ชื่องานวิจัยภาษาไทย
โรคหลอดเลือดใต้กระดูกไหปลาร้าด้านขวาทอดตัวหลังหลอดอาหารร่วมกับลำไส้ใหญ่ตีบแต่กำเนิดซึ่งแสดงอาการคล้ายโรคแพ้โปรตีนนมวัวและภาวะท้องอืดในทารกแรกเกิด
Highlight
รางานฉบับแรกของโรคหลอดเลือดใต้กระดูกไหปลาร้าด้านขวาทอดตัวหลังหลอดอาหารร่วมกับลำไส้ใหญ่ตีบแต่กำเนิดซึ่งแสดงอาการคล้ายโรคแพ้โปรตีนนมวัวและภาวะท้องอืดในทารกแรกเกิด
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
รายงานฉบับนี้นำเสนอกรณีศึกษาที่หายากและซับซ้อนของทารกแรกเกิดไทยคนหนึ่ง ซึ่งมีโรคผิดปกติแต่กำเนิดสองตำแหน่งในระบบทางเดินอาหารซึ่งไม่เคยมีรายงานพบร่วมกันมาก่อน ได้แก่ โรค Retroesophageal right subclavian artery และ Congenital colonic stenosis ซึ่งมีอาการคล้ายโรคที่พบได้บ่อย เช่น โรคแพ้โปรตีนนมวัวหรือภาวะท้องอืดจากการติดเชื้อ ส่งผลให้เกิดการวินิจฉัยผิดพลาด
กรณีนี้ได้เน้นย้ำถึงความสำคัญของการตระหนักถึงโรคแต่กำเนิดที่พบได้น้อยแต่มีผลกระทบรุนแรง ซึ่งหากตรวจพบได้ตั้งแต่เนิ่น ๆ จะช่วยหลีกเลี่ยงการวินิจฉัยผิดและเพิ่มโอกาสในการรักษาทารกในกรณีคล้ายกันในอนาคต
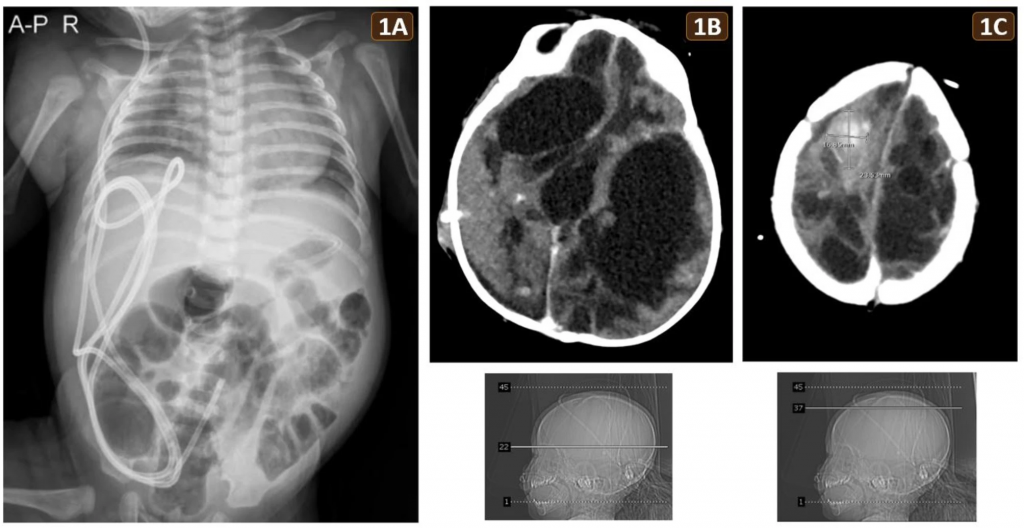
Fig 1.
