
คุณภาพของของบทความกายวิภาคศาสตร์ในวิกิพีเดียภาษาอังกฤษ
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
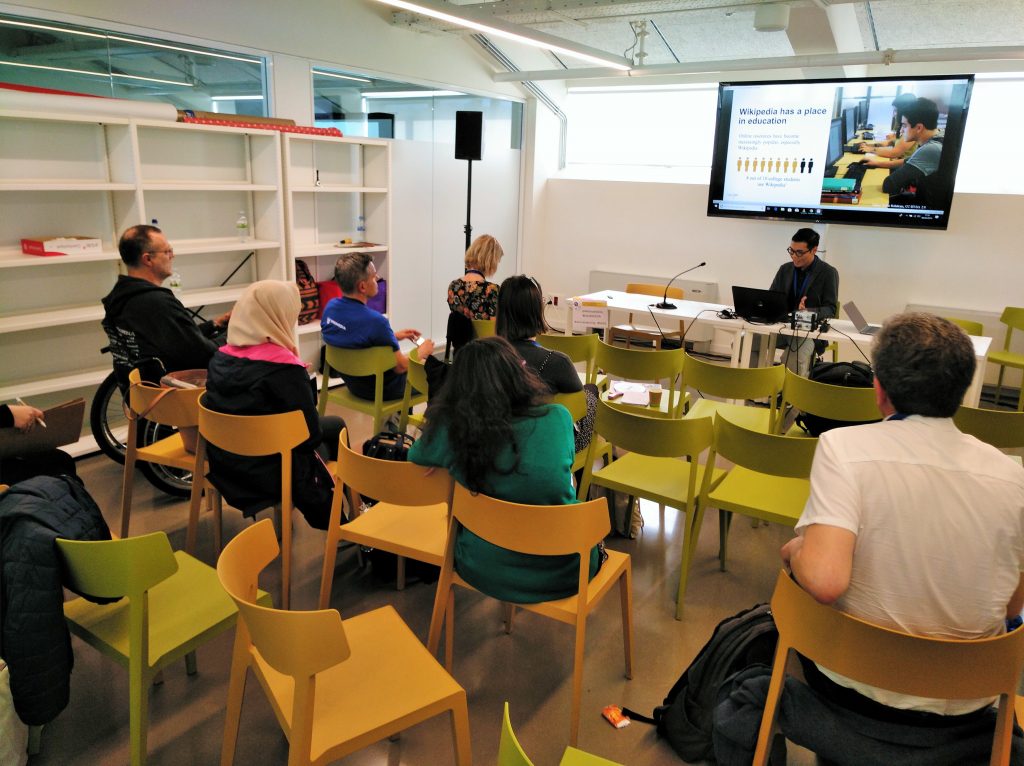
วิกิพีเดียสารานุกรมเสรี เป็นหนึ่งในแหล่งข้อมูลออนไลน์ที่ได้รับความนิยมมากที่สุดแหล่งหนึ่งของโลก วิกิพีเดียจัดตั้งขึ้นในปี 2001 และได้รับการสนับสนุนจากมูลนิธิวิกิมีเดีย องค์กรไม่แสวงผลกำไรจากประเทศสหรัฐอเมริกา เนื้อหากว่า 35 ล้านบทความเกิดขึ้นจากการร่วมเขียนของอาสาสมัครทั่วโลก ทุกคนสามารถเข้าถึงวิกิพีเดียและร่วมแก้ไขได้อย่างเสรี การศึกษาก่อนหน้านี้พบว่าประชาชนทั่วไป รวมถึงแพทย์และนักศักษาแพทย์กว่าร้อยละ 90 ใช้วิกิพีเดียเป็นแหล่งข้อมูลด้านสุขภาพ ดังนั้นจึงกล่าวได้ว่าวิกิพีเดียมีบทบาทเป็นอย่างยิ่งในด้านสาธารณสุขของโลกหรือ global health อย่างไรก็ตามวิกิพีเดียถูกวิพากษ์วิจารณ์ในแวดวงวิชาการอยู่เสมอโดยเฉพาะในเรื่องคุณภาพและความน่าเชื่อถือของข้อมูล ส่งผลให้วิกิพีเดียไม่ได้รับการยอมรับอย่างกว้างขวาง ด้วยข้อจำกัดดังกล่าวภาควิชากายวิภาคศาสตร์ คณะวิทยาศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล ได้พัฒนาโมเดลเพื่อประเมินคุณภาพของบทความในวิกิพีเดีย ทั้งในเชิงประมาณ (quantitative) เชิงคุณภาพ (qualitative) และระบุปัจจัยต่าง ๆ ที่ส่งผลต่อคุณภาพของบทความในวิกิพีเดีย โดยทีมวิจัยได้ศึกษานำร่องโดยการประเมินของบทความกายวิภาคศาสตร์ในวิกิพีเดียภาษาอังกฤษจำนวนทั้งสิ้น 50 บทความ งานวิจัยฉบับนี้จะเป็นพื้นฐานให้กับงานวิจัยในอนาคตและเป็นต้นแบบให้กับนักวิจัยอื่นทั่วโลก ซึ่ง นอกเหนือจากการประเมินบทความในวิกิพีเดียแล้ว สามารถนำไปประยุกต์เพื่อประเมินคุณภาพของสื่อการเรียนรู้ออนไลน์แพลทฟอร์มอื่น ๆ ได้เช่นกัน ข้อมูลที่ได้จากการประเมินดังกล่าวจะมีการนำไปพัฒนาเป็นนโยบายโดยมูลนิธิวิกิมีเดียเพื่อปรับปรุงวิกิพีเดียในระยะยาวโดยมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อให้ข้อมูลในวิกิพีเดียมีความถูกต้องมากยิ่งขึ้น