Highlight
การปรับโครงสร้างสารสกัดซัลเฟต กาแลคแตนจากสาหร่ายผมนางมีผลเพิ่มฤทธิ์ต้านแบคทีเรียก่อโรคในกุ้งชนิดVibrio parahaemolyticus และ Vibrio harveyi
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
อุตสาหกรรมการเพาะเลี้ยงกุ้งได้รับผลกระทบผลผลิตต่ำจากการติดเชื้อแบคทีเรียก่อโรคVibrio parahaemolyticus และ Vibrio harveyi งานวิจัยก่อนหน้าพบสารซัลเฟตโพลิแซคคาไรด์ธรรมชาติที่สกัดจากสาหร่ายผมนางมีฤทธิ์ยับยั้งการเจริญของแบคทีเรียทั้ง 2 ชนิดนี้ได้ ฤทธิ์ทางชีวภาพของสารกลุ่มโพลิแซคคาไรด์มีความสัมพันธ์กับน้ำหนักโมเลกุลและโครงสร้างทางเคมี การศึกษานี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อปรับโครงสร้างสารซัลเฟตกาแลคแตนสกัดธรรมชาติจากสาหร่ายผมนางโดยการย่อยให้มีขนาดเล็กลง ศึกษาโครงสร้างและทดสอบการเพิ่มศักยภาพในการยับยั้งการเจริญและฆ่าแบคทีเรียของสารที่ได้จากการปรับโครงสร้างเปรียบเทียบกับสารสกัดธรรมชาติ เพื่อการใช้ประโยชน์สูงสุดจากการใช้สารสกัดจากสาหร่ายผมนางผสมเป็นสูตรอาหารกุ้งต่อไป
Abstract
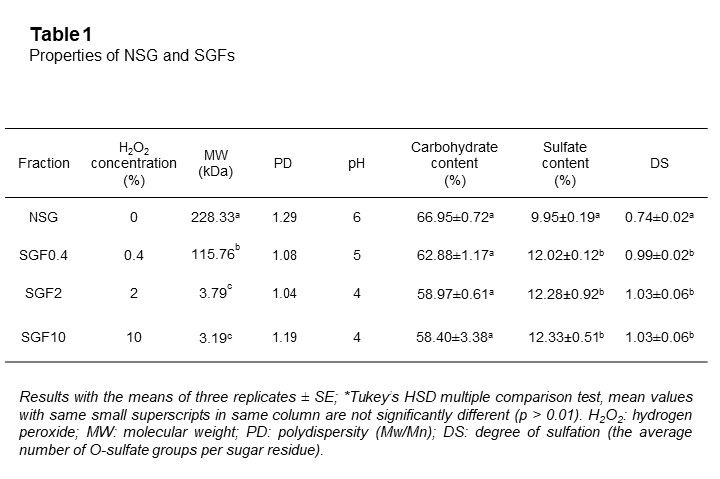
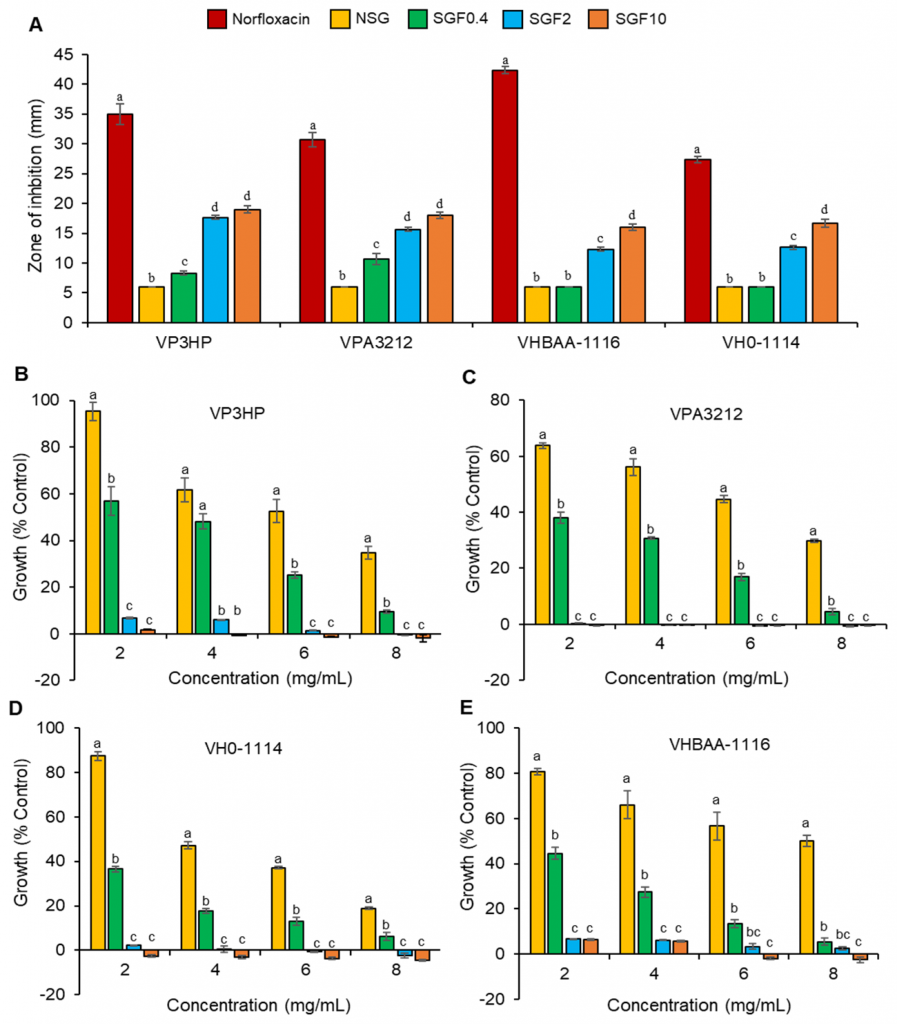
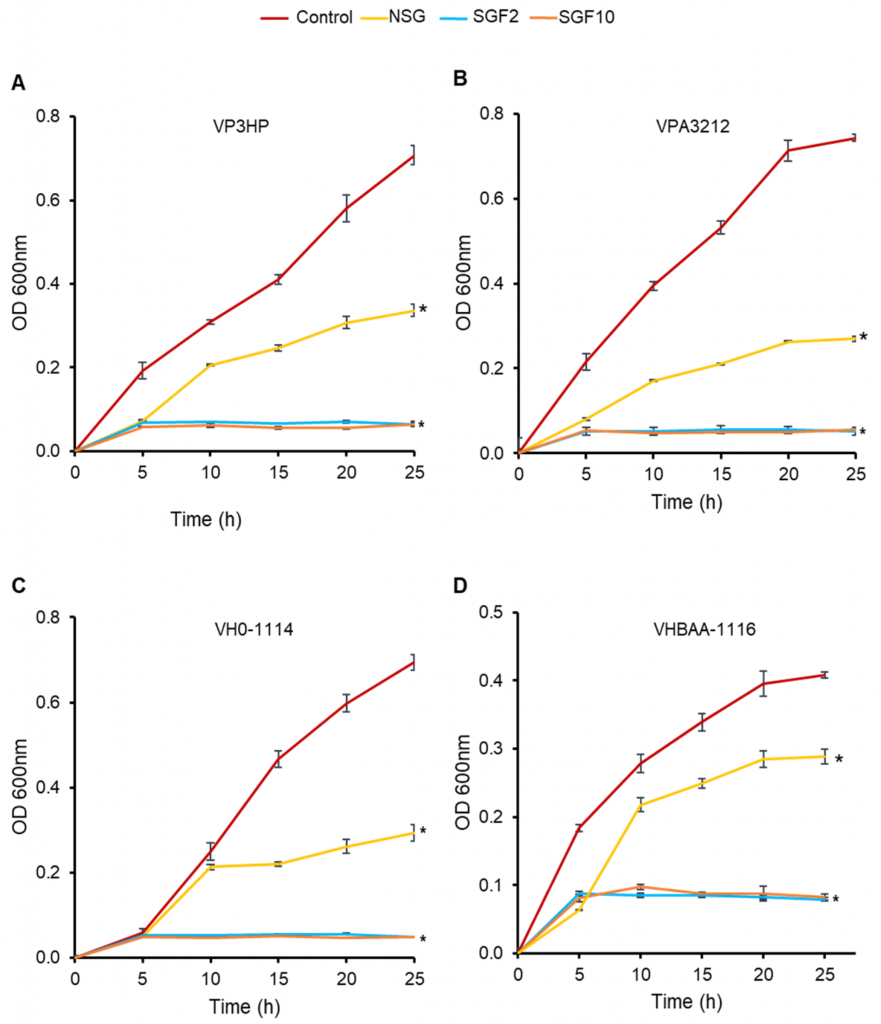
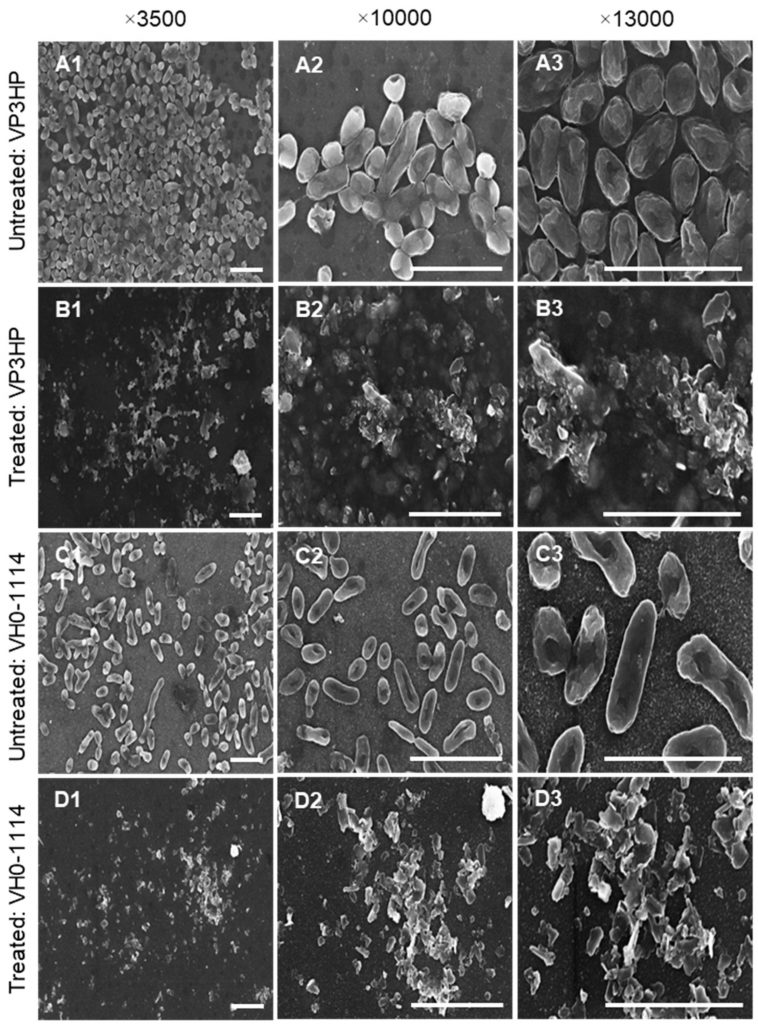
Various seaweed sulfated polysaccharides have been explored for antimicrobial application. This study aimed to evaluate the antibacterial activity of the native Gracilaria fisheri sulfated galactans (NSG) and depolymerized