การวิเคราะห์ความเป็นพิษและคุณสมบัติในการต้านอนุมูลอิสระของสารสกัดลิ้นมังกร
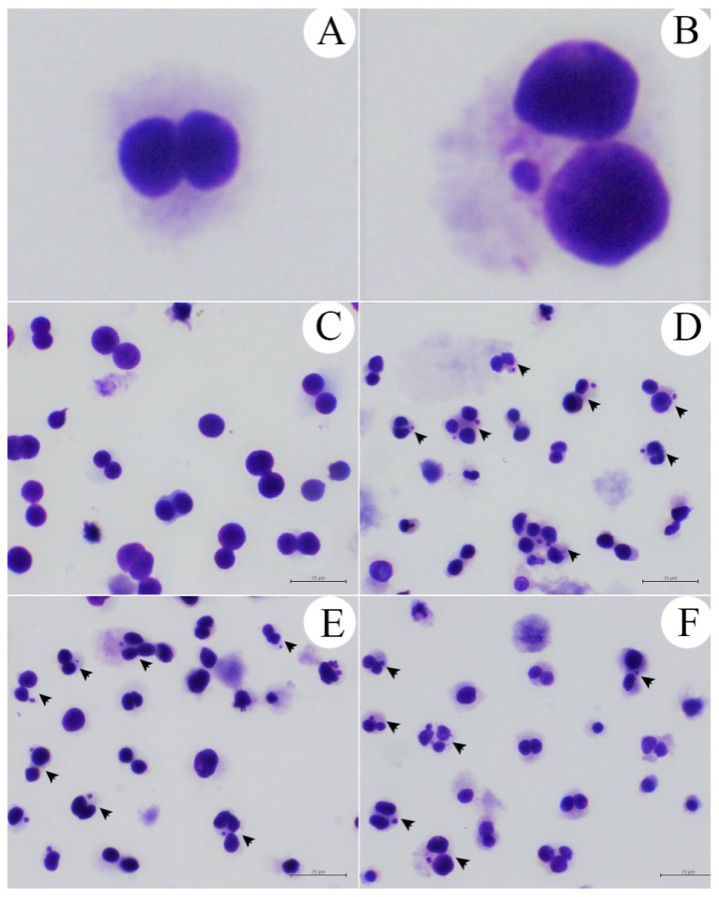
Highlight: สารสกัดสาหร่ายลิ้นมังกรที่สกัดจาก ethanol, butanol และ aqueous มีความเป็นพิษต่อเซลล์ต่ำ ขณะที่สารสกัดที่สกัดด้วย ethyl acetate และ hexane มีความเป็นพิษต่อเซลล์ได้เมื่อใช้ที่ความเข้มข้นสูง อย่างไรก็ตามสารสกัดที่มีฤทธิ์ต้านอนุมูลอิสระได้สูงเป็นสารสกัดที่สกัดจาก ethanol, hexane, ethyl acetate และ butanol จึงสรุปได้ว่าสารสกัดที่สกัดด้วย ethanol, butanol และ aqueous มีความปลอดภัยในการนำมาใช้ประโยชน์ ขณะที่สารที่สกัดโดยใช้ ethyl acetate และ hexane ควรใช้ในปริมาณที่ต่ำกว่า 100 μg/mL ในเซลล์ทดลอง
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
สาหร่ายลิ้นมังกรมีสารออกฤทธิ์ทางธรรมชาติมากมายที่เป็นประโยชน์ทางการแพทย์ และถูกนำมาใช้อย่างเพิ่มขึ้นในด้านการรักษาโรค สารเสริมอาหารเพื่อสุขภาพ และผลิตภัณฑ์ความงาม อย่างไรก็ตาม ยังไม่มีรายงานถึงความเป็นพิษและคุณสมบัติการต้านอนุมูลอิสระของสารสกัดเหล่านี้ ดังนั้นในการศึกษานี้จึงได้ศึกษาความเป็นพิษและการต้านอนุมูลอิสระของสารสกัดจากสาหร่ายลิ้นมังกรขึ้น
Abstract
Halymenia durvillei (HD), a marine red alga, is believed to have potentials for pharmacological, nutritional and cosmetic applications. However, such potentials are acceptable only when their extracts are devoid of any adverse effects on human health. No previous research has been conducted the toxicity and anti-oxidation capacity of HD. Thus, the aim of this work was to investigate toxicity and anti-oxidation activities of HD extracts. In this study, the toxicity and anti-oxidation capacity of 5 fractions of HD solvent extracts, i.e., ethanol (HDET), hexane (HDHE), ethyl acetate (HDEA), butanol (HDBU), and aqueous (HDAQ) were evaluated. The cytotoxicity was evaluated by MTT and LDH assays on 4 cell types, i.e., fibroblast, macrophage, hepatocyte and keratinocyte. The genotoxicity was evaluated by comet assay and micronucleus test using TK6 lymphoblastoid cell line. The anti-oxidation capacity was investigated by DPPH and ABTS assays. The toxicity studies showed that HDET, HDBU, HDAQ had very low to no toxicity as indicated by cytotoxicity and genotoxicity tests while HDEA, HDHE have some toxicity at high concentrations. HDAQ showed low antioxidant activity while HDET, HDEA, HDHE and HDBU possess relatively high antioxidant activity. Overall, our results indicated that HDET and HDAQ could be consumed as they are not toxic and HDHE, HDEA, and HDBU could be safely consumed at doses lower than 100 μg/mL. Further investigation using in vivo assays are needed to ensure the safety of HD extracts for animal and human consumptions.
KEYWORDS: Halymenia durvillei, Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity, Antioxidant, Safety
Citation: Chaiwichien A, Samrit T, Osotprasit S, Kueakhai P, Sobhon P, Meemon K, Niamnont N, Manohong P, Pranweerapaiboon K, Tamtin M, Changklungmoa N*. Evaluation of toxicity and anti-oxidation activity of the extracts from Halymenia durvillei. Trends Sci. 2022; 19(6): 3032. https://doi.org/10.48048/tis.2022.3032
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

14. LIFE BELOW WATER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Agricultural Research Development Agency (Public Organization)
Credit ภาพ: Dr. Narin Changklungmoa
Tags: Antioxidant, Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity, Halymenia durvillei, Safety
