ที่มาและความสำคัญ
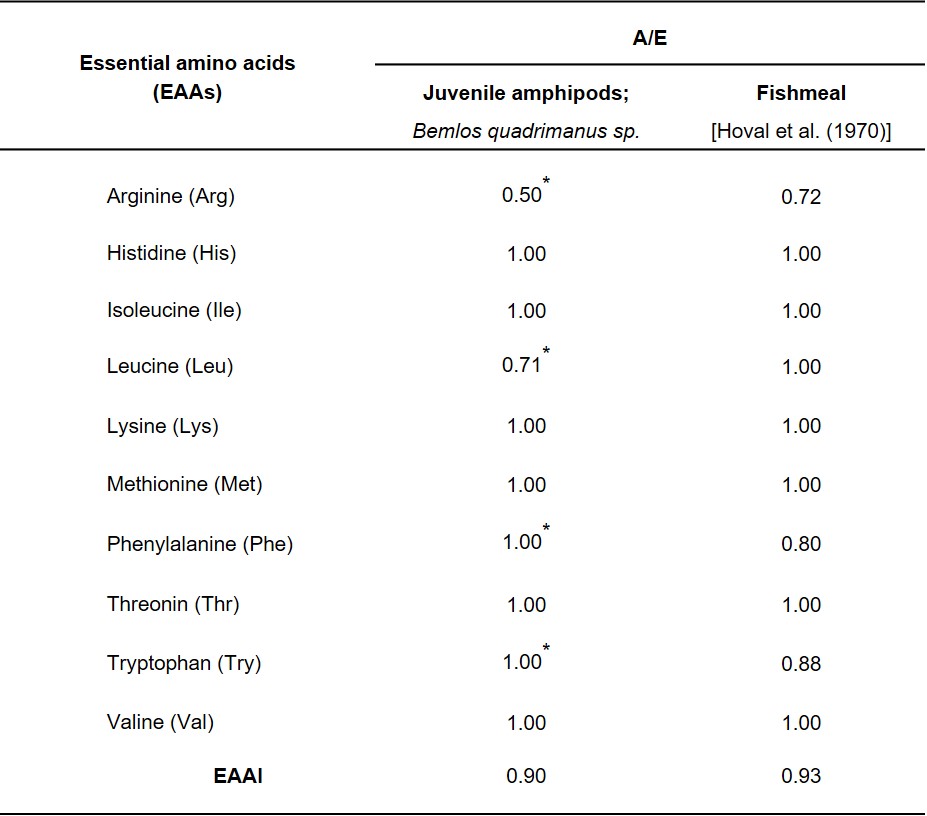
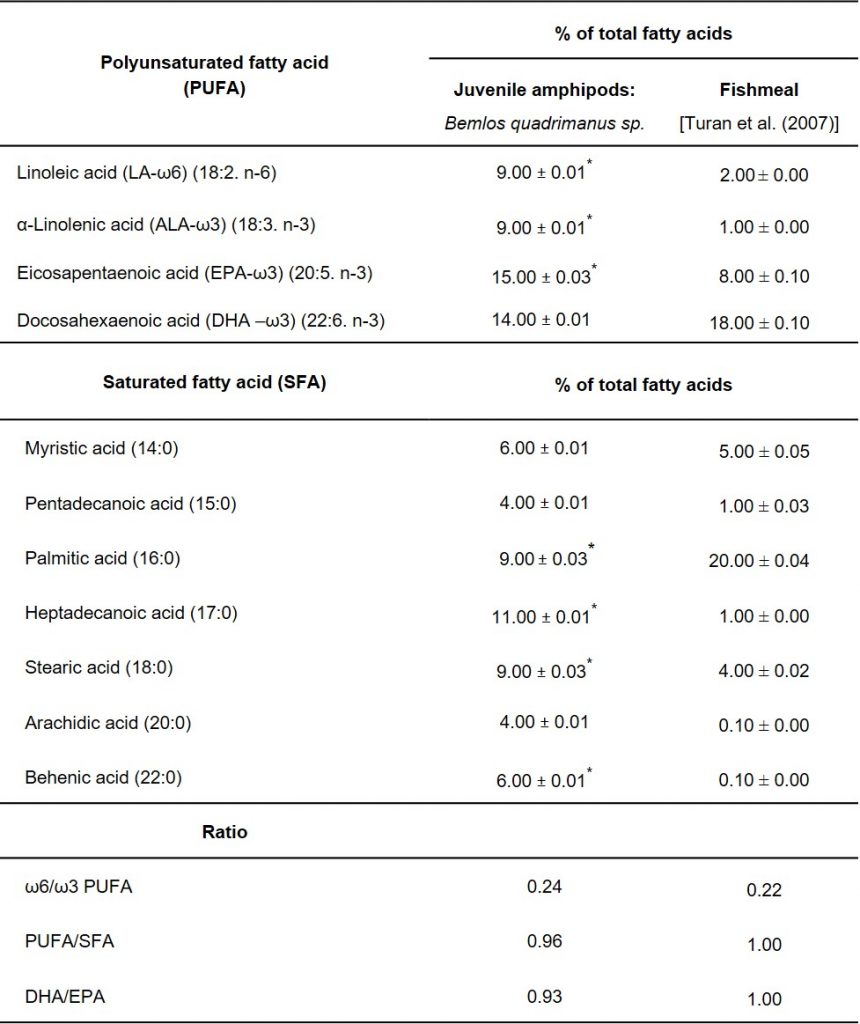
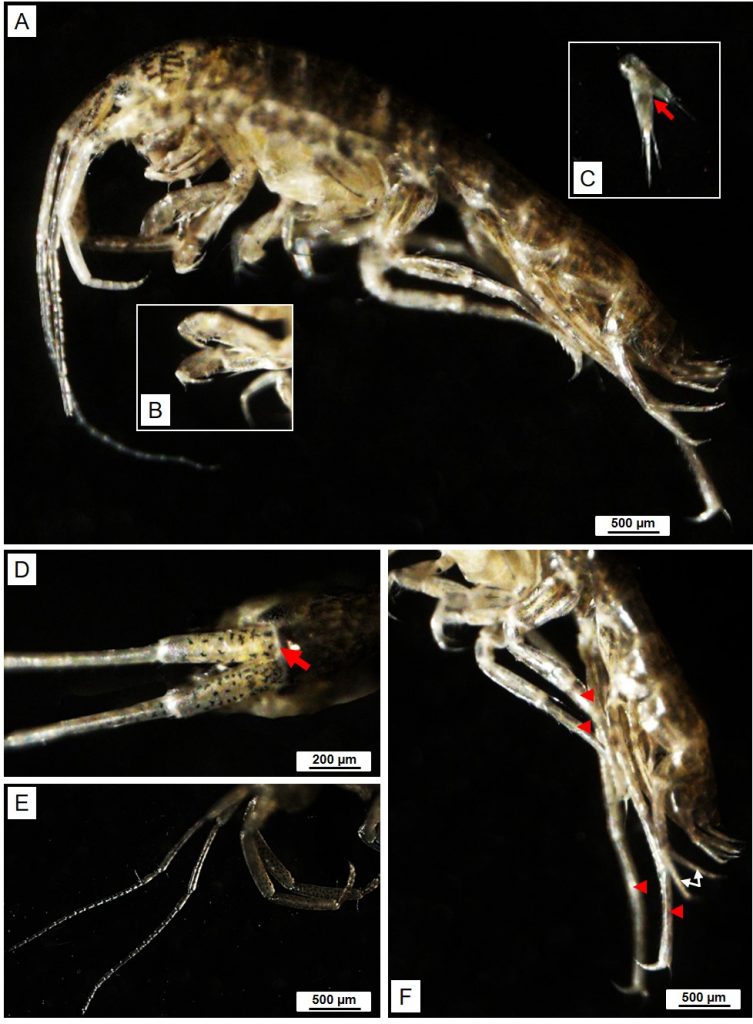
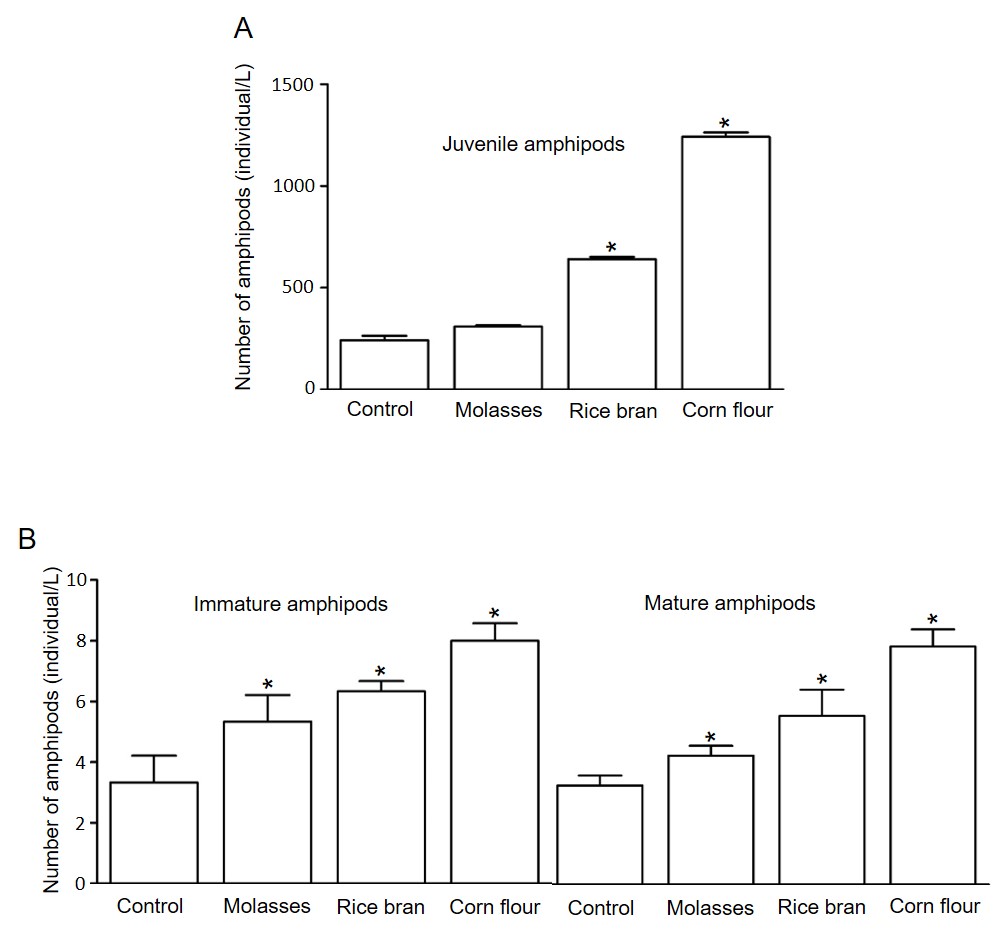
แอมฟิพอด (amphipod) ในตะกอนชีวภาพ (bioflocs) เป็นอาหารทางธรรมชาติที่มีสารอาหารสูงเหมาะสำหรับการเพาะเลี้ยงสัตว์น้ำ งานวิจัยนี้จึงมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาสปีชีส์ของแอมฟิพอดในบ่อเลี้ยงกุ้งที่ใช้ระบบตะกอนชีวภาพ (biofloc technology) ที่ฟาร์มกุ้ง อำเภอไชยา จังหวัดสุราษฎร์ธานี และศึกษาคุณค่าทางโภชนาการและการเพิ่มจำนวนของแอมฟิพอดในบ่อระบบตะกอนชีวภาพ โดยนำพ่อแม่พันธุ์ของแอมฟิพอดมาทำการทดลองเลี้ยงด้วยแหล่งคาร์บอน (carbon sources) ที่ต่างชนิดกัน คือกากน้ำตาล (molasses) รำข้าว(rice bran) และแป้งข้าวโพด (corn flour) ที่ระดับอัตราของคาร์บอนต่อไนโตรเจน (C:N) ratio เท่ากับ 16:1 เป็นเวลา 4 สัปดาห์ แล้วทำการตรวจนับจำนวน ตรวจสอบการวางไข่ และ คุณค่าทางโภชนาการของแอมฟิพอดที่เลี้ยงในตะกอนชีวภาพ ผลการทดลองพบ Bemlos quadrimanus sp เป็นสปีชีส์ของแอมฟิพอดในบ่อเลี้ยงกุ้งที่พบในระบบตะกอนชีวภาพ และระยะ juvenile