Highlight:
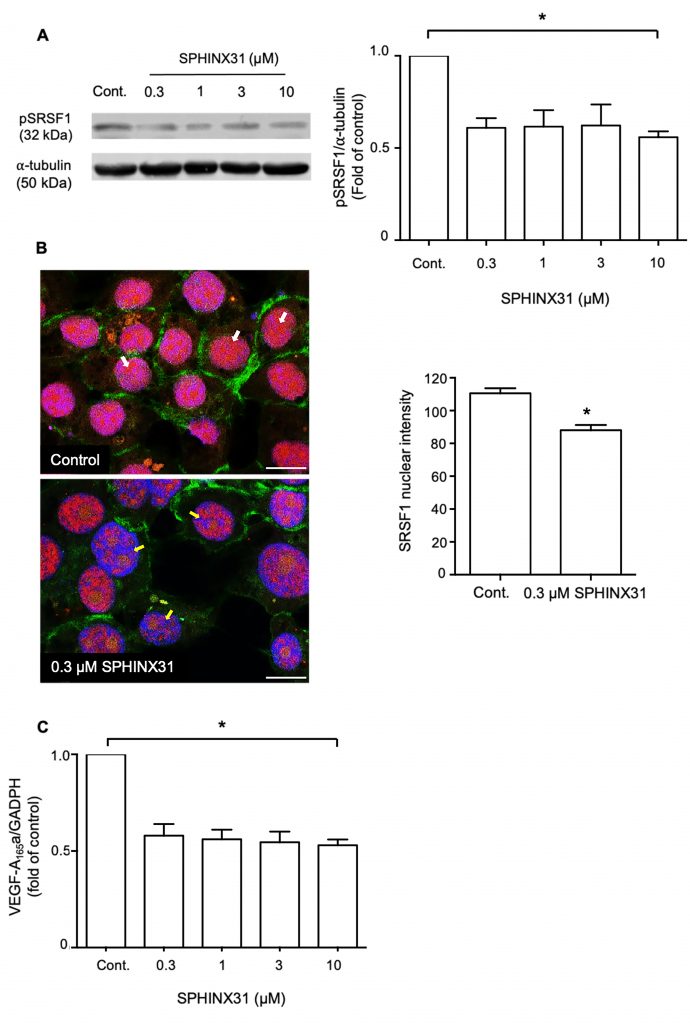
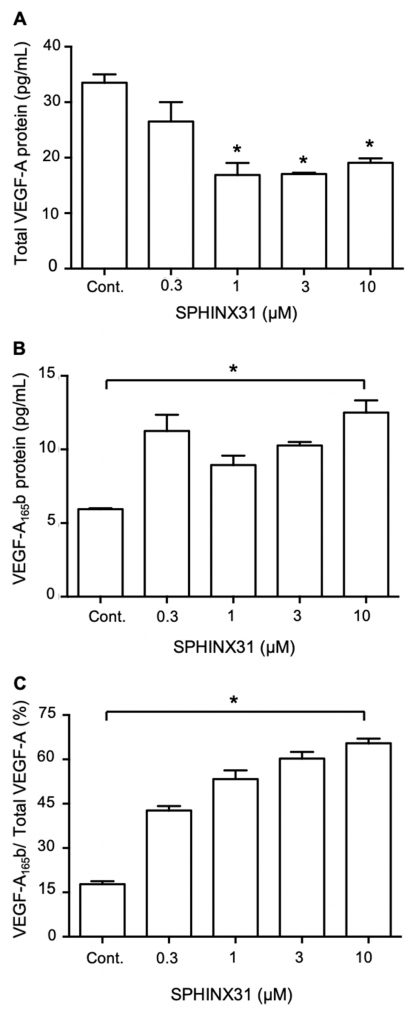
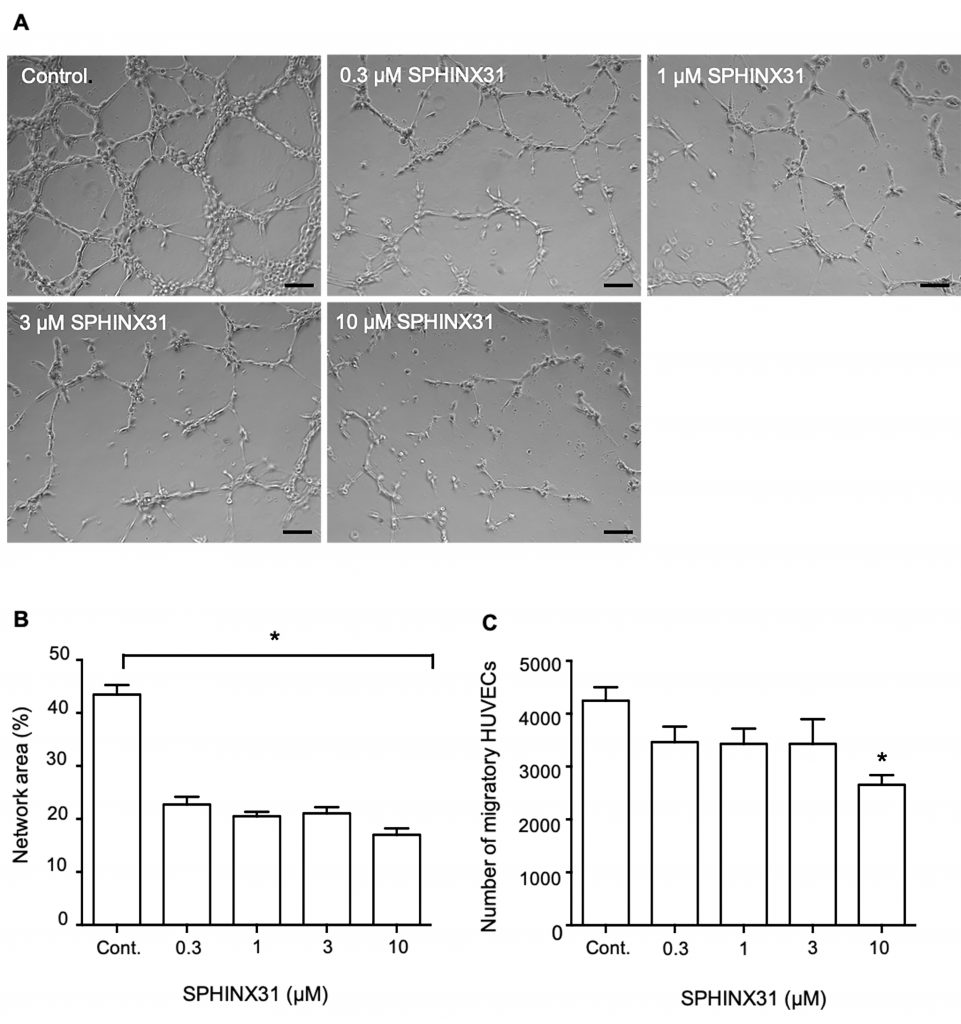
สารยับยั้ง SRPK1 ลดกระบวนการฟอสโฟรีเลชั่นของ SRSF1 ในเซลล์มะเร็งท่อน้ำดี ลดการเคลื่อนย้าย SRSF1 ไปยังนิวเคลียส เซลล์ที่ได้รับสารยับยั้ง SRPK1 มีระดับโปรตีน VEGFA-165b เพิ่มขึ้น เซลล์เยื่อบุผนังหลอดเลือด (HUVEC) ที่เพาะเลี้ยงด้วยอาหารเลี้ยงเซลล์มะเร็งท่อน้ำดีที่ได้รับสารยับยั้ง SRPK1 ที่มีปริมาณ VEGF-A165b สูง เกิดการสร้างหลอดเลือดใหม่น้อยลง
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
มะเร็งหลายชนิดมีการแสดงออกของโปรตีน SRPK1 ซึ่งเป็นโปรตีนควบคุมการ splicing ของ mRNA มากผิดปกติ บ่งชี้ว่ามีศักยภาพเป็นเป้าหมายการรักษามะเร็ง และมะเร็งระยะแพร่กระจายมีการแสดงออกของ angiogenic isoform ของ vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) มาก การศึกษานี้ตรวจสอบการแสดงออกของ SRPK1 และผลของการยับยั้ง SRPK1 ต่อความสามารถในการมีชีวิตและการสร้างหลอดเลือดใหม่ของเซลล์มะเร็งท่อน้ำดีโดยใช้สารยับยั้งต่อ SRPK1 คือ SPHINX31 ซึ่งเป็นโมเลกุลที่ยับยั้ง จำเพาะต่อ SRPK1 โดยมุ่งหวังผลต่อการยับยั้งการ splicing ของ angiogenic isoform ของ VEGF
Abstract
The serine/arginine-rich protein kinase-1 (SRPK1) is an enzyme that has an essential role in regulating numerous aspects of mRNA splicing. SRPK1 has been reported to be overexpressed in multiple cancers, suggesting it as a promising therapeutic target in oncology. No previous studies reported the role of SRPK1 in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cells. This study aimed to examine the expression of SRPK1 and the effects of SRPK1 inhibition on the viability and angiogenesis activity of CCA cells using a selective SRPK1 inhibitor, SPHINX31. Here, we demonstrate that SPHINX31 (0.3‐10 μM) had no inhibitory effects on CCA cells’ viability and proliferation. However, SPHINX31 decreased the