Highlight
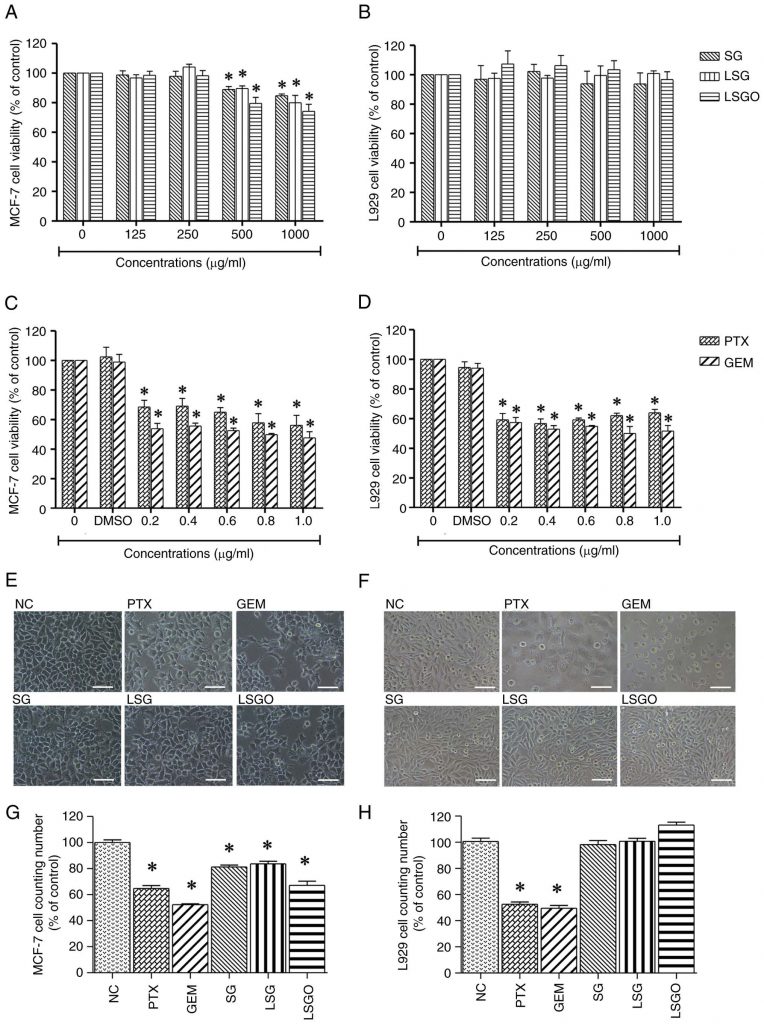
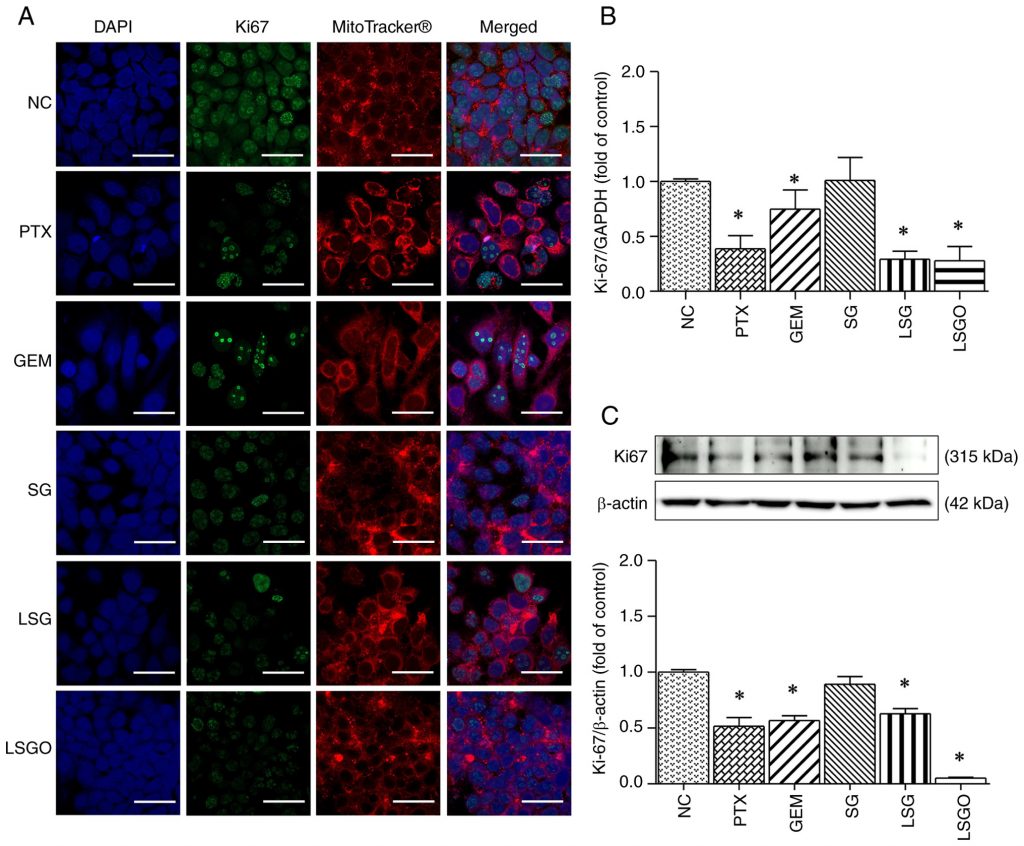
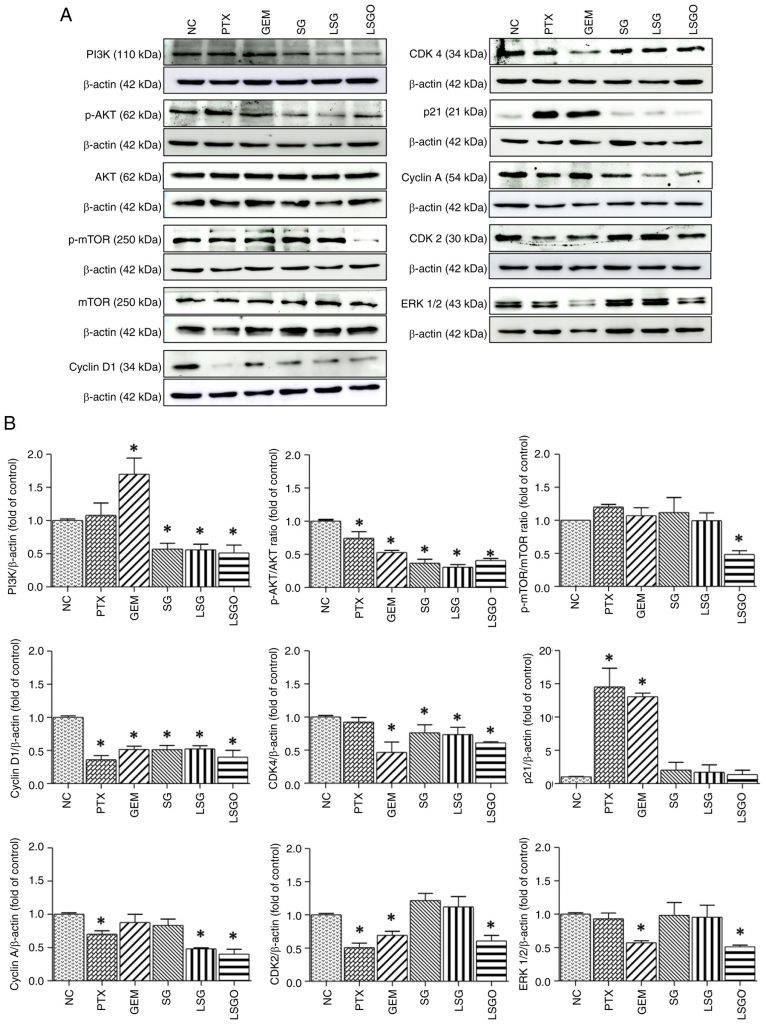
ซัลเฟตกาแลคแตนจากสาหร่าย Gracilaria fisheri และอนุพันธ์ที่ผ่านการปรับโครงสร้าง (LSG และ LSGO) แสดงฤทธิ์ยับยั้งการเพิ่มจำนวนของเซลล์มะเร็งเต้านม MCF-7 โดย LSGO มีประสิทธิภาพสูงสุดผ่านการชะลอวัฏจักรเซลล์ในระยะ G2/M และลดการแสดงออกของโปรตีนควบคุมการแบ่งเซลล์ เช่น Ki-67, Cyclins และ CDKs ผลลัพธ์ชี้ถึงศักยภาพของ LSGO ในการพัฒนาเป็นสารต้านมะเร็งจากธรรมชาติ
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
มะเร็งเต้านมเป็นหนึ่งในมะเร็งที่พบมากที่สุดในสตรีทั่วโลก และยังคงเป็นปัญหาทางสาธารณสุขที่สำคัญ แม้ว่าจะมีแนวทางการรักษาหลายรูปแบบ แต่การดื้อยาและผลข้างเคียงจากเคมีบำบัดยังเป็นข้อจำกัดสำคัญ งานวิจัยก่อนหน้านี้ชี้ให้เห็นว่าซัลเฟตกาแลคแตน (SG) จากสาหร่าย Gracilaria fisheri มีคุณสมบัติทางชีวภาพในการต้านมะเร็ง โดยสามารถยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของเซลล์มะเร็งผ่านกลไกการชะลอวัฏจักรเซลล์และลดการแสดงออกของโปรตีนควบคุมการแบ่งเซลล์ แต่ยังไม่มีข้อมูลที่ชัดเจนเกี่ยวกับผลของ SG และอนุพันธ์ที่ปรับโครงสร้าง เช่น SG โมเลกุลต่ำ (LSG) และ SG ที่เติมหมู่ออกทาโนอิล (LSGO) ต่อเซลล์มะเร็งเต้านม ดังนั้น งานวิจัยนี้จึงมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาฤทธิ์ต้านมะเร็งของ SG และอนุพันธ์ต่อเซลล์มะเร็งเต้านม MCF-7 รวมถึงกลไกทางชีวโมเลกุลที่เกี่ยวข้อง เพื่อประเมินศักยภาพของ SG ในการพัฒนาเป็นสารต้านมะเร็งจากธรรมชาติที่ปลอดภัยและมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น
