ชื่องานวิจัยภาษาไทย
การเพิ่มการแสดงออกของโปรตีน MYC และ BCL2 ในสูตร NCCN-IPI อาจไม่เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการพยากรณ์โรคให้อยู่ในระดับที่ยอมรับได้
Highlight
การเพิ่มการแสดงออกของโปรตีน MYC และ BCL2 ในสูตร NCCN-IPI อาจไม่เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการพยากรณ์โรคให้อยู่ในระดับที่ยอมรับได้
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
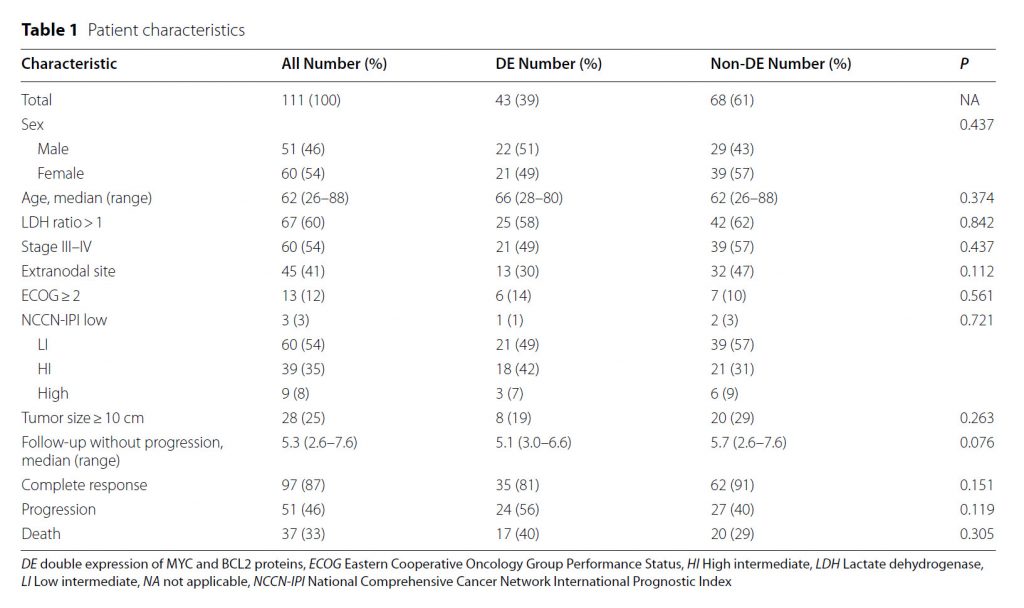
มะเร็งเม็ดเลือดขาวชนิด DLBCL ที่มีการแสดงออกของโปรตีน MYC และ BCL2 จะมีความรุนแรงมากและมีอัตราการรอดชีวิตของผู้ป่วยน้อย คณะวิจัยจึงได้นำข้อมูลทางคลินิกของผู้ป่วยโรคนี้จำนวน 111 คน วิเคราะห์ทางสถิติและพบว่าการเพิ่มการแสดงออกของโปรตีน MYC และ BCL2 ของเซลล์มะเร็งในสูตรของ NCCN-IPI ไม่สามารถเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพของการพยากรณ์โรคในระดับที่ยอมรับได้
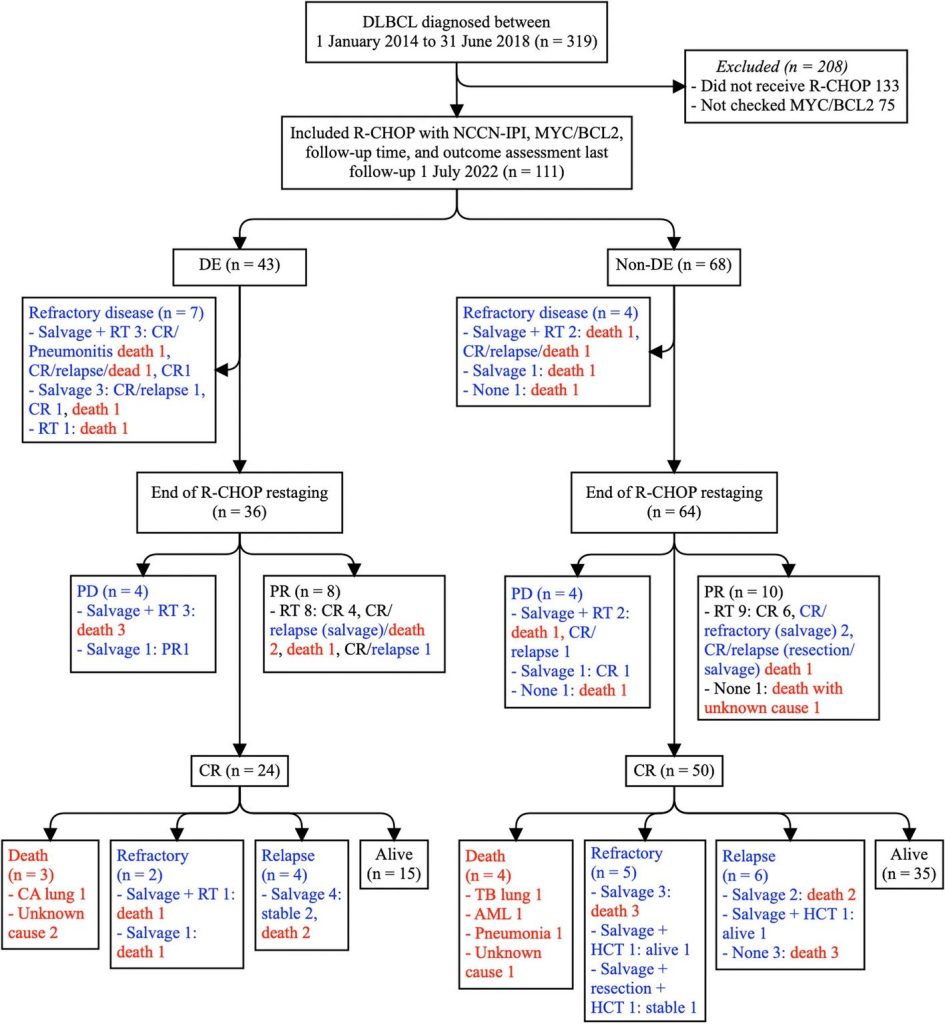
Fig 1. Participant flow diagram
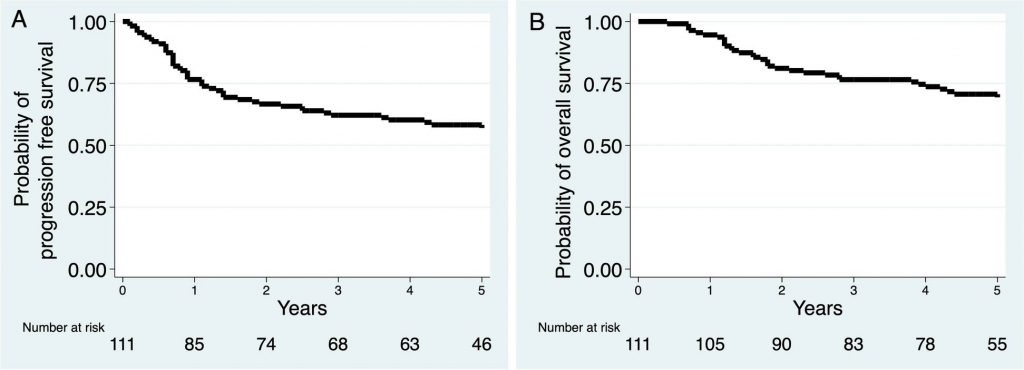
Fig 2. Kaplan–Meier survival curves: A progression-free survival and B overall survival
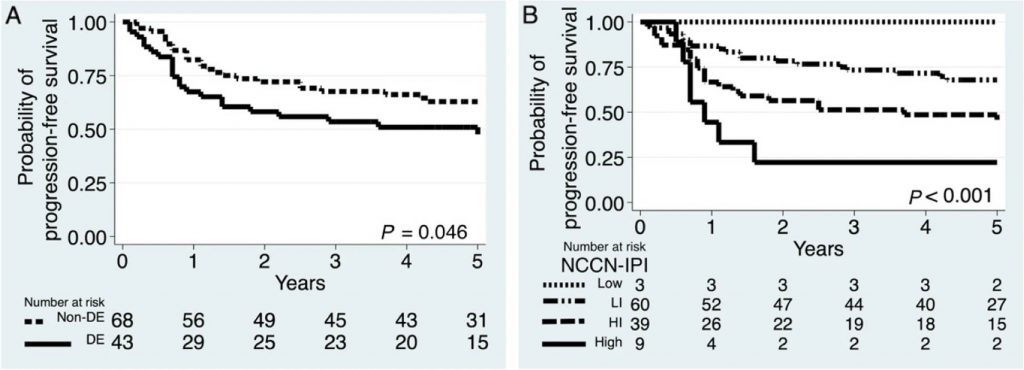
Fig 3. K Kaplan–Meier progression-free survival curves: A DE (P = 0.046) and B NCCN-IPI (P < 0.001)
Abstract
Background
