Highlight:
บรรจุภัณฑ์นาโนที่พัฒนามาจากเปลือกหุ้มไวรัสของกุ้งก้ามกราม สามารถขนส่งพลาสมิดหรือสารพันธุกรรมออกฤทธิ์ (dsRNA) เข้าไปยังเซลล์แมลงเพาะเลี้ยง หรือเนื้อเยื่อของกุ้งได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ กลุ่มวิจัยของเราจึงได้ดัดแปลงบรรจุภัณฑ์นาโนดังกล่าว เพื่อให้สามารถประยุกต์ใช้กับการขนส่งยา เข้าสู่เซลล์มะเร็งแบบเฉพาะเจาะจง โดยการดัดแปลงผิวภายนอกของบรรจุภัณฑ์ด้วยเปปไทด์ GE11 ที่มีความจำเพาะเจาะจงต่อตัวรับ EGFR บนผิวเซลล์มะเร็งลำไส้ใหญ่ของมนุษย์ (SW480) ในตำแหน่งที่แตกต่างกันบนผิวของบรรจุภัณฑ์นาโน ซึ่งจำแนกได้เป็น 3 ชนิด คือชนิดการแทนที่ลำดับกรดอะมิโน (R-MrNV) ชนิดการแทรกลำดับกรดอะมิโน (I-MrNV) และชนิดต่อขยายส่วนปลาย C ของโปรตีนเปลือกหุ้ม (E-MrNV) ผลการทดลองพบว่า บรรจุภัณฑ์ทั้ง 3 ชนิดยังคงรูปร่างของบรรจุภัณฑ์ทรงกลมได้เหมือนเดิม และคงความสามารถในการบรรจุ dsRNA ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ นอกจากนี้บรรจุภัณฑ์ชนิด R-MRNV และชนิด E-MrNV มีประสิทธิภาพในการเกาะเกี่ยว (Binding) และผ่านเข้าสู่ (Internalization) เซลล์มะเร็งลำไส้ใหญ่ SW480 ได้ดีขึ้นมาก เราทำการทดสอบความจำเพาะของการเกาะเกี่ยวด้วยวิธี เปลี่ยนแปลงพันธุกรรมของตัวรับ EGFR บนผิวเซลล์มะเร็ง หรือการใช้เปปไทด์ GE11 รบกวนการเกาะเกี่ยว หรือการใช้เซลล์มะเร็งที่ไม่ปรากฏตัวรับ EGFR แสดงให้เห็นว่าบรรจุภัณฑ์ที่ดัดแปลงทั้ง 2 ชนิด มีความจำเพาะต่อตัวรับบนผิวเซลล์มะเร็งเป็นอย่างมาก นอกจากนี้บรรจุภัณฑ์ทั้ง 2 ชนิด ยังมีความสามารถในการขนถ่ายเวกเตอร์ GFP เข้าสู่เซลล์มะเร็ง ส่งผลให้เกิดการเรืองแสงฟลูออเรสเซนต์สีเขียวภายในเซลล์ได้อย่างชัดเจน จึงสรุปได้ว่าบรรจุภัณฑ์ดัดแปลงของเปลือกหุ้มไวรัสที่ติดเชื้อในกุ้ง (MrNV) มีศักยภาพสูงมากในการพัฒนาต่อยอดเพื่อเป็นผลิตภัณฑ์ในการขนส่งยาเข้าสู่เซลล์มะเร็งต่อไปในอนาคต
Abstract
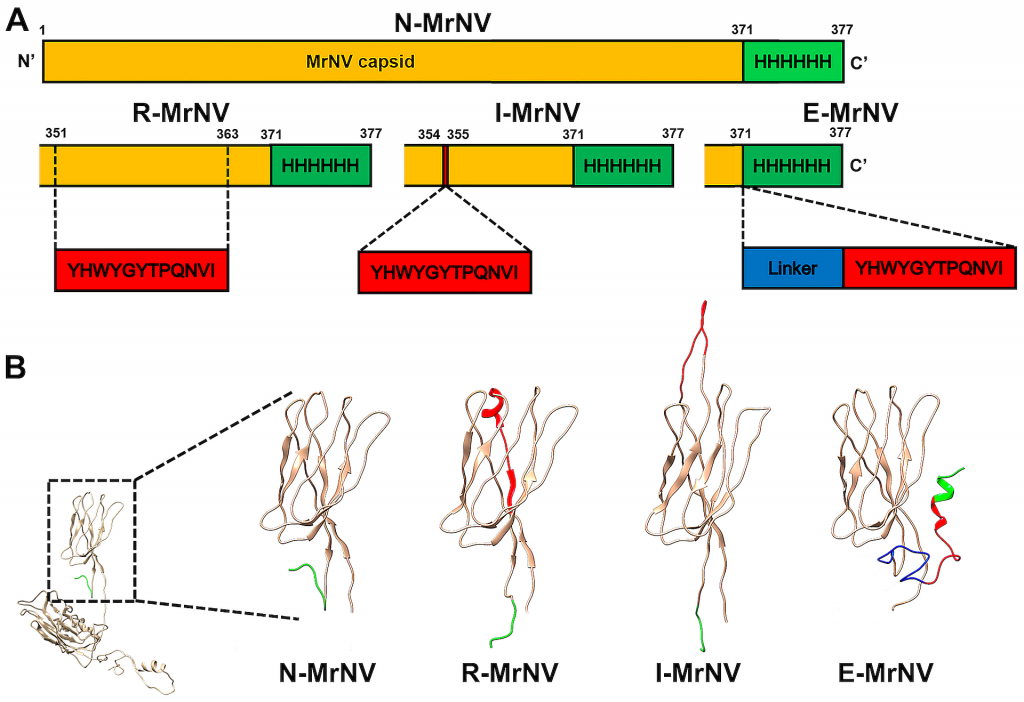
Recombinant MrNV capsid protein has been shown to effectively deliver plasmid DNA and dsRNA into Sf9 insect cells and shrimp tissues. To extend its application to cancer cell-targeting drug delivery, we created three different types of chimeric MrNV virus-like particles (VLPs) (R-MrNV, I-MrNV, and E-MrNV) that have specificity toward the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a cancer cell biomarker, by