Highlight:
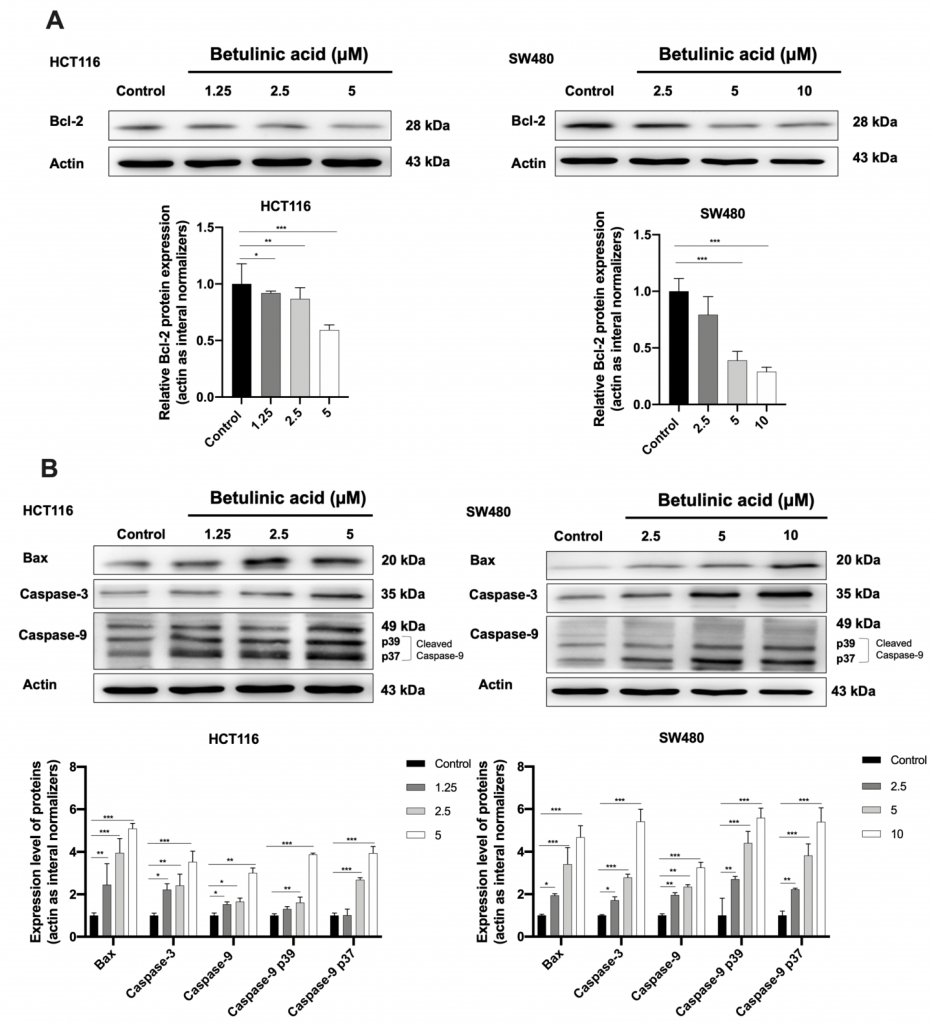
สาร Betulinic acid ชักนำให้เซลล์มะเร็งลำไส้ 2 ชนิด คือ HCT116 และ SW480 เกิดการตายแบบ apoptosis โดยลดการแสดงออกของ HSP70 เป็นต้น
Abstract
Betulinic acid (BA) is a pentacyclic triterpene usually isolated from botanical sources. Numerous studies have reported the inhibitory effect of BA against human colorectal cancer cells (CRC). However, its effect on the expression of the molecular chaperone HSPA is unclear. The aim of this research is to investigate the anti-cancer activities of BA purified from Piper retrofractum and study its effect on the expression of HSPA in colorectal cancer HCT116 and SW480 cells. The viability of both cancer cells was reduced after they were treated with an increasing dosage of BA. Flow cytometry assay revealed that levels of cell apoptosis significantly increased after incubation with BA in both cancer cells. Pro-apoptotic markers including Bax, cleaved-caspase-3 and cleaved-caspase-9 were increased while anti-apoptotic marker Bcl-2 was decreased after BA treatment. Western blot also showed that the expression of HSPA fluctuated upon BA treatment, whereby HSPA was increased at lower BA concentrations while at higher BA concentrations HSPA expression was decreased. Preliminary molecular docking assay showed that BA can bind to the nucleotide binding domain of the HSP70 at its ADP-bound state of the HSP70. Although further research is needed to comprehend the BA-HSPA interaction, our findings indicate that BA can be considered as potential candidate for the development of new treatment for colorectal cancer.
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
Betulinic acid (BA) เป็นสารกลุ่มไตรเตอร์ปีนที่ถูกสกัดจากพืช โดยมีคุณสมบัติเป็นสารที่ต้านมะเร็งในลำไส้ใหญ่ในระดับเซลล์ แต่ยังไม่ทราบเกี่ยวกับกลไกที่เกี่ยวข้องกับโปรตีน heat shock proteins (HSPs) ในการศึกษาวิจัยนี้จึงมุ่งเน้นศึกษาประโยชน์ของสารสกัดโดยงานวิจัยนี้พบว่า สาร BA สามารถยับยั้งการมีชีวิตของเซลล์มะเร็งลำไส้ใหญ่ทั้งสองชนิด HCT116 และ SW480 โดยขึ้นกับความเข้มข้นของสาร BA ผ่านกระบวนการชักนำให้เกิดการตายแบบ apoptosis โดยพบการแสดงออกของ Bax, cleaved-caspase-3 และ cleaved-caspase-9 ที่เพิ่มขึ้น และลดการแสดงออกของ Bcl-2 รวมทั้งพบการแสดงออกของ HSPA ที่จะลดลง ซึ่งสอดคล้องกับการศึกษาทางคอมพิวเตอร์ในเบื้องต้น พบว่า สาร BA สามารถจับกับตำแหน่งของ nucleotide binding domain ของ HSP70 แต่อย่างไรก็ตามคณะผู้วิจัยยังต้องศึกษารายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมของปฏิกิริยาที่เกิดขึ้นระหว่างสาร BA และ HSPA นี้ โดยคาดว่าการศึกษานี้อาจนำไปสู่การพัฒนาการรักษาโรคมะเร็งลำไส้ใหญ่ได้
KEYWORDS: betulinic acid, HSPA, apoptosis, colorectal cancer
Citation:
Yurasakpong L, Nantasenamat C, Nobsathian S, Chaithirayanon K, Apisawetakan S. Betulinic Acid Modulates the Expression of HSPA and Activates Apoptosis in Two Cell Lines of Human Colorectal Cancer. Molecules. 2021; 26(21):6377.
https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216377
RELATED SDGs:
SDG Goal หลัก ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Laphatrada Yurasakpong
ภาพถ่าย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
Tags: Apoptosis, betulinic acid, colorectal cancer, HSPA
