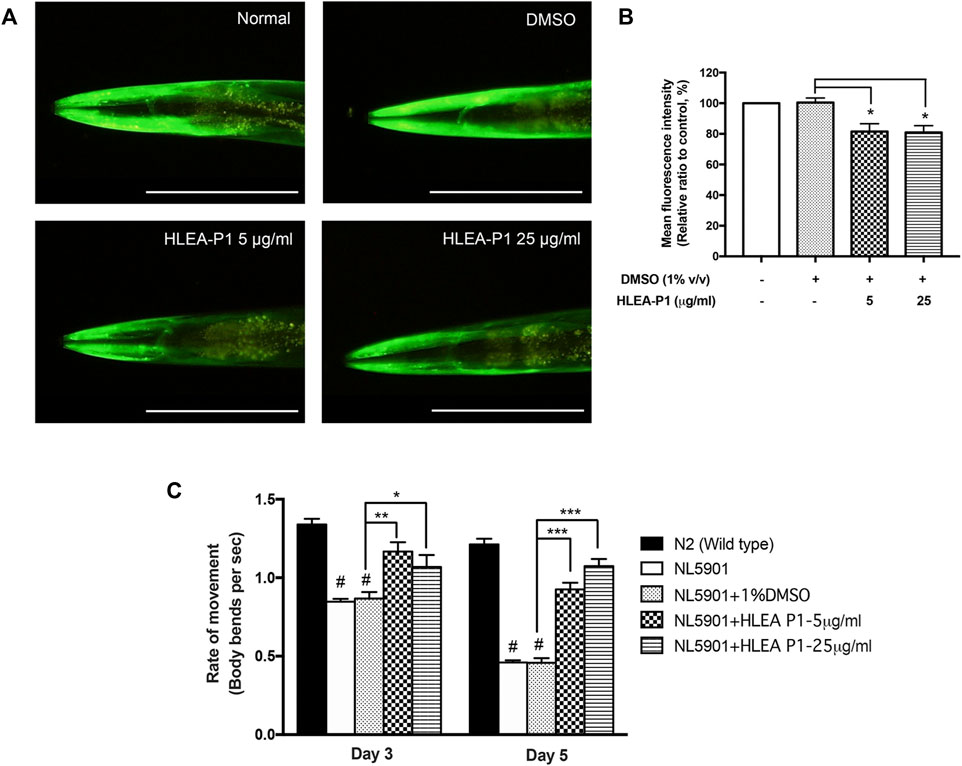
สารสกัด decanoic acid จากปลิงทะเลดำ สามารถลดความเสียหายของเซลล์ประสาท ลดอนุมูลอิสระ ฟื้นฟูการทำงานของเซลล์ประสาท อีกทั้งยังสามารถลดการเกาะกลุ่มของโปรตีนอัลฟ่าไซนิวคลิอิน โดยการกระตุ้นผ่านทาง DAF-16 transcription factor เพื่อกระตุ้นการแสดงออกของยีนต้านอนุมูลอิสระ (sod-3) และยีน heat shock proteins (hsp16.1, hsp16.2 และ hsp12.6)
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
ปลิงทะเลได้นำมาใช้เป็นอาหารและทางการแพทย์ของประเทศแถบเอเชียอย่างยาวนาน การศึกษาวิจัยล่าสุดแสดงให้เห็นว่าสารสกัดจาก ethyl acetate fraction จากปลิงทะเลดำสามารถต้านโรคพาร์กินสันในสัตว์ทดลองได้ การศึกษาวิจัยนี้จึงได้สกัดสารบริสุทธิ์จากปลิงทะเลดำและทดสอบการออกฤทธิ์ในการป้องกันเซลล์ประสาทและต้านโรคพาร์กินสันโดยใช้ C. elegans เป็นสัตว์ทดลองต้นแบบ
Abstract
Sea cucumbers are marine organism that have long been used for food and traditional medicine in Asian countries. Recently, we have shown that ethyl acetate fraction (HLEA) of the crude extract of the black sea cucumber, Holothuria leucospilota, could alleviate Parkinsonism in Caenorhabditis elegans PD models. In this study, we found that the effective neuroprotective activity is attributed to HLEA-P1 compound chemically isolated and identified in H. leucospilota ethyl acetate. We reported here that HLEA-P1 could attenuate DAergic neurodegeneration, improve DAergic-dependent behaviors, reduce oxidative stress in 6-OHDA-induced C. elegans. In addition, HLEA-P1 reduced α-synuclein aggregation, improved behavior deficit and recovered lipid deposition in transgenic C. elegans overexpressing α-synuclein. We also found that HLEA-P1 activates nuclear localization of DAF-16 transcription factor of insulin/IGF-1 signaling (IIS) pathway. Treatment with 25 μg/ml of HLEA-P1 upregulated transcriptional activity of DAF-16 target genes including anti-oxidant genes (such as sod-3) and small heat shock proteins (such as hsp16.1, hsp16.2, and hsp12.6) in 6-OHDA-induced worms. In α-synuclein-overexpressed C. elegans strain, treatment with 5 μg/ml of HLEA-P1 significantly activated mRNA expression of sod-3 and hsp16.2. Chemical analysis demonstrated that HLEA-P1 compound is decanoic acid/capric acid. Taken together, our findings revealed that decanoic acid isolated from H. leucospilota exerts anti-Parkinson effect in C. elegans PD models by partly modulating IIS/DAF-16 pathway.
KEYWORDS: Parkinson’s disease, dopaminergic neurons, α-synuclein, Holothuria leucospilota, C. elegans, decanoic acid
Citation: Sanguanphun T, Sornkaew N, Malaiwong N, Chalorak P, Jattujan P, Niamnont N, Sobhon P and Meemon K (2022) Neuroprotective effects of a medium chain fatty acid, decanoic acid, isolated from H. leucospilota against Parkinsonism in C. elegans PD model. Front. Pharmacol. 13:1004568. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1004568
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Tanatcha Sanguanphun
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Specific League Funds from Mahidol University to KM and Ph.D. scholarship from Science Achievement Scholarship of Thailand (SAST) to TS.
Credit ภาพ: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
Tags: C. elegans, decanoic acid, dopaminergic neurons, Holothuria leucospilota, Parkinson’s Disease, α-Synuclein
