ศักยภาพการเป็นวัคซีนของโปรตีนรีคอมบิแนนท์ cathepsin L1H ต่อการติดเชื้อพยาธิใบไม้ตับในแพะ
Highlight
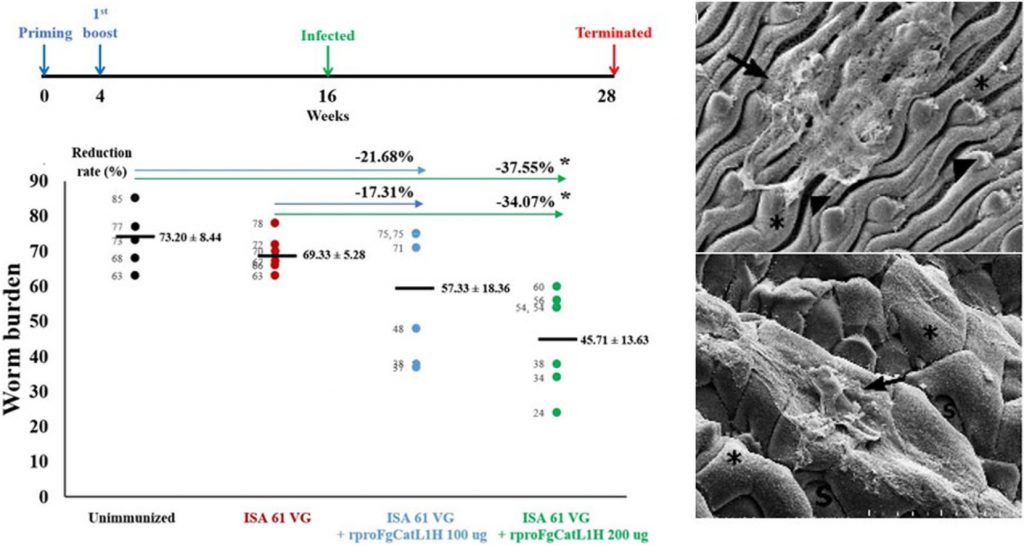
โปรตีนรีคอมบิแนนท์ rproFgCatL1H สามารถลดการติดเชื้อพยาธิใบไม้ตับในแพะได้ คิดเป็นร้อยละ 34-37 และทำให้ผิวพยาธิเกิดความเสียหายอย่างชัดเจนเมื่อตรวจสอบภายใต้กล้องจุลทรรศน์อิเล็กตรอน แม้ความสัมพันธ์กับระดับแอนติบอดียังไม่เด่นชัด ผลการศึกษานี้ชี้ให้เห็นว่าโปรตีน rproFgCatL1H มีศักยภาพสำหรับพัฒนาเป็นวัคซีนลดการติดเชื้อพยาธิใบไม้ตับในแพะ
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
โรคพยาธิใบไม้ตับ (Fasciola gigantica) เป็นปัญหาสำคัญในสัตว์เคี้ยวเอื้อง โดยเฉพาะในแพะและโค ก่อให้เกิดการสูญเสียทางเศรษฐกิจจากการลดน้ำหนัก โตช้า และลดประสิทธิภาพการผลิต ปัจจุบันการควบคุมโรคยังพึ่งพายาถ่ายพยาธิเป็นหลัก ซึ่งมีความเสี่ยงต่อการดื้อยาเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างต่อเนื่อง จึงมีความจำเป็นเร่งด่วนในการพัฒนาวิธีป้องกันใหม่ เช่น วัคซีน การศึกษานี้จึงศึกษาศักยภาพของโปรตีน cathepsin L1H ในการลดการติดเชื้อพยาธิ และเป็นก้าวสำคัญสู่การพัฒนาวัคซีนที่มีประสิทธิภาพสำหรับควบคุมโรคพยาธิใบไม้ตับในแพะในอนาคต
Abstract
Cathepsin L1H has been identified as a potential vaccine candidate against fasciolosis. The present study was conducted to evaluate the immunoprophylactic efficacy of recombinant proFgCatL1H (rproFgCatL1H) antigen in goats subsequently challenged with the parasite. Immunization of goats with 200 µg of rproFgCatL1H formulated in Montanide™ ISA 61 VG conferred statistically significant reduction in worm recovery compared with both the infected control and adjuvant control groups, corresponding to reductions of 37.55 % and 34.07 %, respectively (p < 0.05). A negative correlation was observed between worm burden reduction and serum IgG levels (OD₄₅₀), measured both at the time of infection and at the study endpoint, although the association was not statistically significant. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis of adult F. gigantica recovered from vaccinated goats demonstrated pronounced tegumental damage, characterized by extensive swelling, surface erosion, and the presence of cell-like structures adhering to the tegumental surface. These findings suggest that the recombinant protein rproFgCatL1H holds promise as a potential vaccine candidate for the control of fasciolosis in goats.
KEYWORDS: Fasciola gigantica, Vaccine, Cathepsin l1h, Goat, Montanide
Citation: Sangfuang M, Sungsuwan P, Khumgra G, Kueakhai P, Changklungmoa N, Sobhon P, Suphamungmee W, Roytrakul S, Preyavichyapugdee M, Meemon K, Preyavichyapugdee N*. Vaccine potential of recombinant cathepsin L1H against Fasciola gigantica infection in goat. Acta Trop. 2025;271:107900. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2025.107900.
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
2. ZERO HUNGER

SDG Goal ที่เกี่ยวข้องอื่น ๆ
15: LIFE ON LAND

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.วรวิทย์ ศุภมั่งมี
ภาพถ่าย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Thailand Research Fund
Tags: Cathepsin L1H, Fasciola gigantica, Goat, Montanide, Vaccine
