Highlight
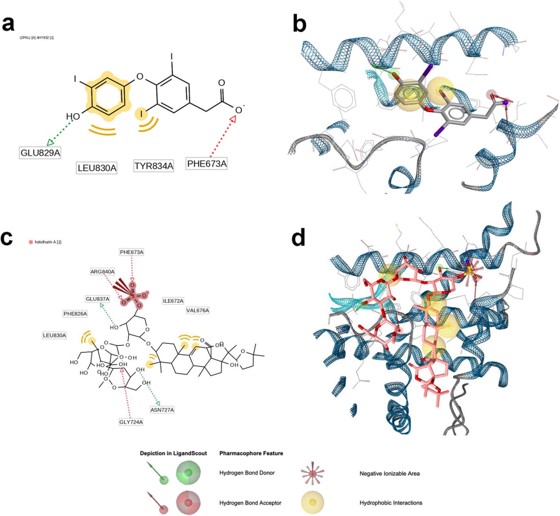
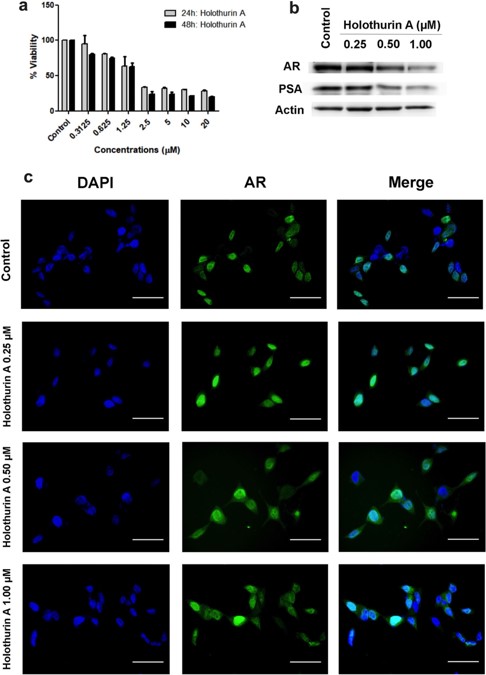
สาร holothurin A สามารถลดการแสดงออกของโปรตีน PSA ทำให้ลดการเจริญเติบโตของเซลล์มะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากที่มีแอนโดรเจนรีเซพเตอร์ โดยพบว่าสาร holothurin A จับกับ BF3 บนแอนโดรเจนรีเซพเตอร์ได้อย่างมั่นคงการจำลองผ่านทางคอมพิวเตอร์ ดังนั้นบริเวณ BF3 น่าจะเป็นตำแหน่งที่สำคัญอีกตำแหน่งในการรักษาโรคมะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากต่อไป
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
Androgen receptor มีหน้าที่สำคัญอย่างนึงที่ช่วยทำให้เซลล์มะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากเจริญเติบโต ทำให้รีเซพเตอร์ชนิดนี้ถูกพิจารณาในการรักษาโรคมะเร็งเบื้องต้น แต่อย่างไรก็ตามเมื่อคนไข้ได้รับการรักษาด้วยฮอร์โมนเป็นระยะเวลานาน เซลล์มะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากจะพัฒนาตัวเองและต้านต่อการรักษาฮอร์โมนได้ เพราะเกิดการกลายพันธุ์ที่ตำแหน่งการจับของ ligand ต่อแอนโดรเจนรีเซพเตอร์ เป็นที่น่าสนใจว่า binding function 3 (BF3) เป็นตำแหน่งที่อยู่บนแอนโดรเจนรีเซพเตอร์นั้น สามารถนำมาใช้ในการรักษาการกลับมาเป็นซ้ำของมะเร็ง ดังนั้นในการศึกษานี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์ในการศึกษาศักยภาพของสาร holothurin A ที่เป็นกลุ่ม triterpenoid saponin ของปลิงทะเลขาว H. scabra ต่อการแสดงออกของแอนโดรเจนของเซลล์มะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากในระดับหลอดทดลองและการจำลองผ่านทางคอมพิวเตอร์ เพื่อใช้เป็นประโยชน์ในการรักษาโรคมะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากต่อไป
Abstract
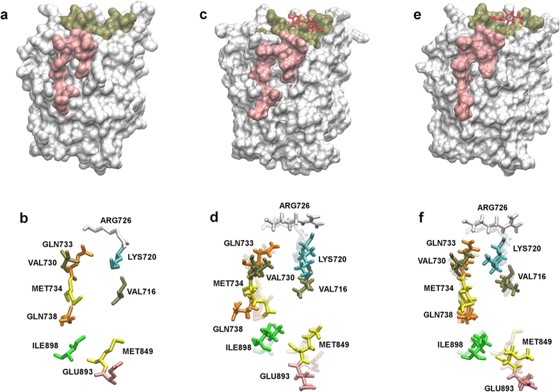
The androgen receptor (AR) plays a crucial role in the growth of prostate cancer, and has long been considered the cancer’s primary strategic therapeutic target. However, despite the early susceptibility, patients receiving hormonal therapy targeting AR are likely to develops resistance to the treatment and progresses to the castration-resistant stage as a consequence of the mutation at the ligand binding pocket of AR. Interestingly, the surface pocket of the AR called binding function 3 (BF3) has been reported as a great benefit for treating a recurrent tumor. Herein, we investigate the potential of using a marine triterpenoid saponin, holothurin A, on targeting AR expression of prostate cancer using in vitro and in silico studies. Holothurin A reduced the PSA expression, leading to the growth inhibition of androgen sensitive prostate cancer cell line through a downregulation of AR activity. The molecular docking study demonstrated that holothurin A could bind strongly in the BF3 pocket by energetically favorable hydrogen acceptor and hydrophobic with a calculated binding affinity of -13.90 kcal/mol. Molecular dynamics simulations provided the additional evidence that holothurin A can form a stable complex with the BF3 pocket through the hydrophobic interactions with VAL676, ILE680, and ALA721. As a consequence, holothurin A modulates the activation function-2 (AF2) site of the AR through repositioning of the residues in the AF2 pocket. Targeting alternatives sites on the surface of AR via holothurin A will provide a potential candidate for future prostate cancer treatment.
Keywords: BF3, Prostate cancer, allosteric, androgen receptor, holothurin A
Citation: Pranweerapaiboon K, Garon A, Seidel T, Janta S, Plubrukarn A, Chaithirayanon K, Langer T. In vitro and in silico studies of holothurin A on androgen receptor in prostate cancer. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Sep 13:1-9. DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1975562.
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

14. LIFE BELOW WATER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: ดร.กันตา ปรานวีระไพบูลย์
เครดิตภาพ: ดร.กันตา ปรานวีระไพบูลย์
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: สำนักงานพัฒนาการวิจัยการเกษตร (องค์การมหาชน)
Tags: allosteric, androgen receptor, BF3, holothurin A, Prostate cancer
