Highlight
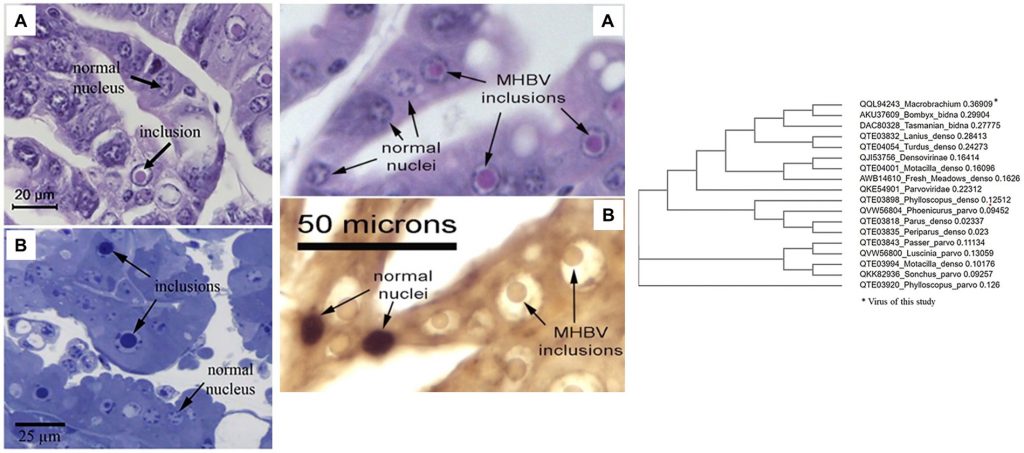
We have discovered Macrobrachium hepatopancreatic bidnavirus (MHBV) as the cause of eosinophilic to magenta, intranuclear inclusions in the hepatopancreas of Mr that are sometimes associated with mortality and sometimes not. Decapod hepanhamaparvovirus (DHPV) has shown no recognizable lesions in our samples, unlike its relatives in penaeid shrimp, although grossly normal nuclei were shown to be infected with it by ISH. PCR testing revealed that the two viruses can occur independently in shrimp samples that show no signs of disease. On the other hand, dual infections of MHBV and DHPV exhibited mortality, raising the possibility that shrimp mortality occurs only with dual infections. Based on the similarity of MHBV’s ssDNA genome structure and a DNA polymerase B domain homologous to that of Bombyx mori bidensovirus V1, we believe that MHBV should currently be classified as a new member of the family Bidnaviridae with a genome consisting of a singlessDNA fragment.
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
Recently, universal PCR detection method with an independent set of Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Mr) samples indicated the presence of a type of decapod hepanhamaparvovirus (DHPV) in the Mr samples. However, the in-situ hybridization (ISH) test results revealed that the hepatopancreatic (HP) cell nuclei of normal morphology gave positive ISH results for DHPV but that the intranuclear inclusions in the same samples did not. The negative ISH results raised the possibility that the intranuclear inclusions arose from something other than a type of DHPV, and possibly a novel virus. Here, we describe the discovery of a novel virus in Mr that is distinct from DHPV and is linked by positive ISH results to the mystery intranuclear inclusions. We call it Macrobrachium hepatopancreatic bidnavirus (MHBV) and we show that it sometimes occurs together with DHPV in dual infections.
Abstract
A purported parvovirus producing circular, eosinophilic inclusions in the nuclei of tubule epithelial cells of the hepatopancreas (HP) of the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Mr) was first reported from Malaysia in 1990. In 2009, similar inclusions in Mr from Thailand were confirmed to contain single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). In 2021, Mr samples showing similar HP inclusions were reported to give positive PCR test results for decapod hepanhamaparvovirus (DHPV) using universal DHPV primers designed from many viral isolates of 3 penaeid shrimp species. However, the matching DNA probe revealed positive in situ hybridization (ISH) results with host HP nuclei only, and not with the intranuclear inclusions. At the time, this anomaly could not be explained. Here we describe metagenomic analysis and de novo assembly from 2016 samples of Mr with similar intranuclear inclusions that showed negative PCR test results using the DHPV universal primers. Genomes identified through metagenomics revealed a novel ssDNA genome sequence of 6723 bases that was confirmed by a single PCR amplicon. ISH using specific probes derived from this genome sequence revealed that the ssDNA was present in both grossly normal nuclei and in the intranuclear inclusions. Tests with archived DNA from the samples used in the 2021 publication yielded positive PCR results for both DHPV and the novel sequence, suggesting that the shrimp had dual infections. Phylogenetic analysis of the novel sequence revealed no relationship to any known DHPV type. Instead, the sequence closely matched the polymerase B gene in the V1 fragment from Bombyx mori bidensovirus 2 (BmBDV2) that is characterized by 2 ssDNA genome fragments and has been classified in the family Bidnaviridae. The 2 BmBDV2 fragments V1 and V2 each produce their own independent capsid protein genes and virions. In contrast, the new Mr virus is independent with a single 6723 base ssDNA genome, and we propose the name Macrobrachium hepatopancreatic bidnavirus (MHBV).
KEYWORDS: Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Mr), DNA polymerase B (polB), ParvovirusMacrobrachium hepatopancreatic bidnavirus (MHBV), Bombyx mori bidensovirus (BmBDV)
Citation: Gangnonngiw, W., Bunnontae, M., Kayansamruaj, P., Senapin, S., Srisala, J., Flegel, T. W., & Wongprasert, K. (2023, April). A novel ssDNA Bidnavirus in the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquaculture, 568, 739340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739340
RELATED SDGs:
2. ZERO HUNGER

14. LIFE BELOW WATER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Warachin Gangnonngiw
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Fundamental Fund
Credit ภาพ: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
Tags: Bombyx mori bidensovirus (BmBDV), DNA polymerase B (polB), Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Mr), ParvovirusMacrobrachium hepatopancreatic bidnavirus (MHBV)