incorporating the EGFR-specific GE11 peptide at 3 different locations within the host cell recognition site of the capsid. All three chimeric MrNV-VLPs preserved the ability to form a mulberry-like VLP structure and to encapsulate EGFP DNA plasmid with an efficiency comparable to that previously reported for normal MrNV (N-MrNV). Compared to N-MrNV, the chimeric R-MrNV and E-MrNV carrying the exposed GE-11 peptide showed a significantly enhanced binding and internalization abilities that were specific towards EGFR expression in colorectal cancer cells (SW480). Specific targeting of chimeric MrNV to EGFR was proven by both EGFR silencing with siRNA vector and a competition with excess GE-11 peptide as well as the use of EGFR-negative colorectal cells (SW620) and breast cancer cells (MCF7). We demonstrated here that both chimeric R-MrNV and E-MrNV could be used to encapsulate cargo such as exogenous DNA and deliver it specifically to EGFR-positive cells. Our study presents the potential use of surface-modified VLPs of shrimp virus origin as nanocontainers for targeted cancer drug delivery.
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
การใช้ VLPs จาก ไวรัส MrNV ของกุ้งมาปรับเปลี่ยนโปรตีนเปลือกให้จำเพาะต่อตัวรับของเซลล์มะเร็งลำไส้ใหญ่ จะทำให้มีผลฆ่าเซลล์มะเร็งได้อย่างจำเพาะ โดยไม่ทำอันตรายต่อเซลล์อื่นของร่างกาย
KEYWORDS: VLP, Nodavirus, EGFR, MrNV, Cancer
Citation: Grataitong, K., Huault, S., Chotwiwatthanakun, C. et al. Chimeric virus-like particles (VLPs) designed from shrimp nodavirus (MrNV) capsid protein specifically target EGFR-positive human colorectal cancer cells. Sci Rep11, 16579 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95891-x
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.วัฒนา วีรชาติยานุกูล
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.วัฒนา วีรชาติยานุกูล
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Khwanthana Grataitong
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Royal Golden Jubilee (RGJ)
ภาพถ่าย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.วัฒนา วีรชาติยานุกูล
