Highlight:
ยาเม็ดคุมกำเนิดแบบผสม (COCs) สามารถลดการแทรกซึมของเซลล์ macrophage ในเยื่อบุโพรงมดลูก รวมทั้งช่วยควบคุมภาวะสมดุลของเซลล์ระบบภูมิคุ้มกันโดยการเพิ่มจำนวน natural killer cells และ regulatory T cells ในบริเวณเยื่อบุโพรงมดลูกที่เจริญผิดที่ด้วย
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
ความผิดปกติของระบบภูมิคุ้มกันสามารถทำให้มีการเกิดและพัฒนาของเยื่อบุโพรงมดลูกเจริญผิดที่ได้ ในกรณีที่มีการไหลย้อนของประจำเดือนบางส่วนเข้าไปในท่อนำไข่ เมื่อระบบภูมิคุ้มกันไม่สามารถกำจัดเลือดและเนื้อเยื่อที่อยู่ในประจำเดือนเหล่านี้ได้หมด จะทำให้เยื่อบุโพรงมดลูกที่เหลืออยู่ยึดเกาะกับผนังในอุ้งเชิงกรานและเจริญต่อไปได้ ซึ่งเยื่อบุโพรงมดลูกที่เจริญผิดที่นี้จะไปกระตุ้นระบบภูมิคุ้มกันทำให้เกิดการกระตุ้นการตอบสนองการอักเสบที่นำไปสู่การหลั่งไซโตไคน์ต่างๆ ในเนื้อเยื่อ และในเลือด รวมทั้งการแทรกซึมของเซลล์เม็ดเลือดขาว เช่น macrophage และ natural killer cells การให้ Progestin และยาเม็ดคุมกำเนิดแบบผสม (combined oral contraceptives, COCs) เป็นวิธีรักษาเริ่มแรกเมื่อมีอาการปวด โดยยาเม็ดคุมกำเนิดแบบผสมเป็นที่นิยมเนื่องจากมีประสิทธิภาพสูง ผลข้างเคียงต่ำ และราคาไม่แพง ยาชนิดนี้จะไปมีผลยับยั้งการหลั่งฮอร์โมน gonadotropins ทำให้เซลล์ในเยื่อบุโพรงมดลูกอยู่ในระยะ decidualization นอกจากนี้ยาเม็ดคุมกำเนิดแบบผสมยังช่วยลดการเพิ่มจำนวนของเซลล์เยื่อบุโพรงมดลูกที่เจริญผิดที่อีกด้วย อย่างไรก็ดียังไม่มีผู้ใดศึกษาผลของยานี้ต่อเซลล์ในระบบภูมิคุ้มกันในเนื้อเยื่อบุโพรงมดลูก ดังนั้นการศึกษาครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อเพื่อประเมินผลของยาเม็ดคุมกำเนิดแบบผสม (COCs) ที่ประกอบด้วย ethinyl estradiol และ desogestrel ในการแทรกซึมของเซลล์ macrophage และ natural killer cells ในเยื่อบุโพรงมดลูก รวมทั้งศึกษาความหนาแน่นของ regulatory T cells ซึ่งเป็นเซลล์ที่ช่วยควบคุมภาวะสมดุลของเซลล์ระบบภูมิคุ้มกัน
Abstract
Background
Dysregulation of immune response is associated with development of endometriosis. The study aim was to evaluate effect of combined oral contraceptive pills (COCs) consisting of ethinyl estradiol (EE) and desogestrel on the expression of macrophage, natural killer cells, and regulatory T cells of ovarian endometriotic cysts.