เป็นระยะที่มีโปรตีนและลิปิดสูงกว่าระยะอื่น นอกจากนี้พบว่าปริมาณกรดอะมิโนและกรดไขมันที่จำเป็นในตะกอนชีวภาพมีค่าใกล้เคียงกับปลาป่น ตะกอนชีวภาพจากแป้งข้าวโพดส่งเสริมการเจริญเติบโตและเพิ่มจำนวนของแอมฟิพอดในระยะ juvenile ทำให้ได้แอมฟิพอดที่มีโปรตีและลิปิดสูงกว่าแหล่งคาร์บอนอื่น งานวิจัยนี้แสดงให้เห็นว่าแอมฟิพอด B. quadrimanus เป็นแหล่งโปรตีนที่สำคัญที่สามารถทดแทนปลาป่นในอาหารของกุ้งได้ และการเพาะเลี้ยงแอมฟิพอดในบ่อระบบตะกอนชีวภาพเป็นการเพิ่มมูลค่าตะกอนชีวภาพในอุตสาหกรรมการเพาะเลี้ยงสัตว์น้ำ
Abstract
Natural food items like amphipods in bioflocs have been shown to provide a nutrient-rich live feed for aquaculture species. In the present study, we aimed to identify the major species of amphipods in the biofloc technology shrimp ponds at Shrimp Village, Surat-Thani, Thailand, determine its nutritional values, and enrich the amphipods in the biofloc technology system (BFS). Breeder stage amphipods were cultured in BFS with different carbon sources; molasses, rice bran, and corn flour at a carbon: nitrogen (C:N) ratio of 16:1 