Highlight:
สาร ilimaquinone มีความเป็นพิษต่อเซลล์มะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากโดยทำให้ DNA ของเซลล์มะเร็งเสียหาย ผ่านกระบวนการ in-situ transformation ไปเป็นสาร active hydroquinones
Abstract
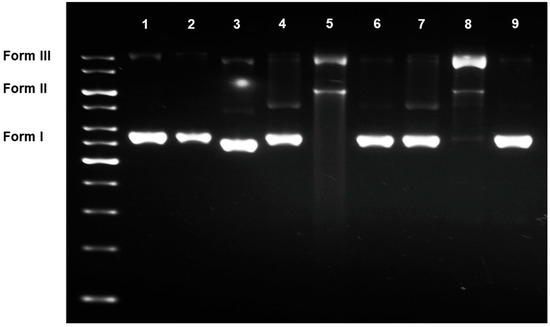
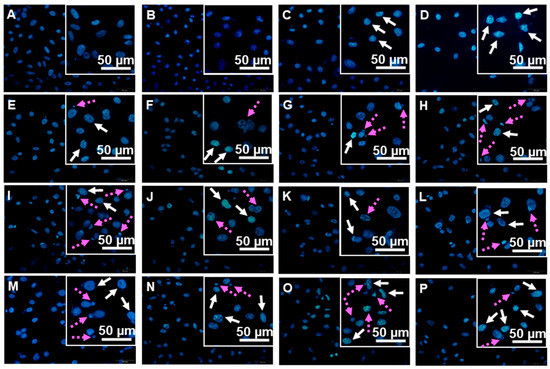
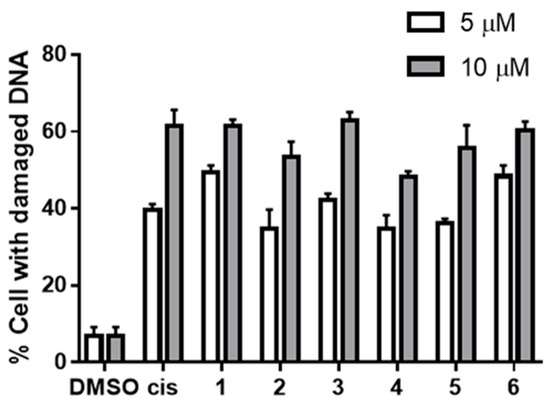
Possessing the quinone moiety, ilimaquinone (1), a sponge–derived sesquiterpene quinone, has been hypothesised to express its cytotoxicity through a redox cycling process, yielding active product(s) that can cause DNA damage. To determine the DNA damaging effects of 1 and examine whether a redox transformation may participate in its functions, the DNA damaging properties of 1, the corresponding hydroquinone (2) and hydroquinone triacetates (3) and their 5-epimeric counterparts (4–6) were tested and compared. When incubated directly with plasmid DNA, the hydroquinones were the only active species capable of cleaving the DNA. In cell-based assays, however, the quinones and hydroquinone triacetates were active in the same range as that of the corresponding hydroquinones, and all damaged the cellular DNA in a similar manner. The in situ reduction of 1 and 4 were supported by the decreases in the cytotoxicity when cells were pre-exposed to dicoumarol, an NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) inhibitor. The results confirmed the DNA damaging activities of the ilimaquinones 1 and 4, and indicated the necessity to undergo an in-situ transformation into the active hydroquinones, thereby exerting the DNA damaging properties as parts of the cytotoxic mechanisms.
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
สาร ilimaquinone ที่เป็นอนุพันธ์จากกลุ่ม sesquiterpene quinone ของฟองน้ำทะเลได้ถูกสันนิษฐานว่ามีความเป็นพิษผ่านกระบวนการ redox cycling ส่งผลให้ active products ที่ได้สามารถทำให้เกิดความเสียหายต่อ DNA ของเซลล์ได้ ในการทดสอบนี้จึงศึกษาฤทธิ์ของสารเหล่านี้ที่ทำให้ความเสียหายต่อ DNA โดยเปรียบเทียบระหว่างสาร ilimaquinone, hydroquinone และ hydroquinone triacetates และ สารกลุ่ม 5-epimeric counterparts ชนิดที่ 4-6 โดยการใช้ plasmid DNA ผลการทดสอบพบว่า สาร hydroquinones เป็นสารชนิดเดียวที่สามารถตัดชิ้นส่วนของ plasmid DNA ได้ เมื่อทดสอบในระดับเซลล์มะเร็งต่อมลูกหมากด้วยการย้อมสี Hoechst 33324 พบว่า สาร quinones และ hydroquinone triacetates สารมารถทำให้ DNA ภายในเซลล์เกิดกความเสียหายได้เหมือนกับสาร hydroquinones สอดคล้องกับการศึกษา in-situ reduction ของสาร ilimaquinone และ 5-epi-ilimaquinone ที่สามารถลดความเป็นพิษต่อเซลล์ที่ได้รับสาร dicoumarol (NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) inhibitor) จากผลการทดลองสรุปได้ว่าความเสียหายของ DNA ของเซลล์เกิดจากกระบวนการ in-situ transformation ของสาร ilimaquinone และสาร 5-epi-ilimaquinone ไปเป็น hydroquinones ที่อยู่ในรูป active form ส่งผลให้เกิดความเป็นพิษต่อเซลล์ได้
KEYWORDS: sesquiterpene quinones, cytotoxicity, redox cycling, marine natural products
Citation:
Jiso A, Yurasakpong L, Janta S, Chaithirayanon K, Plubrukarn A. Exerting DNA Damaging Effects of the Ilimaquinones through the Active Hydroquinone Species. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2021; 89(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89020026
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
14. LIFE BELOW WATER

SDG Goal ที่เกี่ยวข้องอื่น ๆ
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Sirorat Janta, Laphatrada Yurasakpong
ภาพถ่าย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
Tags: Cytotoxicity, marine natural products, redox cycling, sesquiterpene quinones