fractions against the marine pathogenic bacteria Vibrioparahaemolyticus and Vibrio harveyi. NSG was hydrolyzed in different concentrations of H2O2 to generate sulfated galactans degraded fractions (SGF). The molecular weight, structural characteristics, and physicochemical parameters of both NSG and SGF were determined. The results revealed that the high molecular weight NSG (228.33 kDa) was significantly degraded to SGFs of 115.76, 3.79, and 3.19 kDa by hydrolysis with 0.4, 2, and 10% H2O2, respectively. The Fourier transformed spectroscopy (FTIR) and 1H- and 13C-Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyses demonstrated that the polysaccharide chain structure of SGFs was not affected by H2O2 degradation, but alterations were detected at the peak positions of some functional groups. In vitro study showed that SGFs significantly exerted a stronger antibacterial activity against V. parahaemolyticus and V.harveyi than NSG, which might be due to the low molecular weight and higher sulfation properties of SGF. SGF disrupted the bacterial cell membrane, resulting in leakage of intracellular biological components, and subsequently, cell death. Taken together, this study provides a basis for the exploitation and utilization of low-molecular-weight sulfated galactans from G. fisheri to prevent and control the shrimp pathogens.
KEYWORDS: Low-molecular-weight sulfated galactans, Gracilaria fisheri, Hydrogen peroxide, Antibacterial activity, V. parahaemolyticus, V. harveyi
Citation: Kamble MT, Rudtanatip T, Soowannayan C, Nambunruang B, Medhe SV, Wongprasert K. Depolymerized Fractions of Sulfated Galactans Extracted from Gracilaria fisheri and Their Antibacterial Activity against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio harveyi. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(8):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080469
RELATED SDGs:
2. ZERO HUNGER

14. LIFE BELOW WATER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: Manoj Tukaram Kamble, Boottoh Nambunruang
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Mahidol University (Fundamental Fund: Basic Research Fund: fiscal year 2022, Grant no. BRF1-054/2565 and the Postdoctoral Research Sponsorship, Project No. MU-PD_2020_3), and the CIF and CNI Grant, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University
Credit ภาพ: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กนกพรรณ วงศ์ประเสริฐ
Tags: Antibacterial activity, Gracilaria fisheri, Hydrogen peroxide, Low-molecular-weight sulfated galactans, V. harveyi, V. parahaemolyticus
