Highlight
งานวิจัยฉบับนี้อธิบายถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลงค่าพารามิเตอร์ทางชีวเคมีในซีรั่มและไทโรซีน ฟอสโฟรีเลชั่นในไตและตับของหนูแรทที่เกิดจากความเครียดเรื้อรัง ผลงานวิจัยฉบับนี้แสดงให้เห็นว่าความเครียดเรื้อรังส่งผลต่อการทำงานของไตและตับได้
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
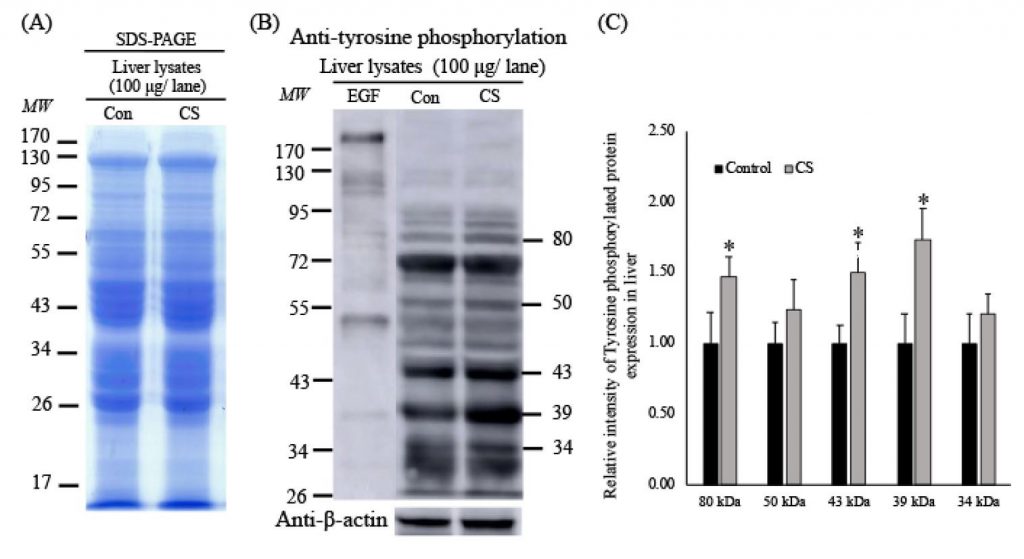
ความเครียดเรื้อรังอาจส่งผลต่อการทำงานผิดปกติของอวัยวะต่างๆ รวมทั้งตับและไต การศึกษานี้ดำเนินการเพื่อตรวจสอบการเปลี่ยนแปลงของชีวเคมีในซีรั่ม โครงสร้างทางเนื้อเยื่อวิทยา รวมถึงการแปลโปรตีนไทโรซีนฟอสโฟรีเลต (TyrPho) และโปรตีนฮีตช็อต 70 (Hsp-70) ในตับและเนื้อเยื่อไตของหนูที่ถูกกระตุ้นด้วยความเครียดเรื้อรังติดต่อกัน 60 วัน (โดยการกักขังและบังคับว่ายน้ำ) หลังจากนั้น มีการเก็บตัวอย่างเลือด ตับ และไตจากหนู Sprague–Dawley ที่โตเต็มวัยในแต่ละกลุ่มมาวิเคราะห์ ผลลัพธ์ของเราแสดงให้เห็นว่าค่าพารามิเตอร์ทางชีวเคมีในซีรั่ม ได้แก่ คอร์ติโคสเตอโรน น้ำตาลในเลือด ยูเรียไนโตรเจน ครีเอตินิน คอเลสเตอรอล ไตรกลีเซอไรด์ ในกลุ่มหนูที่มีความเครียดเรื้อรัง แตกต่างอย่างมีนัยสำคัญจากค่าพารามิเตอร์ในกลุ่มปกติในตับทั้งสอง และเนื้อเยื่อไต แม้ว่าโครงสร้างเนื้อเยื่อจะไม่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง การแสดงออกของ TyrPho เพิ่มขึ้นอย่างมีนัยสำคัญในตับ lysate แต่ลดลงอย่างมากในไต การแสดงออกของ Hsp-70 ในตับเพิ่มขึ้น ในขณะที่ไตลดลง ผลการทดลองเหล่านี้สรุปได้ว่า ความเครียดเรื้อรังสามารถกระตุ้นการเปลี่ยนแปลงของการทำงานของตับและไต
Abstract
Chronic stress (CS) can contribute to dysfunction in several organs including liver and kidney. This study was performed to investigate the changes in serum biochemistry, histological structure, as well as in localization of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins (TyrPho) and Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp-70) in liver and kidney tissues of CS rats induced by two stressors (restrained and force swimming) for 60 consecutive days. Samples of blood, liver, and kidney were collected from adult male Sprague-Dawley rats in each group. Our results showed that serum biochemical parameters including corticosterone, blood sugar, urea nitrogen, creatinine, cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL-C, LDL-C, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase in CS group were significantly different from that in normal group in both liver and kidney tissues. Although histological structure was not changed. TyrPho expression was significantly increased in liver lysate but significantly decreased in kidney. Hsp-70 expression in liver increased whereas in kidney decreased. In conclusion, CS can induce changes in liver and kidney functions.
KEYWORDS: chronic stress, tyrosine phosphorylation, heat shock protein 70, liver, kidney
Citation: Khanthiyong, B., Arun, S., Bunsueb, S., Thongbuakaew, T., Suwannakhan, A., Wu, A., Iamsaard, S. & Chaiyamoon, A. (2024). Alterations of serum biochemical parameters and tyrosine phosphorylation in kidney and liver of chronic stress-induced rats. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 84, e254646. DOI: 10.1590/1519-6984.254646
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
Credit ภาพ: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
Tags: chronic stress, heat shock protein 70, kidney, liver, tyrosine phosphorylation