(A) Abdominal X-ray at 2 months of age, taken during an episode of sepsis, showing multiple dilated bowel loops without air-fluid levels or pneumoperitoneum, consistent with marked abdominal distension. The VP shunt was visible. (B, C) Brain CT at 6 months of age revealing extensive bilateral encephalomalacia, hydrocephalus, and a hyperdense lesion (2.4 × 1.7 cm) in the right high frontal lobe, indicative of recent hemorrhage
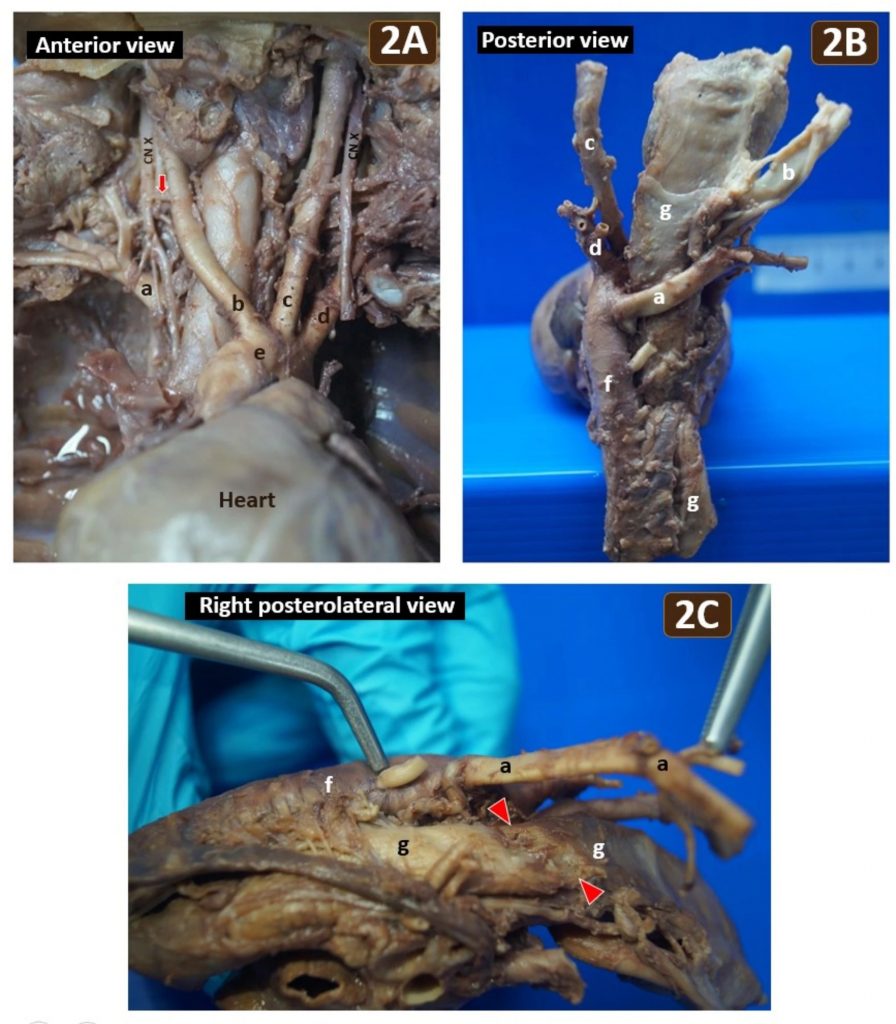
Fig 2.
