สารสกัด Hexadecanoic acid จากสาหร่ายลิ้นมังกรสามารถกระตุ้นการตายของเซลล์มะเร็งเต้านมผ่านทาง ER stress
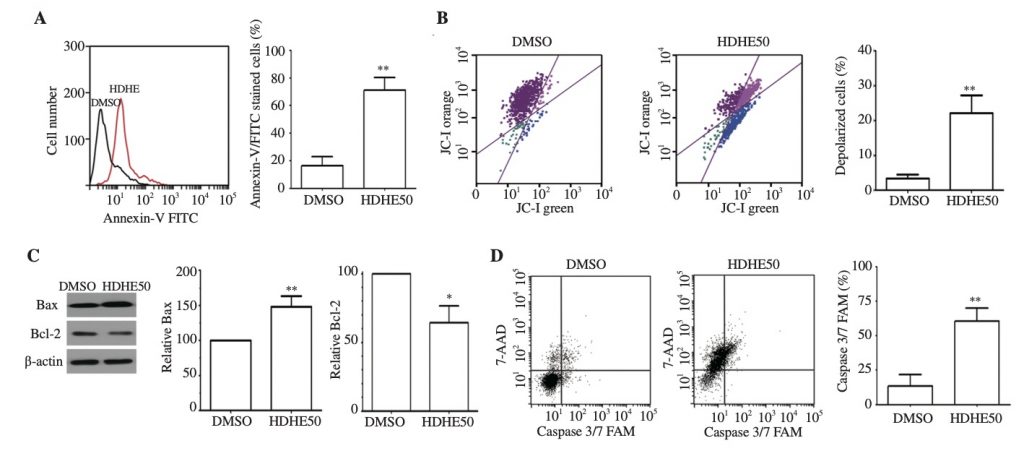
Highlight: สารสกัด hexadecanoic acid จากสาหร่ายลิ้นมังกร สามารถเพิ่มการตายของเซลล์มะเร็งเต้านม MDA-MB-231 ทั้งในรูปแบบ apoptosis และ autophagy และทำให้เกิดการเปลี่ยนแปลงของเยื้อหุ้มไมโตคอนเดรีย การทำลาย DNA และ ER stress
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
สาหร่ายลิ้นมังกรมีสารออกฤทธิ์ทางธรรมชาติมากมายที่เป็นประโยชน์ทางการแพทย์ เช่น carotenoids, flavonoids, sulfated polysaccharides, terpenoids และ fatty acids โดยในการศึกษานี้มีความสนใจในการใช้สารสกัดจากสาหร่ายลิ้นมังกรในการต้านโรคมะเร็งเต้านมชนิด triple-negative ซึ่งดื้อต่อการรักษาโดยใช้ฮอร์โมนหรือแอนติบอดี และศึกษากลไกในการต้านโรคมะเร็งเต้านมชนิดดังกล่าว
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of the hexane solvent fraction of Halymenia durvillei (HDHE) on triple-negative breast cancer.
Methods
The phytochemical profile of HDHE was investigated by GC-MS. The cytotoxicity of HDHE against MDA-MB-231 cells was determined. The apoptotic and autophagic effects of HDHE were analyzed. The expression of molecular markers controlling apoptosis, autophagy, DNA damage, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress was determined.
Results
HDHE contains a mixture of fatty acids, mainly hexadecanoic acid. HDHE at a cytotoxic concentration induced apoptotic death of MDA-MB-231 cells through mitochondrial membrane dysfunction, and induction of apoptosis markers, and increased the expression of proteins related to DNA damage response. HDHE also induced the expression of LC-3, a marker of autophagic cell death at a cytotoxic concentration. Moreover, HDHE modulated the expression of ER stress genes.
Conclusions
The hexadecanoic acid-enriched extract of Halymenia durvillei promotes apoptosis and autophagy of human triple-negative breast cancer cells. This extract may be further explored as an anticancer agent for triple-negative breast cancer.
KEYWORDS: Apoptosis, Autophagy, Endoplasmic reticulum stress, Halymenia durvillei, Hexadecanoic acid, Red algae, Triple-negative breast cancer
Citation: Sangpairoj K, Settacomkul R, Siangcham T, Meemon K, Niamnont N, Sornkaew N, Tamtin M, Sobhon P, Vivithanaporn P*. Hexadecanoic acid-enriched extract of Halymenia durvillei induces apoptotic and autophagic death of human triple-negative breast cancer cells by upregulating ER stress. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2022; 12(3):132-140. DOI: 10.4103/2221-1691.338922
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

14. LIFE BELOW WATER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
Credit ภาพ: Dr. Kant Sangpairoj
Tags: Apoptosis, Autophagy, Endoplasmic reticulum stress, Halymenia durvillei, Hexadecanoic acid, Red algae, Triple-negative breast cancer