มีความน่าเชื่อถือ มีความครบถ้วน ได้รับการยอมรับในแวดวงวิชาการและนำไปใช้เป็นสื่อการเรียนรู้สากลโดยที่ทุกคนสามารถเข้าถึงได้อย่างเท่าเทียม ตรงตามวิสัยทัศน์ของมูลนิธิวิกิมีเดียที่กล่าวไว้ว่า “Imagine a world in which every single human being can freely share in the sum of all knowledge. That is our commitment.” งานวิจัยฉบับนี้ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในฉบับเดือนกรกฎาคม-สิงหาคม ปี 2020 ในวารสาร Anatomical Sciences Education ซึ่งอยู่ในระดับ top 10 percentile ของวารสารวิชาการในสาขาการศึกษาในฐานข้อมูล Journal Citation Reports นอกจากนี้หัวหน้าโครงการวิจัยยังได้รับเงินทุนสนับสนุนจากมูลนิธิวิกิมีเดีย (Wikimedia Foundation) สหรัฐอเมริกาเพื่อนำเสนอผลงานและเป็น co-chair ของการนำเสนอผลงานในสาขา anatomy education ของงานประชุมวิชาการ International Federation of Associations of Anatomists ในเดือนสิงหาคมปี 2019 ณ กรุงลอนดอน สหราชอาณาจักร และนำเสนอเป็น workshop ในงาน Wikimedia Education Conference ในเดือนเมษายนปี 2019 ณ เมืองซาน เซบาสเตียน แคว้นบาสก์ ประเทศสเปน
Abstract
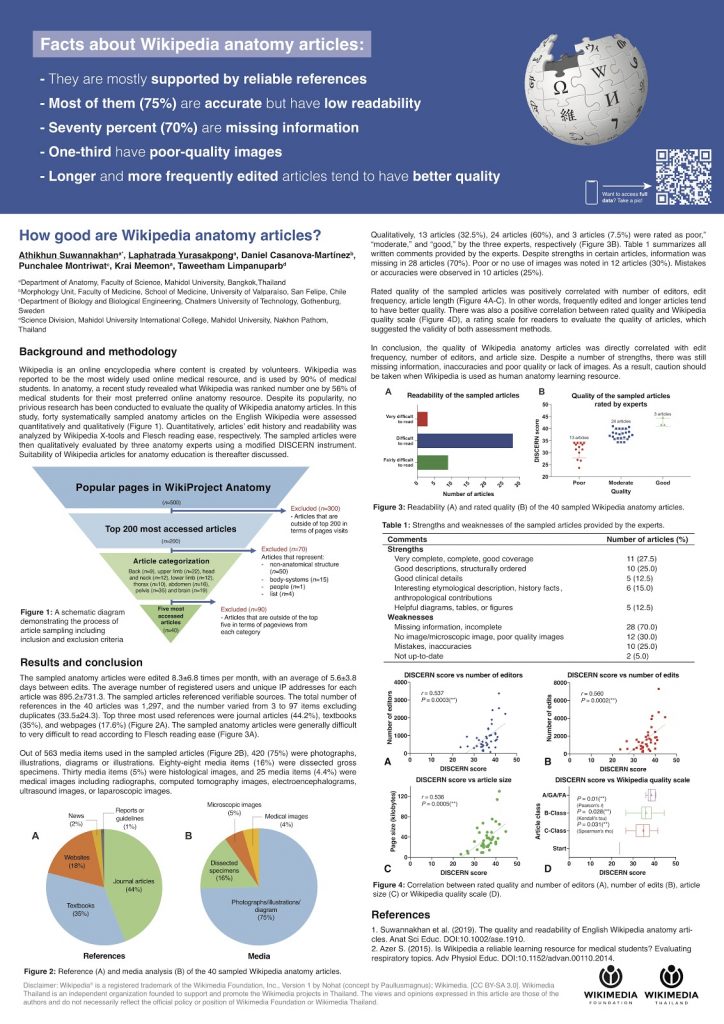
Forty anatomy articles were sampled from English Wikipedia and assessed quantitatively and qualitatively. Quantitatively, each article’s edit history was analyzed by Wikipedia X‐tools, references and media were counted manually, and two readability indices were used to evaluate article readability. This analysis revealed that each article was updated 8.3 ± 6.8 times per month, and referenced with 33.5 ± 24.3 sources, such as journal articles and textbooks. Each article contained on average 14.0 ± 7.6 media items. The readability indices including: (1) Flesch–Kincaid Grade Level Readability Test and (2) Flesch Reading Ease Readability