Highlight
งานวิจัยนำร่องฉบับนี้เป็นงานวิจัยแรกของสาขาที่ใช้ชุดข้อมูลสาธารณะมาเป็นข้อมูลดิบในการทำงานวิจัยทางกายวิภาคซึ่งเป็นระเบียบวิธีใหม่ที่ยังไม่เคยมีการศึกษาใดกระทำมาก่อน
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
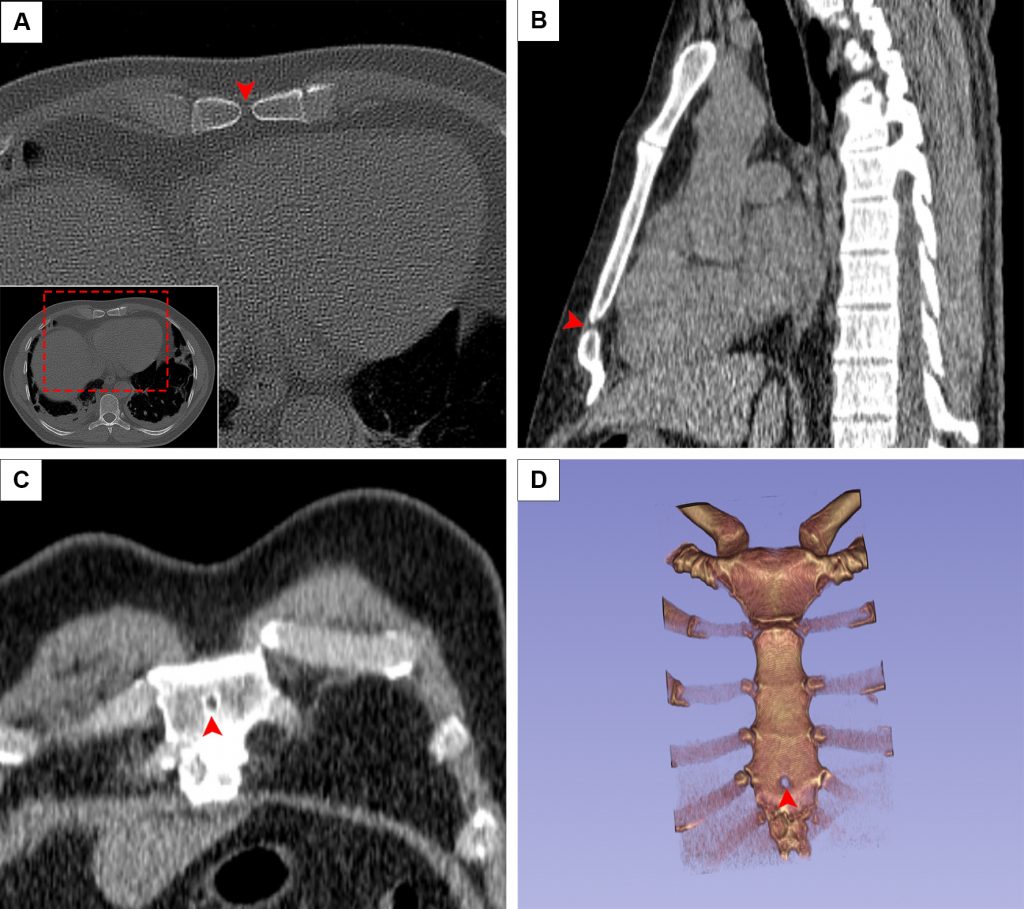
การตรวจเอกซเรย์คอมพิวเตอร์ (CT) ของทรวงอกมีความจำเป็นอย่างยิ่งยวดในช่วงต้นของการระบาดของโรค COVID-19 เนื่องจากเชื้อ COVID-19 สายพันธุ์ดั้งเดิมสามารถก่อให้เกิดการติดเชื้อที่ปอดอย่างรุนแรง ด้วยเหตุนี้ชุดภาพ CT ทรวงอกของผู้ป่วยด้วยโรค COVID-19 จำนวนมากถูกอัปโหลดไว้ในฐานข้อมูลออนไลน์ ซึ่งนักวิจัยจากทั่วโลกสามารถนำไปใช้เพื่อดำเนินงานวิจัยในด้านการนำปัญญาประดิษฐ์มาใช้เพื่อตรวจพบโรค COVID-19 อย่างไรก็ตาม การนำชุดข้อมูลสาธารณะเหล่านี้มาใช้ในงานวิจัยด้านอื่นยังไม่เคยเกิดขึ้นมาก่อน ในการศึกษานี้ ผู้วิจัยได้ศึกษาความชุกของโครงสร้างแปรผันทางกายวิภาค (anatomical variations) เป็นที่รู้จักกันดี 6 ชนิดในทรวงอกโดยใช้ชุดภาพ CT สาธารณะของผู้ป่วยด้วยโรค COVID-19 ชาวอิหร่านกว่า 1,000 ราย ผลการวิจัยพบว่าในระบบทางเดินหายใจ มีโครงสร้างแปรผัน azygos lobe (ในร้อยละ 0.8) และ tracheal bronchus (ในร้อยละ 0.2) ในระบบโครงกระดูกและกล้ามเนื้อพบ sternal foramen (ในร้อยละ 9.6), episternal ossicles (ในร้อยละ 2.9) และ sternalis muscle (ในร้อยละ 1.5) ผู้วิจัยเชื่อว่านักกายวิภาคศาสตร์จะได้รับประโยชน์จากการใช้ชุดข้อมูลสาธารณะเป็นข้อมูลดิบสำหรับการวิจัย เนื่องจากชุดข้อมูลเหล่านี้มีจำนวนมากและสามารถเข้าถึงได้อย่างเสรีและง่ายดาย
Abstract
Chest computed tomography (CT) has been the preferred imaging modality during the pandemic owing to its sensitivity in detecting COVID-19 infections. Recently, a large number of COVID-19 imaging datasets have been deposited in public databases, leading to rapid advances in COVID-19 research. However, the application of these datasets beyond COVID-19-related research has been little explored. The authors believe that they could be used in anatomical research