ที่มาและความสำคัญ
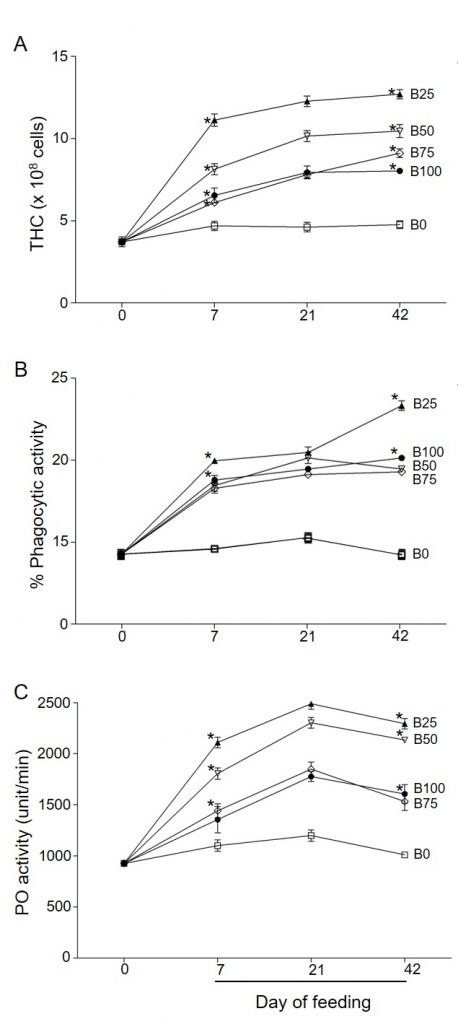
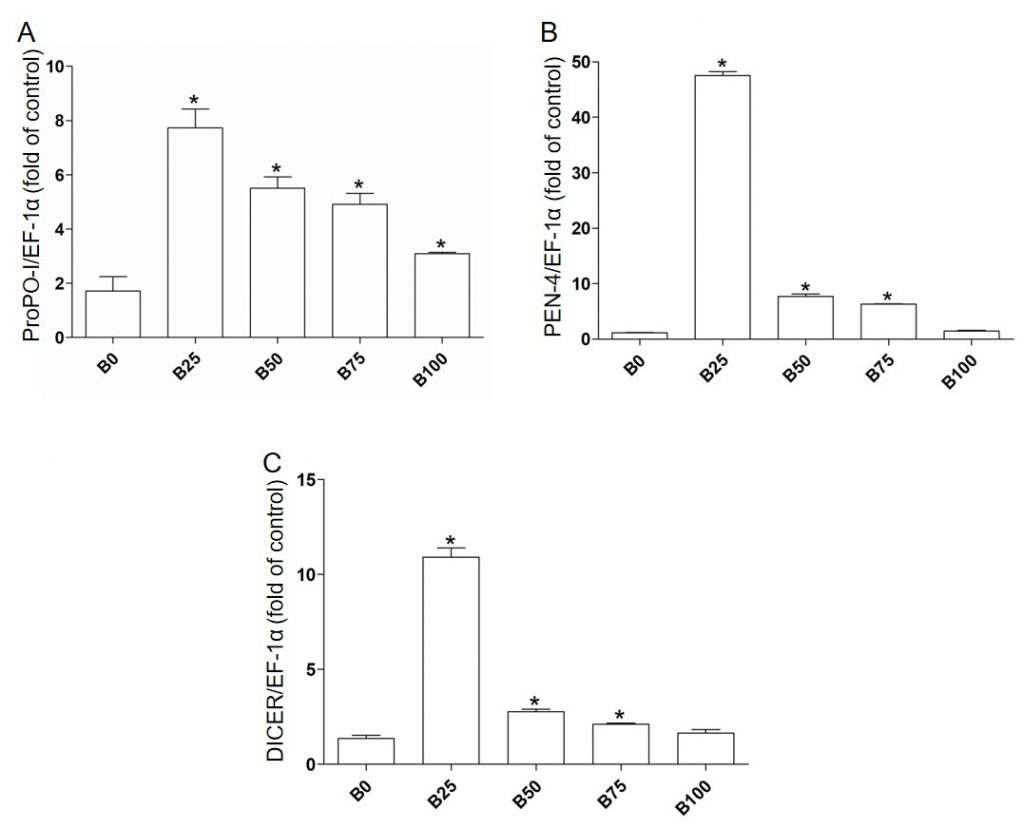
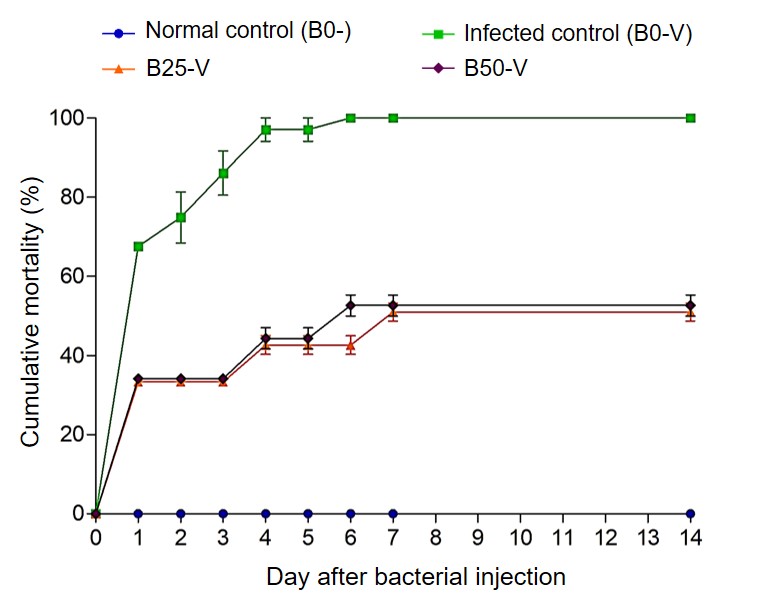
ปลาป่น (fish meal) เป็นแหล่งโปรตีนที่สำคัญในอุตสาหกรรมผลิตอาหารกุ้ง ปลาป่นได้มาการลากอวนปลาเล็กปลาน้อยจากทะเลซึ่งเป็นการทำลายระบบนิเวศอย่างมาก ดังนั้นการหาแหล่งโปรตีนคุณภาพดีเพื่อทดแทนปลาป่นจึงมีความจำเป็นอย่างเร่งด่วน งานวิจัยนี้จึงมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาคุณค่าทางโภชนาการในตะกอนชีวภาพ (bioflocs) การใช้ตะกอนชีวภาพทดแทนปลาป่นในอาหารกุ้ง และผลของตะกอนชีวภาพต่อการเจริญเติบโตและภูมิคุ้มกันของกุ้ง ตะกอนชีวภาพได้จากการเก็บเกี่ยวจากบ่อเลี้ยงกุ้ง (C:N ratio > 12:1) ที่ Shrimp Village อำเภอไชยา จังหวัดสุราษฎร์ธานี ผลการทดลองพบว่าโปรตีนและลิปิดในตะกอนชีวภาพมีค่าเท่ากับ 48% และ 5% ตามลำดับ ปริมาณกรดอะมิโนและกรดไขมันที่จำเป็นในตะกอนชีวภาพมีค่าใกล้เคียงกับปลาป่น เมื่อให้กุ้งกินอาหารที่ใช้ตะกอนชีวภาพแทนปลาป่นในปริมาณแตกต่างกัน (25, 50, 75 และ 100%) เป็นเวลา 42 วัน พบว่าผลของการเจริญเติบโตของกุ้ง (น้ำหนักที่เพิ่มขึ้น ความเฉพาะเจาะจงของการเจริญเติบโตและอัตราแลกเนื้อ) ในกลุ่มกินอาหารที่ใช้ตะกอนชีวภาพแทนปลาป่นไม่มีความแตกต่างจากอาหารปกติ นอกจากนี้ยังพบว่าอัตราการรอด ระดับของภูมิคุ้มกัน และการแสดงออกของยีน (proPO-I, PEN-4 and dicer) สูงขึ้นในกุ้งทุกกลุ่มที่กินอาหารตะกอนชีวภาพแทนปลาป่น และเมื่อให้กุ้งติดเชื้อVibrio parahaemolyticus กุ้งกลุ่มที่กินอาหารตะกอนชีวภาพแทนปลาป่น 25 และ 50% มีระดับของภูมิคุ้มกันและอัตราการรอดหลังจากการติดเชื้อV. parahaemolyticus) สูงกว่ากุ้งที่กินอาหารปกติอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ งานวิจัยนี้แสดงให้เห็นว่าตะกอนชีวภาพที่คุณค่าโปรตีนเทียบเท่าปลาป่น นำไปใช้ทดแทนปลาป่นในอาหารกุ้งได้ และยังเพิ่มภูมิคุ้มกันในกุ้ง