Abstract
Breast cancer is one of the most prevalent diseases affecting the female population, with its incidence increasing globally. Previous studies have identified cyclins, CDKs and upstream signaling molecules as key therapeutic targets, as their overexpression can drive the transformation of normal cells into cancerous ones. Sulfated galactan (SG), a polysaccharide derived from Gracilaria fisheri, has demonstrated potential in modulating cellular functions. Recent research suggests that low molecular weight SG (LSG), when supplemented with an octanoyl ester (LSGO), exhibits an enhanced biological activity. However, the anticancer effects of SG and its derivatives in breast cancer remain underexplored. The present study thus aimed to examine the effects of SG, LSG and LSGO on MCF‑7 breast cancer cells. Cytotoxicity was initially assessed in L929 normal fibroblast cells and MCF‑7 cells. While all three forms were non‑toxic to L929 cells, LSGO exhibited slight cytotoxicity and significantly induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. Mechanistically, LSGO suppressed the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK pathways, downregulated cyclins and CDKs, and led to cell cycle arrest and reduced cell proliferation. These results suggest that the structural modification of SG enhances its anti‑proliferative capacity, highlighting LSGO as a promising candidate for the treatment of MCF‑7 cells. Overall, these findings provide insight into the molecular mechanisms by which SG derivatives affect breast cancer cell proliferation and underscore their potential as anti‑proliferative agents targeting cell cycle regulatory proteins.
KEYWORDS: Gracilaria fisheri, sulfated galactan derivatives, MCF‑7 cell, anti‑proliferation, cell cycle arrest
Citation: Phanphak J, Somintara S, Sakaew W, Senarai T, Kovensky J, Wongprasert K and Rudtanatip T: Sulfated galactan derivatives from Gracilaria fisheri suppress the proliferation of MCF‑7 breast cancer cells by inducing cell cycle arrest. World Acad Sci J 7: 77, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3892/wasj.2025.365
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
Credit ภาพ: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
Webmaster: ว่าที่ ร.อ. นเรศ จันทรังสิกุล
Tags: anti‑proliferation, Cell cycle arrest, Gracilaria fisheri, MCF‑7 cell, sulfated galactan derivatives