to elucidate the link between anatomy and disease and to study disease-related alterations to normal anatomy. Therefore, the present study was designed to investigate the prevalence of six well-known anatomical variants in the thorax using open-access CT images obtained from over 1000 Iranian COVID-19 patients aged between 6 and 89 years (60.9% male and 39.1% female). In brief, we found that the azygos lobe, tracheal bronchus, and cardiac bronchus were present in 0.8%, 0.2%, and 0% of the patients, respectively. Variations of the sternum, including sternal foramen, episternal ossicles, and sternalis muscle, were observed in 9.6%, 2.9%, and 1.5%, respectively. We believe anatomists could benefit from using open-access datasets as raw materials for research because these datasets are freely accessible and are abundant, though further research is needed to evaluate the uses of other datasets from different body regions and imaging modalities. Radiologists should also be aware of these common anatomical variants when examining lung CTs, especially since the use of this imaging modality has increased during the pandemic.
KEYWORDS: COVID-19, lung, anatomical variation, dataset, computed tomography
Citation: Yurasakpong, L., Asuvapongpatana, S., Weerachatyanukul, W., Meemon, K., Jongkamonwiwat, N., Kruepunga, N., Chaiyamoon, A., Sudsang, T., Iwanaga, J., Tubbs, R.S., Suwannakhan, A. (2022). Anatomical variants identified on chest computed tomography of 1000+ COVID‐19 patients from an open‐access dataset. Clinical Anatomy, 35(6), 723-731.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.23873
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: นางสาวลภัสรดา ยุรศักดิ์พงศ์
Credit ภาพ: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
Tags: anatomical variation, computed tomography, COVID-19, dataset, lung
