Highlight: เห็นถึงความสำคัญของน้ำตาล mannose บนผิวของอสุจิ ว่าสามารถใช้เป็นได้ทั้งตัวบ่งชี้ความสมบูรณ์ของอสุจิเอง และยังบ่งบอกว่าน้ำตาลบนผิวของอสุจิมีความเกี่ยวข้องกับการจับและการเจาะไข่อีกด้วย ดังนั้นการศึกษานี้จึงทำให้เราเข้าใจกระบวนการปฏิสัมพันธ์ระหว่างไข่กับเสปิร์มในสปีชีส์นี้ดีขึ้น และอาจสามารถใช้น้ำตาลบนผิวอสุจิเพื่อพัฒนาในการผสมเทียมในกุ้งก้ามกรามต่อไปในอนาคตได้อีกด้วย
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
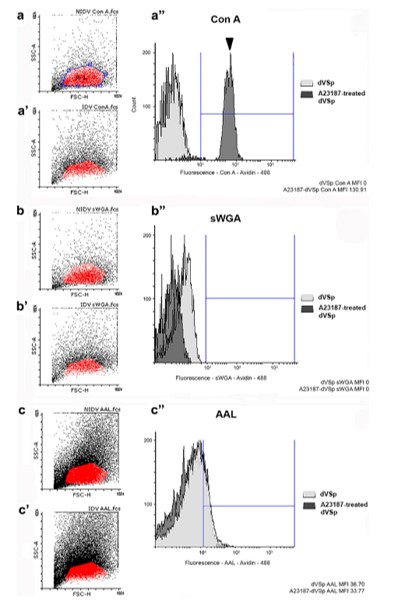
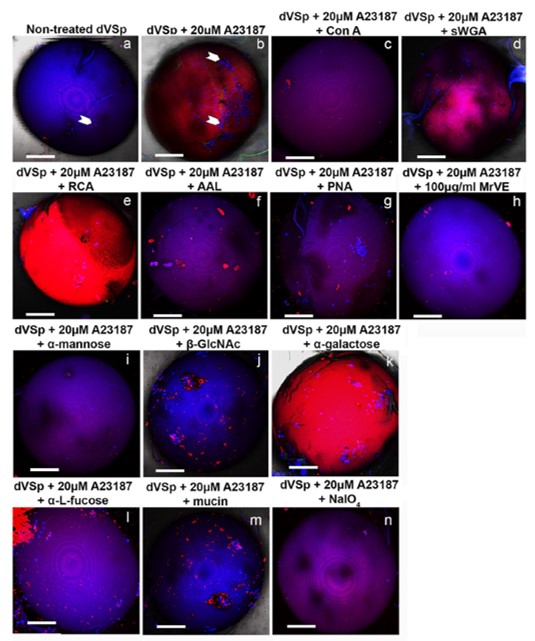
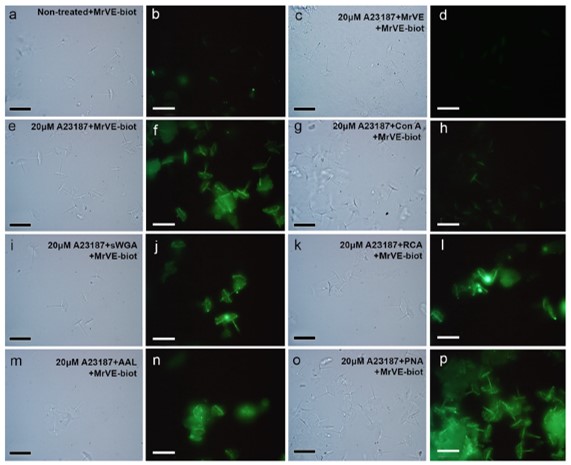
โครงสร้าง acrosome (ถุงเอนไซม์ในการเจาะไข่) ของตัวอสุจิ และการปล่อยเอนไซม์ออกมา สามารถระบุความสมบูรณ์ของอสุจิได้ ในสัตว์ชนิดอื่นสามารถระบุโครงสร้างนี้ได้ง่าย แต่โครงสร้าง acrosome ในกุ้งก้ามกรามเป็นโครงสร้างที่ระบุยาก ทำให้ไม่สามารถที่จะระบุความสมบูรณ์ของอสุจิได้ด้วยตาเปล่า และอสุจิแต่ละส่วนในถุงเก็บอสุจิและท่ออสุจิก็มีความพร้อมในการผสมพันธุ์ไม่เท่ากัน อย่างไรก็ตามอสุจิในท่อนำอสุจิส่วนปลายซึ่งปกติยังไม่สมบูรณ์พอที่จะผสมพันธุ์ แต่สามารถกระตุ้นให้พร้อมด้วย calcium ionophore A23187 เพราะเมื่อกระตุ้นแล้วพบว่ามีเอนไซม์ถูกปล่อยออกมาทำงาน และเพิ่มความสามารถในการจับและการเจาะไข่ อย่างไรก็ตามเอนไซม์เหล่านี้มีการทำงานในระยะเวลาสั้นมาก ทำให้ไม่สามารถใช้การปลดปล่อยเอนไซม์ เป็นตัวบ่งชี้ว่าอสุจิสมบูรณ์และพร้อมทำงานแล้ว ทั้งทางด้านปริมาณและคุณภาพ ดังนั้นเพื่อหาตัวบ่งชี้ความสมบูรณ์พร้อมในการทำงานของอสุจิ การศึกษานี้ได้ดูจากน้ำตาลบนผิวของอสุจิแทน โดยพบว่า หลังจากกระตุ้นอสุจิด้วย A23187 บนผิวของอสุจิมีการแสดงออกของหมู่น้ำตาล mannose เป็นจำนวนมาก ยืนยันด้วยการย้อมด้วยเลคติน ConA นอกจากนี้ยังพบว่าการกำจัดน้ำตาลออกด้วย sodium metaperiodate แช่อสุจิด้วย เลคติน ConA รวมทั้งแช่อสุจิด้วยน้ำตาล mannose ก่อน เพื่อยับยั้งหมู่น้ำตาลบนผิวของอสุจิ พบว่าหลังการยับยั้งน้ำตาล อสุจิถูกกระตุ้นได้ลดลงด้วย A23187 และเมื่อนำอสุจิที่โดนยับยั้งน้ำตาลบนผิวนี้ไปจับกับโปรตีนบนผิวของไข่ ก็พบว่าอสุจิไม่สามารถที่จะจับกับผิวไข่ได้ ดังนั้นการศึกษานี้จึงแสดงในเห็นถึงความสำคัญของน้ำตาล mannose บนผิวของอสุจิว่า สามารถใช้เป็นได้ทั้งตัวบ่งชี้ความสมบูรณ์ของอสุจิเอง และยังบ่งบอกว่าน้ำตาลบนผิวของอสุจิมีความเกี่ยวข้องกับการจับและการเจาะไข่อีกด้วย ดังนั้นการศึกษานี้จึงทำให้เราเข้าใจกระบวนการปฏิสัมพันธ์ระหว่างไข่กับเสปิร์มในสปีชีส์นี้ดีขึ้น และอาจสามารถใช้น้ำตาลบนผิวอสุจิเพื่อพัฒนาในการผสมเทียมในกุ้งก้ามกรามต่อไปในอนาคตได้อีกด้วย
Abstract