for 4 weeks. The number and the growth of spawned juveniles, and the nutritional compositions of the amphipods enriched bioflocs were examined. We found that the major species of amphipods in bioflocs produced in the cultured shrimp ponds was Bemlos quadrimanus sp. Proximate analysis revealed that the juvenile stage B. quadrimanus had higher levels of protein and lipid contents than those in other stages. Moreover, their essential amino acid index (EAAI) and ratios of polyunsaturated fatty acid/saturated fatty acid (PUFA/SFA) and docosahexaenoic acid/eicosapentaenoic acid (DHA/EPA) were similar to those values in fishmeal. The bioflocs produced with corn flour enhanced the growth and increased the number of juvenile amphipods greater than in bioflocs produced with the other two carbon sources, and had the highest levels of crude protein and lipid. In summary, this study demonstrates that amphipod B. quadrimanus provide an important source of protein that shows potential to replace fishmeal in shrimp feed, and reveals the benefit of a culture of amphipods with BFS in the aquaculture industry.
KEYWORDS: Amphipod, Bemlos quadrimanus sp., Nutritional value, Bioflocs, Carbon source
Citation: Phennapa Promthale, Boonsirm Withyachumnarnkul, Peter Bossier, Kanokpan Wongprasert,
Nutritional value of the amphipod Bemlos quadrimanus sp. grown in shrimp biofloc ponds as influenced by different carbon sources,
Aquaculture, Volume 533, 2021, 736128, ISSN 0044-8486,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736128.
RELATED SDGs:
12. RESPONSIBLE CONSUMPTION AND PRODUCTION

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: เพ็ญนภา พรมทะเล
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Thailand Research Fund (TRF) through the Research and Researchers for Industries (RRi) (PHD58I0094, 2015), Thai-union feedmill Co., Ltd. (TUF), and Faculty of Science CIF and CNI Grant, Government Budget Grant No. 11825, Mahidol University.
Tags: Amphipod, Bemlos quadrimanus sp., Bioflocs, Carbon source, Nutritional value