(A) Anterior view of the mediastinum and neck unveiled the retroesophageal right subclavian artery (a), right common carotid artery (b), left common carotid artery (c), left subclavian artery (d) and the right non-recurrent inferior laryngeal nerve (red arrow) of the vagus nerve (CN X). Arteries (b) to (d) directly originated from the aortic arch (e). No brachiocephalic trunk was observed. (B) Posterior view of the same specimen showing the retroesophageal right subclavian artery (a) arising from the proximal thoracic aorta (f) and coursing obliquely behind the esophagus (g). (C) Right posterolateral view of the same specimen illustrating notable esophageal impression (red arrowheads) caused by the retroesophageal right subclavian artery (a), which was reflected to the left
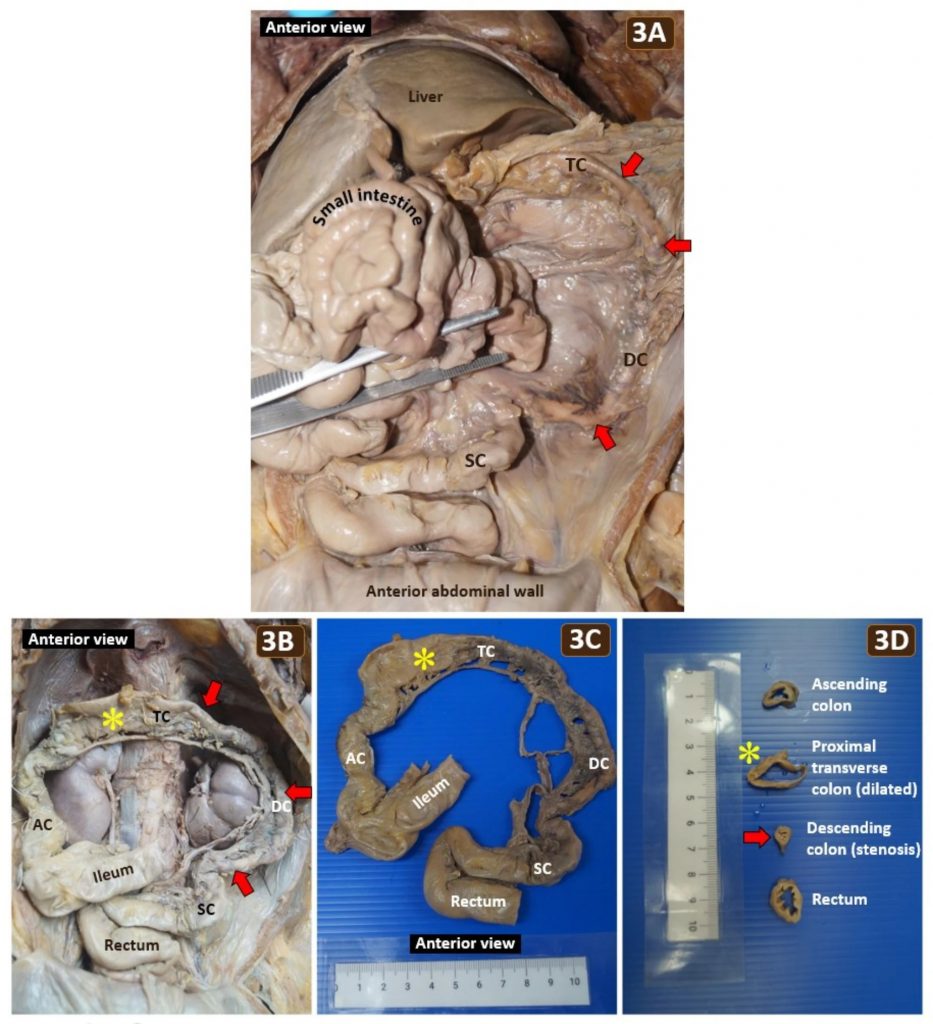
Fig 3.
