ความชุกชุมที่ลดลงของหลอดเลือด thyroid ima: การวิเคราะห์อภิมานด้วยปัญญาประดิษฐ์
Highlight:
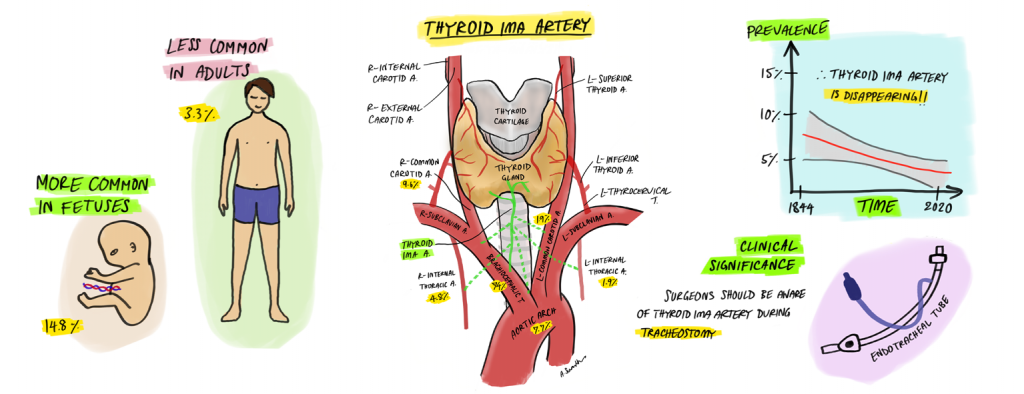
ในงานวิจัยฉบับนี้เราพบว่าหลอดเลือดแดง thyroid ima มีความชุกชุมอยู่ที่ 3.8% และพบในตัวอ่อนมนุษย์มากกว่าในผู้ใหญ่ ถึง 4.5 เท่า (14.8% และ 3.3% ตามลำดับ) ซึ่งสอดคล้องกับสมมติฐานที่ว่าโครงสร้างที่เป็น varition ที่พบในผู้ใหญ่อาจเป็นโครงสร้างที่พบได้เป็นปกติในตัวอ่อน หลอดเลือดนี้มักมีแขนงมาจากหลอดเลือดแดง brachiocephalic (74%) และแตกแขนงมาจากทางด้านขวาของหลอดลม (88%) ดังนั้นหากพบหลอดเลือดนี้การใส่ท่อช่วยหายใจควรใส่ค่อนไปทางด้านซ้ายของหลอดลม เพื่อป้องกันความเสียหายซี่งซึ่งอาจนำไปสู่การเสียชีวิตได้ นอกจากนี้เราพบว่าหลอดเลือดนี้กำลังสูญหายไปตามกาลเวลาซึ่งอาจเป็นปรากฏการณ์ทาง epigenetics ที่ต้องศึกษาวิจัยต่อไป การวิจัยนี้เป็นการวิเคราะห์ภิมานฉบับแรกที่ใช้ปัญญาประดิษฐ์เป็นตัวช่วยวิเคราะห์ผลการวิจัย ซึ่งบ่งชี้ให้เห็นถึงความเป็นไปได้ของการนำปัญญาประดิษฐ์มาประยุกต์ใช้ในงานวิจัยแบบ evidence-based ต่อไป
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
หลอดเลือดแดง thyroid ima เป็นหลอดเลือดแดงที่พบได้ยากในลำคอบริเวณด้านหน้าของหลอดลม มีหน้าไปเลี้ยงต่อมไทรอยด์ส่วนล่างในประชากรประมาณ 3-10% หลอดเลือดนี้มีความเสี่ยงสูงเมื่อต้องเจาะคอเพื่อใส่ท่อหลอดลม (tracheostomy) ซึ่งอาจเสียหายได้โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งในผู้ป่วย COVID-19 ขั้นวิกฤติซึ่งต้องใช้เครื่องช่วยหายใจ วัตถุประสงค์ของงานวิจัยนี้คือการทำวิเคราะห์อภิมานเพื่อศึกษาความชุกชุมในประชากรของหลอดเลือด thyroid ima โดยใช้ปัญญาประดิษฐ์เป็นตัวช่วยวิเคราะผลการวิจัย และนำเสนอวิธีการทำ tracheostomy เมื่อพบหลอดเลือด thyroid ima เพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้เกิดการฉีกขาดของหลอดเลือดซึ่งอาจนำไปสู่การเสียเลือดอย่างรุนแรงซึ่งอาจนำไปสู่การเสียชีวิตได้
Abstract
Introduction
Thyroid ima artery is a variant artery found on the anterior surface of the trachea. The aim of this meta-analysis was to obtain pooled prevalence data of the thyroid ima artery and discuss its clinical importance especially for tracheostomy.
