ฤทธิ์ของสาร 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran จากปลิงทะเลขาวในการลดการเกาะกลุ่มและความเป็นพิษจาก α-Synuclein ในสัตว์ทดลอง Caenorhabditis elegans
Highlight
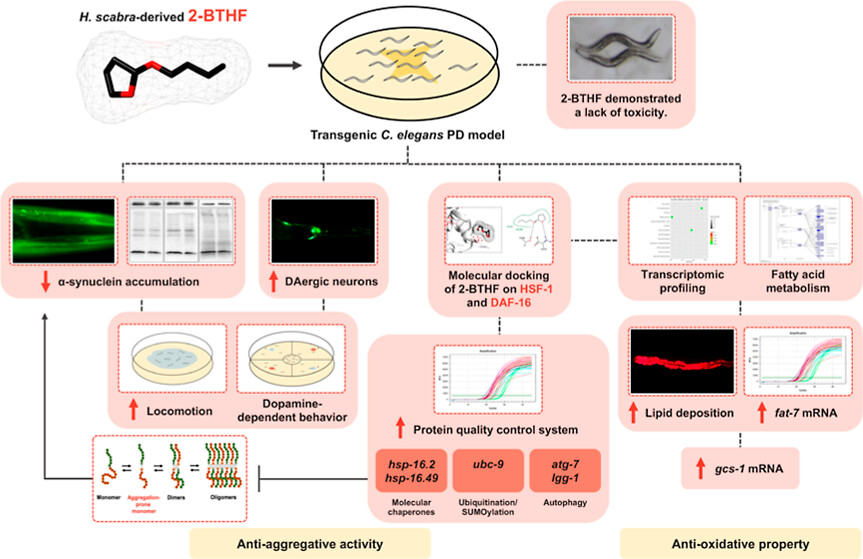
สารสกัด 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran (2-BTHF) จากปลิงทะเลขาว Holothuria scabra สามารถลดการเกาะกลุ่มของโปรตีน α-synuclein กระบวนการออกซิเดชัน และการเสื่อมสภาพของเซลล์ประสาทโดปามีน รวมถึงฟื้นฟูการเคลื่อนไหวและพฤติกรรมของสัตว์ทดลองได้ โดยมีกลไกการทำงานในการเพิ่มการแสดงออกของยีนที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการรักษาเสถียรภาพของโปรตีนและการเผาผลาญกรดไขมัน และเพิ่มการสังเคราะห์กลูตาไธโอน
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
ปลิงทะเลมีฤทธิ์ป้องกันโรคความเสื่อมของระบบประสาทและฟื้นฟูเซลล์ประสาทจากการถูกทำลาย โดยมีสารออกฤทธิ์ที่สำคัญคือ 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran (2-BTHF) โดยสามารถลดการเกาะกลุ่มและความเป็นพิษของ amyloid-beta ในโรคอัลไซเมอร์ได้ การศึกษาวิจัยนี้จึงได้ศึกษาการออกฤทธิ์ของ 2-BTHF ต่อโรคพาร์กินสันที่เกิดจากการเกาะกลุ่มและความเป็นพิษต่อเซลล์ประสาทโดปามีนจากโปรตีน alpha-synuclein
Abstract
Aggregative α-synuclein and incurring oxidative stress are pivotal cascading events, leading to dopaminergic (DAergic) neuronal loss and contributing to clinical manifestations of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Our previous study demonstrated that 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran (2-BTHF), isolated from Holothuria scabra (H. scabra), could inhibit amyloid-β aggregation and its ensuing toxicity, which leads to Alzheimer’s disease. In the present study, we found that 2-BTHF also attenuated the aggregative and oxidative activities of α-synuclein and lessened its toxicity in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) PD model. Such worms treated with 100 μM of 2-BTHF showed substantial reductions in α-synuclein accumulation and DAergic neurodegeneration. Mechanistically, 2-BTHF, at this concentration, significantly decreased aggregation of monomeric α-synuclein and restored locomotion and dopamine-dependent behaviors. Molecular docking exhibited potential bindings of 2-BTHF to HSF-1 and DAF-16 transcription factors. Additionally, 2-BTHF significantly increased the mRNA transcripts of genes encoding proteins involved in proteostasis, including the molecular chaperones hsp-16.2 and hsp-16.49, the ubiquitination/SUMOylation-related ubc-9 gene, and the autophagy-related genes atg-7 and lgg-1. Transcriptomic profiling revealed an additional mechanism of 2-BTHF in α-synuclein-expressing worms, which showed upregulation of PPAR signaling cascades that mediated fatty acid metabolism. 2-BTHF significantly restored lipid deposition, upregulated the fat-7 gene, and enhanced gcs-1-mediated glutathione synthesis in the C. elegans PD model. Taken together, this study demonstrated that 2-BTHF could abrogate aggregative and oxidative properties of α-synuclein and attenuate its toxicity, thus providing a possible therapeutic application for the treatment of α-synuclein-induced PD.
KEYWORDS: 2-butoxytetrahydrofuran, Holothuria scabra,antiaggregation, antioxidation, α-synuclein toxicity, C. elegans
Citation: Promtang S, Sanguanphun T, Chalorak P, Pe LS, Niamnont N, Sobhon P, Meemon K. 2-Butoxytetrahydrofuran, Isolated from Holothuria scabra, Attenuates Aggregative and Oxidative Properties of α-Synuclein and Alleviates Its Toxicity in a Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Jun 5;15(11):2182-2197. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00008.
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Sukrit Promtang
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Mahidol University (MU’s Strategic Research Fund: 2023)
ภาพถ่าย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
