Highlight
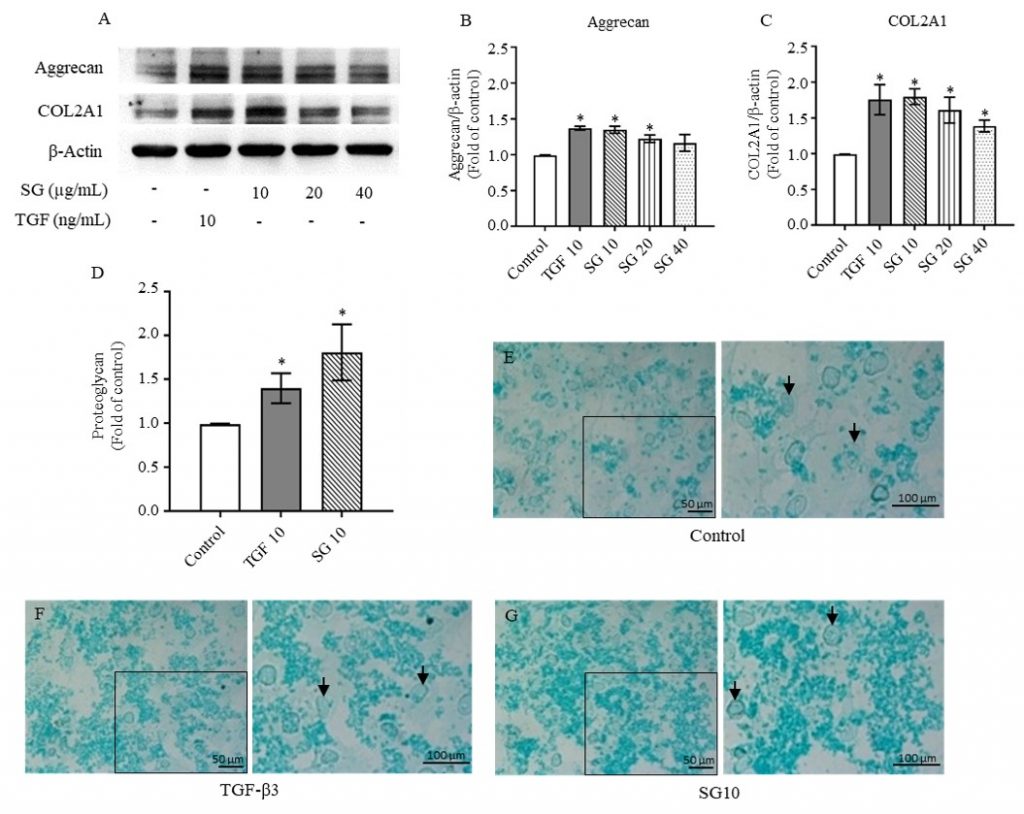
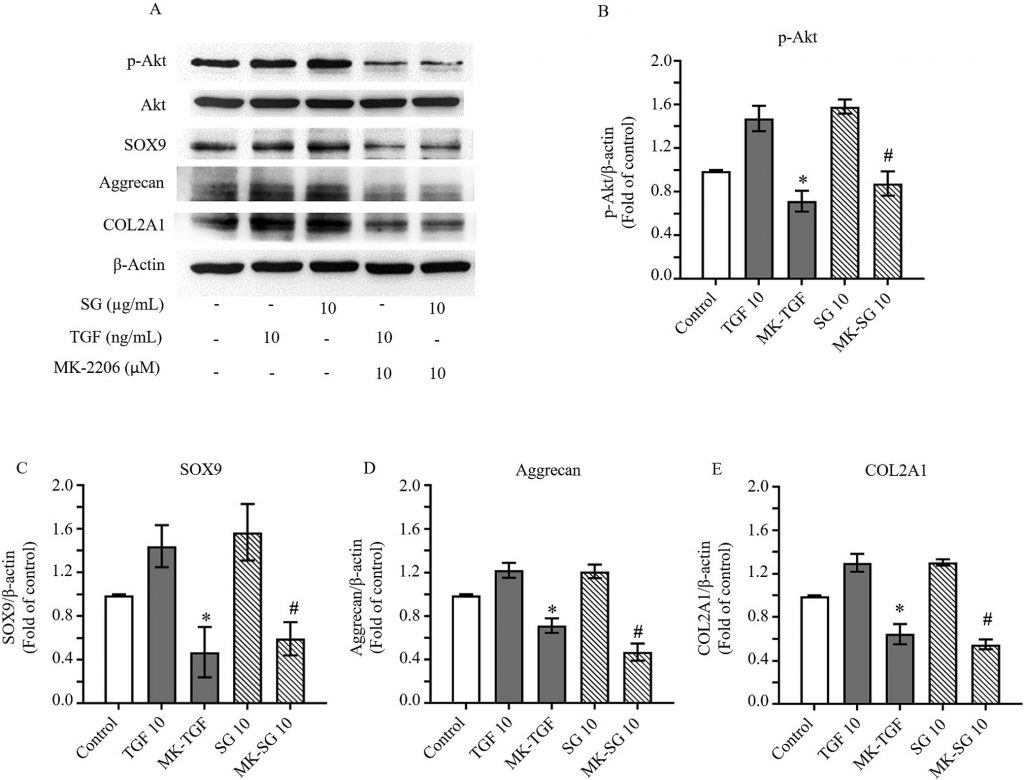
ซัลเฟตกาแลคแตนจากสาหร่ายแดง Gracilaria fisheri กระตุ้นการสร้างเนื้อเยื่อกระดูกอ่อนโดยเพิ่มการแสดงออกของ Aggrecan, COL2A1 และยีน SOX9 ผ่านการกระตุ้นสัญญาณ integrin-β1/FAK/Akt ในเซลล์กระดูกอ่อนมนุษย์ นอกจากนี้ยังส่งเสริมการยึดเกาะและเพิ่มการแบ่งตัวของเซลล์ ชี้ให้เห็นศักยภาพของซัลเฟตกาแลคแตนในการพัฒนาเป็นสารธรรมชาติสำหรับฟื้นฟูกระดูกอ่อนในโรคข้อเข่าเสื่อม
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
โรคข้อเข่าเสื่อมเป็นภาวะเสื่อมเรื้อรังที่พบมากในผู้สูงอายุ เนื้อเยื่อกระดูกอ่อนในข้อต่อถูกทำลาย ส่งผลต่อการเคลื่อนไหวและคุณภาพชีวิต แนวทางการรักษาในปัจจุบันมุ่งบรรเทาอาการแต่ไม่สามารถฟื้นฟูเนื้อเยื่อที่สูญเสียได้อย่างแท้จริง จึงมีความจำเป็นต้องค้นหาสารชีวภาพที่สามารถกระตุ้นการสร้างกระดูกอ่อน งานวิจัยนี้มุ่งศึกษาซัลเฟตกาแลคแตนจากสาหร่ายแดง Gracilaria fisheri ซึ่งมีโครงสร้างคล้ายไกลโคซามิโนไกลแคนในเนื้อเยื่อกระดูกอ่อนเพื่อประเมินศักยภาพในการส่งเสริมการสร้าง Aggrecan และ COL2A1 ในเซลล์กระดูกอ่อนมนุษย์ นำไปสู่การพัฒนาทางเลือกใหม่ในการฟื้นฟูเนื้อเยื่อกระดูกอ่อนสำหรับการรักษาโรคข้อเสื่อมในอนาคต
Abstract
Osteoarthritis (OA) is characterized by progressive cartilage degradation and limited tissue regeneration, commonly affecting older adults. Current treatment strategies mainly alleviate symptoms without effectively restoring cartilage integrity. Sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae have attracted attention for their potential biological effects in promoting cartilage repair. This study examined the chondrogenic activity of sulfated galactans (SG) isolated from the marine red alga Gracilaria