Highlight
งานวิจัยนี้พัฒนาเทคนิค qPCR แบบหลอดเดียวที่มีความแม่นยำและความไวสูง สำหรับตรวจหาไวรัส Macrobrachium hepatopancreatic bidnavirus (MHBV) ในกุ้งก้ามกราม (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) อย่างรวดเร็วและแม่นยำ พบว่าไวรัสนี้มีอยู่ในประเทศไทยมาตั้งแต่ปี 2005 วิธีการนี้ช่วยให้เกษตรกรสามารถติดตามสุขภาพกุ้งได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ป้องกันการระบาดของโรค และลดความสูญเสียในฟาร์ม
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
การตรวจพบไวรัสชนิดใหม่ Macrobrachium hepatopancreatic bidnavirus (MHBV) ในกุ้งก้ามกราม (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) ค้นพบในปี 2023 การระบาดของไวรัสนี้อาจส่งผลกระทบต่อการเพาะเลี้ยงกุ้งและก่อให้เกิดความสูญเสียอย่างรุนแรง ดังนั้นการพัฒนาวิธีตรวจที่รวดเร็ว แม่นยำ และมีความไวสูงจึงมีความจำเป็นอย่างยิ่ง เพื่อให้สามารถตรวจคัดกรองและควบคุมการแพร่ระบาดของ MHBV ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพในฟาร์มกุ้ง การใช้เทคนิคการตรวจวิเคราะห์ที่แท่นยำเป็นสิ่งที่จำเป็น งานวิจัยพัฒนาเทคนิค qPCR ที่แม่นยำไม่เพียงแต่ช่วยในการป้องกันและจัดการโรคเท่านั้น แต่ยังทำให้เห็นการมีอยู่ของไวรัสนี้ในประเทศไทยมาตั้งแต่ปี 2005 ซึ่งช่วยให้เกิดความเข้าใจในประวัติการแพร่ระบาดและวางแผนการป้องกันโรคในอนาคตได้ดียิ่งขึ้น
Abstract
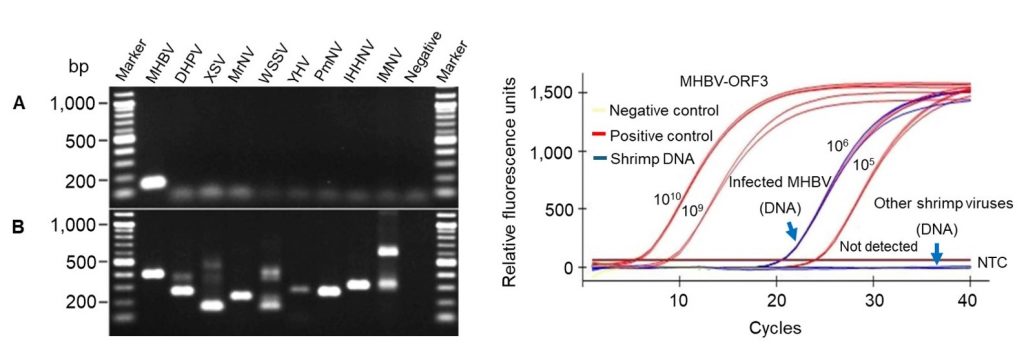
Macrobrachium hepatopancreatic bidnavirus (MHBV) was first identified in 2023 from the hepatopancreas of moribund river prawns, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Mr) post-larvae (PL). Developing a rapid and precise quantitative PCR (qPCR) method would enable accurate screening of broodstock river prawns and PL for MHBV. This study developed a specific and sensitive probe-based qPCR assay for the detection of MHBV. Primers and probes were designed from the MHBV genome sequence MN714903 available at GenBank. Two MHBV genes, ORF3 (non-capsid protein) and ORF4 (DNA polymerase domain) were evaluated as target genes. ORF3 exhibited approximately 4-cycles higher sensitivity, thus it was selected for further development. The method developed in this study involved a one tube, duplex qPCR designed to simultaneously target ORF3 from MHBV and an internal housekeeping gene (elongation factor) from prawns. Subsequently, the protocol was validated using templates comprising DNA extracted from Mr, both infected and uninfected with MHBV, and standard DNA plasmids containing the qPCR target sequences. The duplex qPCR method demonstrated high efficiency (92.14 %) with an analytical sensitivity as low as 10 plasmid copies per reaction and a Cq value cut off at 36.40 (± 0.63). Analytical specificity testing was performed using templates extracted from shrimp infected with various viruses (DHPV, XSV, MrNV, WSSV, YHV, PmNV, IHHNV, and IMNV) and all gave negative results. Furthermore, the application of this qPCR method to archived DNA samples extracted from asymptomatic Mr in 2005, 2006, 2010, and 2011 revealed the long presence of MHBV in Thailand before its discovery in 2023 in moribund Mr PL dually infected with MHBV and DHPV. This qPCR method not only provides a valuable tool for the specific detection of MHBV in shrimp but also sheds light on the historical prevalence of MHBV in river prawns.
KEYWORDS: Duplex qPCR, Shrimp diseases, Shrimp viruses, Detection, Diagnostic
Citation: Gangnonngiw, W., Bunnontae, M., Senapin, S., & Wongprasert, K. (2025). One-tube, probe-based, quantitative PCR assay for bidnavirus MHBV in the river prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquaculture, 595, 741566
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741566
RELATED SDGs:
2. ZERO HUNGER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: นายวราชินย์ กางโนนงิ้ว
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: สำนักงานคณะกรรมการส่งเสริมวิทยาศาสตร์ วิจัยและนวัตกรรม (สกสว.) Fundamental Fund ปี 2566
Credit ภาพ: ศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
Tags: Detection, Diagnostic, Duplex qPCR, Shrimp diseases, Shrimp viruses