Methods
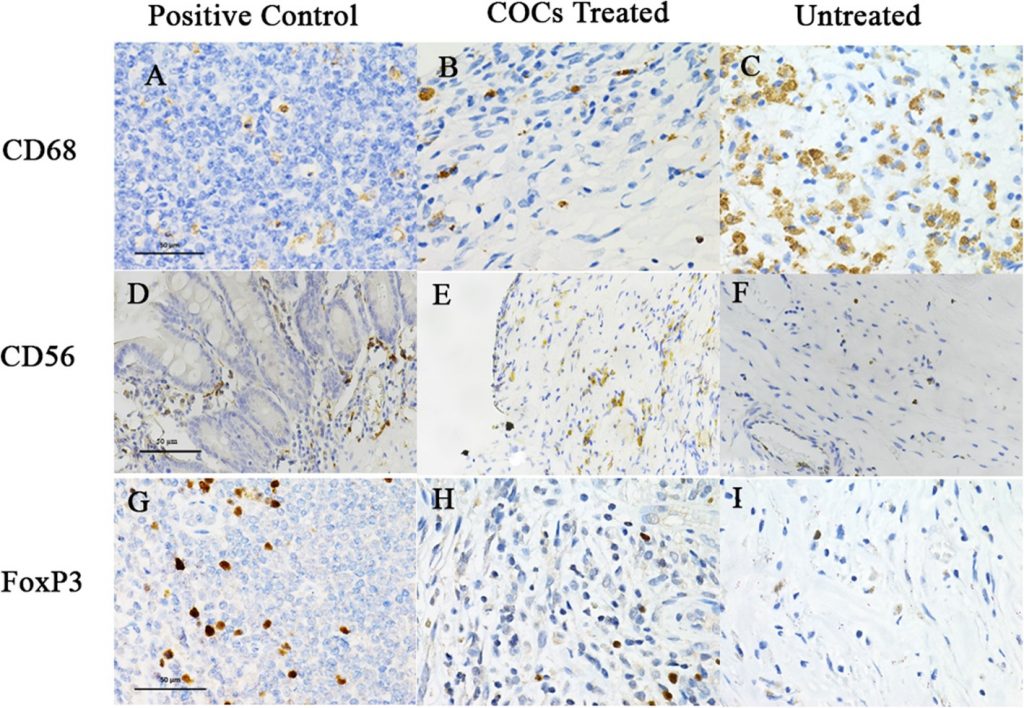
Endometriotic cyst wall tissues were collected from women with endometriosis who were treated (n = 22) with COCs (one table per day of EE 0.03 mg and desogestrel 0.15 mg administered for 28 to 35 days before surgery) or untreated (n = 22). The tissues were collected from endometriotic cyst wall during laparoscopic or laparotomy ovarian cystectomy. Immunohistochemistry for anti-CD68, anti-CD56, and anti-forkhead–winged helix transcription factor (FoxP3), a marker for macrophages, natural killer cells, and regulatory T cells, respectively, were investigated.
Results
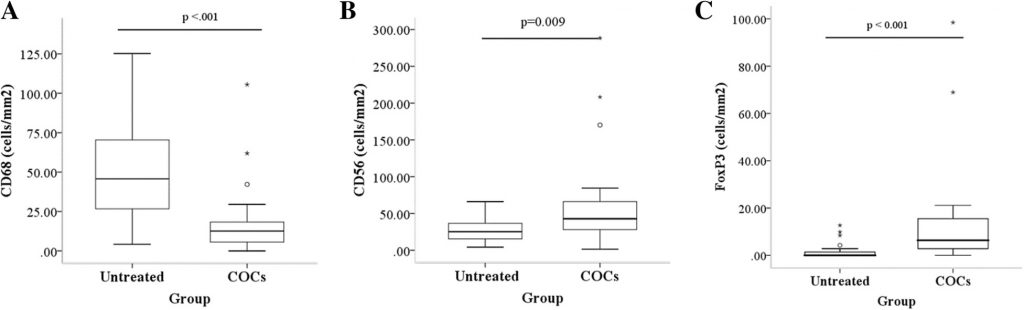
The median (interquartile range [IQR]) number of anti-CD68 positive cells in the COC group was significantly lower than in the untreated group (12.7; 4.9–19.3) versus 45.7 (26.0–70.7), p < 0.001). Tissue infiltration of anti-CD56 positive cells in endometriotic cyst was significantly higher after the treatment when compared with tissue from untreated group (42.9, 27.4–68.9 versus 25.3 (14.1–37.3; p = 0.009). The number of regulatory T cells was also significantly increased in the COC group (6.3, 2.8–15.5) versus 0 (0–1.8; p < 0.001).
Conclusions
The effects of COC, containing EE 0.30 mg with desogestrel 0.15 mg, on the immune system was demonstrated by a significant decrease in the number of macrophages and an increase in natural killer and regulatory T cells.
KEYWORDS: Combined contraceptive, Endometriosis; Immune cells, Macrophage, Natural killer cell, Regulatory T-cell
Citation: Waiyaput, W., Wattanakamolchai, K., Tingthanatikul, Y. et al. Effect of combined contraceptive pill on immune cell of ovarian endometriotic tissue. J Ovarian Res14, 66 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-021-00819-8
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.มรกต สร้อยระย้า
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.มรกต สร้อยระย้า
ภาพถ่าย: ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.มรกต สร้อยระย้า
Tags: Combined contraceptive, Endometriosis; Immune cells, Macrophage, Natural killer cell, Regulatory T-cell