Formula demonstrated that the articles had low readability and were more appropriate for college students and above. Qualitatively, the sampled articles were evaluated by experts using a modified DISCERN survey. According to the modified DISCERN, 13 articles (32.5%), 24 articles (60%), 3 articles (7.5%), were rated as “good,” “moderate,” and “poor,” respectively. There were positive correlations between the DISCERN score and the number of edits (r = 0.537), number of editors (r = 0.560), and article length (r = 0.536). Strengths reported by the panel included completeness and coverage in 11 articles (27.5%), anatomical details in 10 articles (25%), and clinical details in 5 articles (12.5%). The panel also noted areas which could be improved, such as providing missing information in 28 articles (70%), inaccuracies in 10 articles (25%), and lack or poor use of images in 17 articles (42.5%). In conclusion, this study revealed that many Wikipedia anatomy articles were difficult to read. Each article’s quality was dependent on edit frequency and article length. Learners and students should be cautious when using Wikipedia articles for anatomy education due to these limitations.
KEYWORDS: gross anatomy educations, medical education, undergraduate education, medical students, Wikipedia, online resources
RELATED SDGs: 4. QUALITY EDUCATION

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: อ.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล, อ.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: นส.ลภัสรดา ยุรศักดิ์พงศ์
Tags: gross anatomy educations, medical education, medical students, online resources, undergraduate education, Wikipedia