mRNA expression of pro-angiogenic VEGF-A165a isoform. In addition, SPHINX31 attenuated SRSF1 phosphorylation and nuclear localization, and increased the ratio of VEGF-A165b/total VEGF-A proteins. Moreover, when HUVECs were grown in conditioned medium from SPHINX31-treated CCA cells, migration slowed, and tube formation decreased. The present study demonstrates that targeting SRPK1 in CCA cells effectively attenuates angiogenesis by suppressing pro-angiogenic VEGF-A isoform splicing. These findings suggest a potential therapeutic treatment using SRPK1 inhibitors for the inhibition of angiogenesis in cholangiocarcinoma.
KEYWORDS: Angiogenesis, VEGF-A, SRPK1, SPHINX31, Cholangiocarcinoma, Endothelial cells
Citation: Kittiya Supradit, Boonyakorn Boonsri, Jinchutha Duangdara, Thanvarin Thitiphatphuvanon, Chinnawut Suriyonplengsaeng, Thaned Kangsamaksin, Tavan Janvilisri, Rutaiwan Tohtong, Kiren Yacqub-Usman, Anna M. Grabowska, David O. Bates, Kanokpan Wongprasert, Inhibition of serine/arginine-rich protein kinase-1 (SRPK1) prevents cholangiocarcinoma cells induced angiogenesis, Toxicology in Vitro,Volume 82,2022,105385.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2022.105385
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

SDG Goal ที่เกี่ยวข้องอื่น ๆ
17. Partnerships for the goals

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ, ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ นพ.ชินวุฒิ สุริยนเปล่งแสง
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Kittiya Supradit, Jinchutha Duangdara
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Thailand research fund, Medical research council UK, Newton fund
ภาพถ่าย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
Tags: Angiogenesis, Cholangiocarcinoma, Endothelial cells, SPHINX31, SRPK1, VEGF-A