MYC/BCL2 double expression (DE) is associated with poor prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) receiving rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone (R-CHOP). This study aimed to determine whether the addition of DE to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Internal Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) could improve the prediction of disease progression in patients with DLBCL treated with R-CHOP.
Methods
This confirmatory prognostic factor study retrospectively recruited patients with newly diagnosed DLBCL between January 1, 2014, and January 31, 2018, at Ramathibodi Hospital (RA) and Thammasat University Hospital (TU). The follow-up period ended on July 1, 2022. Tumors expressing MYC ≥ 40% and BCL2 ≥ 50% were classified as DE. We calculated the hazard ratios (HR) for progression-free survival (PFS) from the date of diagnosis to refractory disease, relapse, or death. Discrimination of the 5-year prediction was based on Cox models using Harrell’s concordance index (c-index).
Results
A total of 111 patients had DE (39%), NCCN-IPI (8%), and disease progression (46%). The NCCN-IPI adjusted HR of DE was 1.6 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.9–2.8; P = 0.117). The baseline NCCN-IPI c-index was 0.63. Adding DE to the NCCN-IPI slightly increased Harrell’s concordance index (c-index) to 0.66 (P = 0.119).
Conclusions
Adding DE to the NCCN-IPI may not improve the prognostic value to an acceptable level in resource-limited settings. Multiple independent confirmatory studies from a large cohort of lymphoma registries have provided additional evidence for the clinical utility of DE.
Keywords: DLBCL, MYC/BCL2 double expression, R-CHOP, Prognosis, NCCN-IPI, REMARK
Citation: Warnnissorn N, Kanitsap N, Niparuck P, Boonsakan P, Kulalert P, Limvorapitak W, Bhoopat L, Saengboon S, Suriyonplengsaeng C, Chantrathammachart P, Puavilai T, Chuncharunee S. Adding MYC/BCL2 double expression to NCCN-IPI may not improve prognostic value to an acceptable level. Blood Res. 2024 Feb 19;59(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44313-024-00006-w. PMID: 38485822; PMCID: PMC10903517.
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

15. LIFE ON LAND

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ นพ.ชินวุฒิ สุริยนเปล่งแสง
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ นพ.ชินวุฒิ สุริยนเปล่งแสง
เครดิตภาพ: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ นพ.ชินวุฒิ สุริยนเปล่งแสง
Tags: DLBCL, MYC/BCL2 double expression, NCCN-IPI, Prognosis, R-CHOP, REMARK