fisheri in human C28/I2 chondrocytes, using transforming growth factor-beta 3 (TGF-β3) as a comparative control. SG treatment significantly increased the synthesis of essential cartilage extracellular matrix (ECM) components, such as type II collagen and aggrecan. These effects were mediated through the integrin β1/FAK/Akt signaling pathway, as demonstrated by reduced ECM synthesis following treatment with the Akt inhibitor, MK2206. Additionally, SG improved chondrocyte adhesion and proliferation. These results suggest that sulfated galactans from Gracilaria fisheri may support cartilage ECM synthesis and exhibit potential as biologically active components for osteoarthritis management.
KEYWORDS: Sulfated galactans, Chondrocytes, Type II collagen, ECM, Akt pathway, Integrin β1
Citation: Nambunruang B, Hemstapat R, Supokawej A, Kongchanagul A, Tawonsawatruk T, Wongprasert K. Bioactive sulfated galactans from Gracilaria fisheri promote chondrogenic activity via integrin-β1/FAK/Akt signaling in human chondrocytes. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jun 17;319 (Pt 1):145322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145322
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

SDG Goal ที่เกี่ยวข้องอื่น ๆ
17. Partnerships for the goals

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: นายบุตรโต งามบุญเรือง
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Fundamental Fund 67
Credit ภาพ: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
Webmaster: ว่าที่ ร.อ. นเรศ จันทรังสิกุล
Tags: Akt pathway, Chondrocytes, ECM, Integrin β1, sulfated galactans, Type II collagen