The unusual morphology and poorly defined acrosome-like structure in the mature sperm of the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii has led to difficulties in identifying the state of sperm activation. Mature distal vas deferens sperm (dVSp) can be activated by the calcium ionophore A23187 to show acrosome reaction-like enzymatic activities that increase their binding and penetration capabilities. However, these short-lived enzymatic activities limit their usefulness as a marker of sperm activation for further qualitative and quantitative analyses, leading to our examining the alterations in the exposure of sperm surface glycoconjugates both as markers of sperm activation and for their role in gamete interaction. Our results showed that after A23187 treatment, there was an increased exposure of mannosylated glycoconjugates on the sperm surface revealed by significant Concanavalin A (Con A) staining. Furthermore, sodium metaperiodate pre-treatment, Con A pre-incubation, or co-incubation with α-mannose monosaccharides all significantly reduced A23187-induced dVSp binding to the egg vitelline envelop, demonstrating the importance of sperm surface mannosylated glycoconjugates in the binding process. These same pre-treatments of sperm also resulted in the inhibition of the binding of soluble vitelline envelop proteins (MrVE) to both the sperm surface and to mannosylated dVSp protein bands. Therefore, the present study demonstrated the importance of the exposure of mannosylated glycoconjugates on the surface of activated dVSp, both as a reliable marker of sperm activation and as a binding factor in the gamete interaction process. Furthermore, these findings allow for a better understanding of the surface glycoconjugate-mediated interaction process between gametes in this species of prawn.
KEYWORDS: A23187, Egg, Glycoconjugates, Lectins, Mannose, Prawn, Sperm
Citation:
Somrit M, Weerachatyanukul W, Asuvapongpatana S, Timklay W, Watthammawut A. Mannosylated glycoconjugates on the surface of activated sperm in the giant freshwater prawn are crucial for sperm binding with the egg vitelline envelop. Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Apr;384(1):179-193. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03324-4. Epub 2021 Jan 11. PMID: 33427951.
RELATED SDGs: 2. ZERO HUNGER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: อาจารย์ ดร.มนสิชา สมฤทธิ์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.วัฒนา วีรชาติยานุกูล, รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.สมลักษณ์ อสุวพงษ์พัฒนา, อาจารย์ ดร.มนสิชา สมฤทธิ์
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Thailand research fund (MRG6080113), Sirnakharinwirot University Grant (493/2559) and Research support grant of the faculty of Science, Mahidol university
Tags: A23187, Egg, Glycoconjugates, Lectins, Mannose, Prawn, Sperm
