การศึกษาผลของ short neuropeptide F ต่อการพัฒนาของรังไข่ การตกไข่ และกลไกการควบคุม ในกุ้งก้ามกรามเพศเมีย Macrobrachium rosenbergii
Highlight:
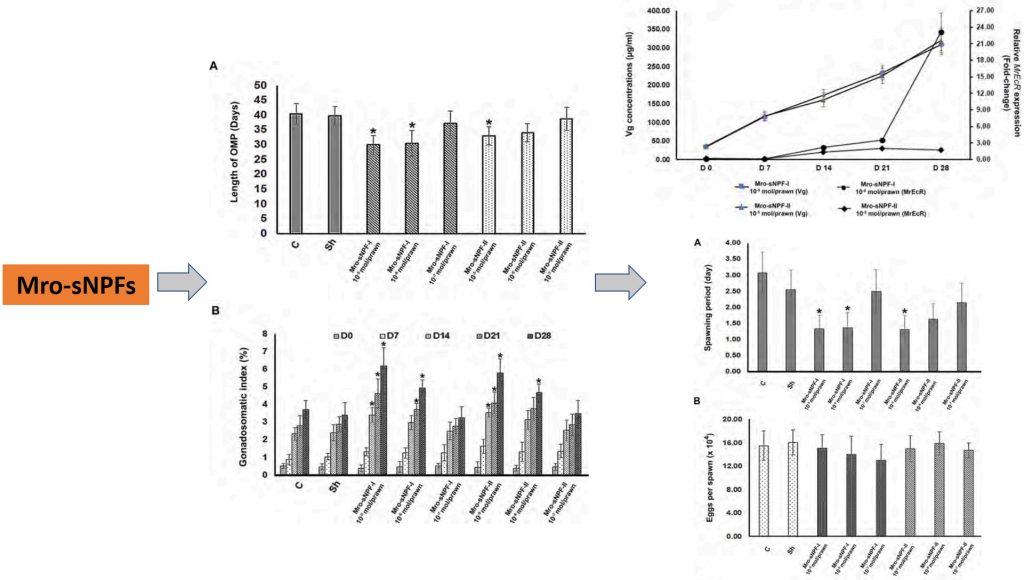
คณะผู้วิจัยได้พบองค์ความรู้พื้นฐานใหม่ที่สำคัญคือ short neuropeptide F (Mro-sNPF) มีผลต่อการพัฒนาของรังไข่และการตกไข่ในกุ้งก้ามกรามเพศเมีย Macrobrachium rosenbergii โดยพบว่า เปปไทด์ Mro-sNPF ทำให้ระยะเวลาการพัฒนาของรังไข่สั้นลง เพิ่มดัชนีโกนาโดโซมาติก (GSI) เพิ่มขนาดเส้นผ่านศูนย์กลางไข่ (OD) และการเพิ่มจำนวนการแบ่งเซลล์ เมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับกลุ่มควบคุม (P<0.05) นอกจากนี้พบว่า เปปไทด์ Mro-sNPF เพิ่มระดับความเข้มข้นของ hemolymph vitellogenin และการเพิ่มระดับของ MrEcR เมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับกลุ่มควบคุม อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (P<0.05) เปปไทด์ Mro-sNPF ยังคงเหนี่ยวนำให้เกิดการตกไข่ได้เร็วขึ้นโดยลดระยะเวลาลงครึ่งหนึ่ง เมื่อเทียบกับระยะเวลาการตกไข่ของกลุ่มควบคุม (P<0.05) เปปไทด์ Mro-sNPF มีศักยภาพในการกระตุ้นการผลิตเซลล์สืบพันธุ์ การพัฒนาของไข่ และการตกไข่ในกุ้งก้ามกราม ตลอดจนน่าจะสามารถนำไปการประยุกต์ใช้ในระบบเพาะเลี้ยงต่อไป
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
In decapod crustaceans, eyestalk ablation has been practiced by aquaculturists to enhance commercial production through the induction of ovarian maturation; however, this technique eventually leads to undesirable effects of decline in egg quality and quantity, precocious development of gonads, and early death of spawners. In recent years, hormonal manipulation has proven a more sustainable alternative to successfully promote ovarian development, and this approach has the potential to replace eyestalk ablation. Understanding of hormones controlling the development of gonads, which produce quality gametes for larval production, is essential to the success of crustacean aquaculture. Thus, in this study, we are the first to report the potent effect and regulatory mechanisms of short neuropeptide F (Mro-sNPFs) on the induction of ovarian maturation and spawning, and associated regulatory mechanisms in M. rosenbergii females. Therefore, Mro-sNPF treatment could be applied to solve prawn aquaculture problems by increasing gamete production of this crustacean species for aquaculture.
Abstract
In the present study, we investigated the effects of two short neuropeptide F (Mro-sNPF) mature sequences, namely APALRLRFamide and DRTPALRLRFamide, on ovarian maturation and spawning in Macrobrachium rosenbergii females. At doses of 10−5 and 10−6 mol/prawn, both Mro-sNPF peptides significantly shortened the ovarian developmental period (P < 0.05), but enhanced the gonadosomatic index (GSI), oocyte diameter (OD), and cell proliferation, compared with control values (P < 0.05). However, at the lowest dose (10−7 mol/prawn), neither peptide significantly affected ovarian maturation, GSI, nor OD compared with the control values. Females treated with the two peptides at the dose of 10−5 or 10−6 mol/prawn attained mature oocyte stages faster than did control females. Treatment with both peptides significantly elevated hemolymph vitellogenin concentrations and upregulated MrEcR transcripts, compared with the control treatment (P < 0.05). Finally, both Mro-sNPFs induced spawning by shortening its duration by half (∼1.5 days) compared with the control duration (∼3.1 days) (P < 0.05). The number of eggs per spawn was approximately 15.4 × 104 eggs in the experimental group and in the control group (∼15.35 × 104 eggs), albeit without significance. Therefore, among the treatment groups, using APALRLRFamide at 10−5 mol/prawn showed promising effects on the induction of ovarian maturation and spawning. Taken together, Mro-sNPF peptides can promote ovarian development and spawning, indicating their potential application to stimulate gamete and larval production in this important crustacean aquaculture species.
Keywords: Short neuropeptide F, Ecdysteroids, Ovarian development, Spawning, Freshwater prawn
Citation: Yotsawan Tinikul, Ruchanok Tinikul, Attakorn Engsusophon, Prasert Sobhon, The effects of short neuropeptide F on ovarian maturation and spawning in female giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, and associated regulatory mechanisms, Aquaculture, Volume 569, 2023, 739361, ISSN 0044-8486, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739361.
RELATED SDGs:
14. LIFE BELOW WATER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ยสวันต์ ตินิกุล
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.ยสวันต์ ตินิกุล
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: Thailand Science Research and Innovation, Mahidol University (TRF Mid-Career Research Grant), Mahidol University (Fundamental Fund: Basic Research Fund, fiscal year 2022), The NSRF via the Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development, Research and Innovation, and Faculty of Science, Mahidol University.
Tags: Ecdysteroids, Freshwater prawn, Ovarian development, Short neuropeptide F, Spawning