Methods
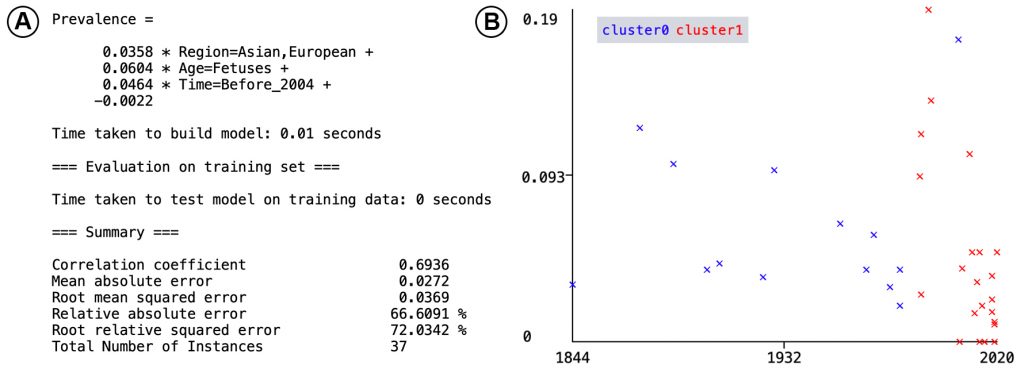
A systematic literature search was performed through five electronic databases until May 2021. A set of inclusion and exclusion criteria based on AQUA guidelines were used to select relevant studies. Meta-analysis, subgroup analyses, meta-regression, and tests for publication bias were performed. Factors that influence the prevalence of the thyroid ima artery were detected using simple and interpretable machine learning (linear regression and K means).
Results
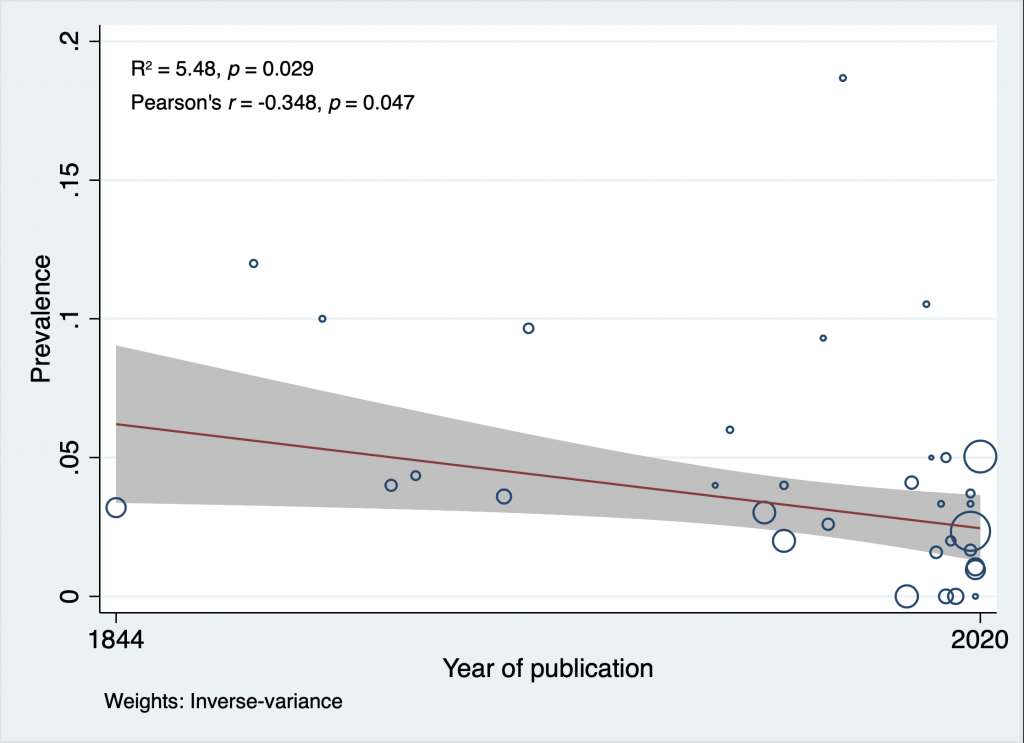
Thirty-six studies with a total of 4,335 subjects met the inclusion criteria. The prevalence of the thyroid ima artery was 3.8% (95% CI: 0.027-0.049,I2 = 56.2%). Machine learning identified age, region and year of publication as potential covariates. Subgroup analysis showed that the prevalence of the thyroid ima artery was almost five times higher in fetuses (14.8%) than adults (3.3%) (z=-6.76, p < 0.01). There was a significant negative correlation between the adult prevalence of the thyroid ima artery and the year of publication (Pearson’s r = -0.354, p = 0.040) thereby suggesting a decline in thyroid ima artery prevalence over time. This artery, if present, may originate from the brachiocephalic trunk (74%), right common carotid artery (9.6%), arch of aorta (7.7%), right internal thoracic artery (4.8%), left common carotid artery (1.9%) and left internal thoracic artery (1.9%).
Conclusion
In addition to evidence-based synthesis of the thyroid ima artery, this study is the first ever study to report the decreasing prevalence over time of a human body structure in the postnatal life. Knowledge of the thyroid ima artery is of vital importance for surgeons to avoid accidental hemorrhage during tracheostomy.
KEYWORDS: thyroid ima artery, tracheostomy, meta-analysis, systematic review, machine learning
Citation: Yurasakpong L, Nantasenamat C, Janta S, Eiamratchanee P, Coey J, Chaiyamoon A, Kruepunga N, Senarai T, Langer MF, Meemon K, Suwannakhan A. (2021). The decreasing prevalence of thyroid ima artery: a systematic review and machine learning assisted meta-analysis. Ann Anat, doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2021.151803.
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: อาจารย์อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ไกร มีมล อาจารย์ ดร.ณัฐเมธี เครือภูงา อาจารย์อธิคุณ สุวรรณขันธ์
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: น.ส.ลภัสรดา ยุรศักดิ์พงศ์
Tags: machine learning, meta-analysis, systematic review, thyroid ima artery, tracheostomy