Abstract
Fishmeal is the main source of protein in the shrimp feed industry and is normally derived from trash fish. As such, the production of fishmeal has an adverse effect on the marine environment by taking away small and juvenile fish, leading to depletion of marine species. There is a need for alternative sources of protein which will substitute fishmeal in the aquaculture industry. This study evaluated the components and nutritional efficacy of bioflocs, which were used to substitute fishmeal protein. The effect of bioflocs diets on growth performance, survival rate, and immune response in shrimp compared to normal fishmeal feed were determined. Bioflocs were harvested from the shrimp ponds (C:N ratio >12:1) at Shrimp Village, Chaiya district, Surat Thani, Thailand. The total protein in bioflocs was about 48% and the total lipid was about 5% (dried weight) and the percentages of essential amino acids (EAA) and fatty acids (EFA) in bioflocs were similar to those of fishmeal feed. Shrimp fed with the different dietary bioflocs feed regimens [% to replace fishmeal; 0% (B0), 25% (B25), 50% (B50), 75% (B75), and 100% (B100)] for 42 days revealed that all growth parameters were almost similar to those of the control shrimp (shrimp fed with normal fishmeal, B0) including final body weight, weight gain, specific growth rate, and feed conversion ratio. Remarkably, the survival rates, the levels of immune parameters, and expression of immune genes (proPO-I, PEN-4 and dicer) were significantly higher in bioflocs fed shrimp, especially in B25 and B50 shrimp. Moreover, B25 and B50 bioflocs fed shrimp showed notably increased survival rates following Vibrio parahaemolyticus (V. parahaemolyticus) infection. In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that shrimp survival and immunity are enhanced by biofiocs substituted fishmeal. Significantly, the bioflocs diets activated the immune response to prevent V. parahaemolyticus infection.
KEYWORDS: Bioflocs, Fishmeal protein, Shrimp feed, Growth, Immune parameters
Citation: Phennapa Promthale, Pattira Pongtippatee, Boonsirm Withyachumnarnkul, Kanokpan Wongprasert,
Bioflocs substituted fishmeal feed stimulates immune response and protects shrimp from Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection, Fish & Shellfish Immunology, Volume 93, 2019, Pages 1067-1075, ISSN 1050-4648,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.07.084.
RELATED SDGs:
12. RESPONSIBLE CONSUMPTION AND PRODUCTION

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: เพ็ญนภา พรมทะเล
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Thailand Research Fund (TRF) through the Research Career Development Grant (RSA5980043) and Research and Researchers for Industries (RRi) (PHD58I0094), Thai-Union Feedmill Co., Ltd. (TUF), and Faculty of Science, Mahidol University.
Tags: Human stem cells from apical papilla, Neural progenitor-like cells, Resveratrol