(A) Reflection of the small intestine revealing the in situ colonic stenosis (red arrows) affecting the distal transverse colon (TC), descending colon (DC) and proximal sigmoid colon (SC) without fibrous adhesion between abdominal viscera. (B) The resected distal ileum to the rectum was repositioned into the abdominal cavity to illustrate the extent of colonic stenosis (red arrows) and a dilatated segment (yellow asterisk) of the transverse colon proximal to the stenosis. (C) The stenotic colon, comprising nearly 50% of the total colonic length, was significantly narrower than the ascending colon (AC) and rectum. (D) Comparative cross sections of the ascending colon, dilated proximal transverse colon, stenotic descending colon, and rectum. Mucosal folding was absent in the dilated transverse colon (yellow asterisk). The descending colon measured 0.6 cm in diameter at the narrowest stenotic segment (red arrow), making it 40–60% narrower than the unaffected colonic segment
Abstract
Background
Double alimentary tract obstruction due to congenital anomalies is a rare clinical occurrence, with limited cases published in medical literature. This article presents a unique case of coexisting retroesophageal right subclavian artery (RRSA) and congenital colonic stenosis (CCS), conditions that have not been previously documented together in pediatric population.
Case presentation
A Thai male newborn was born by cesarean section at gestational age of 41 weeks. One week before birth, intrauterine asphyxia and idiopathic bilateral intracerebral hemorrhage were diagnosed by prenatal ultrasonography. Despite postnatal interventions including a ventriculoperitoneal shunt and subsequent external ventricular drain, the intracerebral hemorrhage recurred and progressed. Concurrently, the patient experienced multiple episodes of post-feeding vomiting, intermittent abdominal distension, and regular defecation without constipation. Sepsis secondary to an infected shunt occurred, accompanied by marked abdominal distension. The physician clinically suspected non-IgE-mediated cow’s milk protein allergy and ileus associated with sepsis. Tragically, the patient succumbed at seven months due to a brain abscess stemming from an infected external ventricular drain. Ultimately, postmortem examination unraveled double alimentary tract obstruction, consisting of RRSA and CCS. The RRSA, originating from proximal thoracic aorta, caused notable esophageal compression and functional stenosis which led to the frequent vomiting and reflux. The CCS involved the distal transverse colon, descending colon and proximal sigmoid colon, accounting for nearly 50% of the colon. The CCS was therefore the exact cause of intermittent abdominal distension. The stenotic colon contained submucosal and myenteric plexuses, excluding Hirschsprung disease.
Conclusion
This case highlights the diagnostic complexities of RRSA and CCS resulting in double gut obstruction and masquerading as non-IgE-mediated cow’s milk protein allergy and sepsis-induced ileus. Awareness of these rare coexisting congenital anomalies can aid in early recognition, prevent misdiagnosis, enable timely management and improve outcomes for affected pediatric patients.
Keywords: Retroesophageal right subclavian artery, Congenital colonic stenosis, Gut obstruction, Cow’s milk protein allergy, Ileus, Sepsis, Neonatal vomiting, Reflux, Abdominal distension, Misdiagnosis
Citation: Trerattanavong P, Chaweeborisuit P, Tankruad S, Hataimala A, Limsuksrikul B, Laemad P, Kittichayathon K, Thintharua P, Meemon K, Suriyonplengsaeng C. Unravelling a pediatric enigma: coexisting retroesophageal right subclavian artery and congenital colonic stenosis masquerading as cow’s milk protein allergy and ileus in a neonate. BMC Pediatr. 2025 Apr 3;25(1):271. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-025-05642-4
PMID: 40175956; PMCID: PMC11967120.
Reference link:
- https://bmcpediatr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12887-025-05642-4
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40175956/
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

4. QUALITY EDUCATION

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ นพ.ชินวุฒิ สุริยนเปล่งแสง
ชื่ออาจารย์และบุคลากรที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล, ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ นพ.ชินวุฒิ สุริยนเปล่งแสง, คุณสิรินาถ ตันกร๊วด
เครดิตภาพ: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล, ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ นพ.ชินวุฒิ สุริยนเปล่งแสง, คุณสิรินาถ ตันกร๊วด
Tags: Abdominal distension, Congenital colonic stenosis, Cow's milk protein allergy, Gut obstruction, Ileus, Misdiagnosis, Neonatal vomiting, Reflux, Retroesophageal right subclavian artery, Sepsis
