ฤทธิ์การป้องกันและการซ่อมแซมของสารสกัดหยาบปลิงทะเลขาว Holothuria scabra ในหนูทดลองและเซลล์ทดลองที่ถูกชักนำให้เกิดโรคพาร์กินสันด้วย MPTP/MPP+
Highlight:
สารสกัดหยาบปลิงทะเลขาว Holothuria scabra (HS) มีฤทธิ์ในการป้องกันและซ่อมแซมเซลล์ประสาทในหนูทดลองและเซลล์ที่คล้ายเซลล์โดปามีนที่ถูกชักนำให้เกิดโรคพาร์กินสัน โดยผ่านขบวนการลดการตายแบบ apoptosis ยับยั้งการสร้าง α-synuclein protein และเพิ่มการแสดงออกของ tyrosine hydroxylase
ที่มาและความสำคัญ
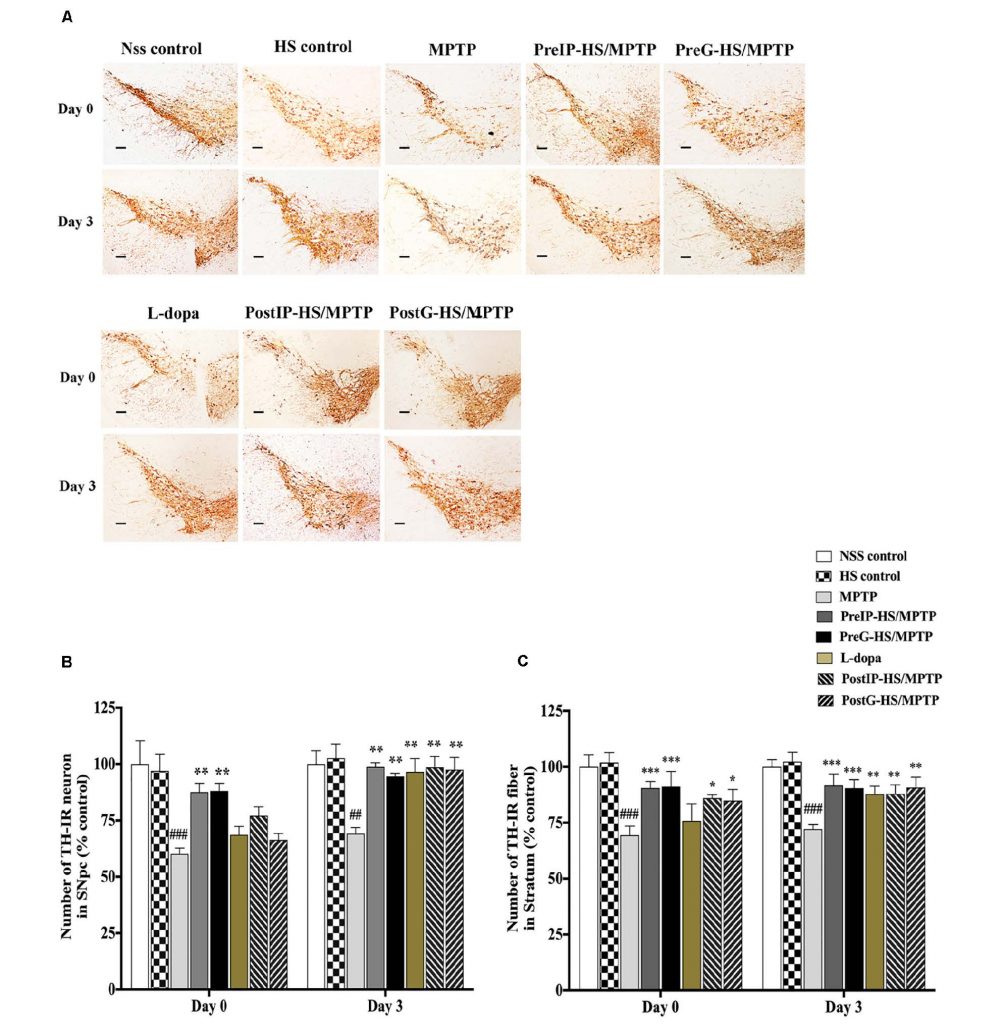
สารสกัดหยาบปลิงทะเลขาว Holothuria scabra (HS) มีคุณสมบัติที่ต้านการอักเสบ ต้านอนุมูลอิสระ และต้านมะเร็ง รวมทั้งมีศักยภาพในการป้องกันการเสื่อมของเซลล์ประสาทที่พบในหนอน Caenorhabditis elegans ที่เป็นโรคพาร์กินสัน การศึกษาวิจัยนี้จึงมุ่งเน้นศึกษาประโยชน์ของสารสกัดปลิงทะเลขาว HS ที่มีคุณสมบัติในการป้องกันและซ่อมแซมเซลล์ประสาทโดปามีนในเซลล์ทดลองและหนู พบว่าการรักษาด้วยวิธีก่อนและหลังให้สารสกัดนี้ในหนูทดลองที่ถูกชักนำให้เกิดโรคพาร์กินสันด้วย 1- methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) ทำให้หนูมีการเคลื่อนไหวแบบ grid walk ดีขึ้น ร่วมกับการเพิ่มจำนวนเซลล์ประสาทโดปามีนและเส้นใยประสาทใน substantia nigra pars compacta และ striatum ส่วนในระดับเซลล์พบว่าสารสกัดนี้ลดการตายแบบ apoptosis ในเซลล์ประสาทที่มีลักษณะคล้ายเซลล์โดปามีนที่ถูกชักนำให้เกิดโรคพาร์กินสันด้วยสาร 1-methyl- 4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) โดยการเพิ่มการแสดงออกของ Bcl-2, ลดการแสดงออกของ cleaved caspase 3 และป้องกันการเกิด depolarization ของผนังไมโตคอนเดรีย รวมทั้งยังเพิ่มการแสดงออกของ tyrosine hydroxylase และ ยับยั้งการสร้าง α-synuclein protein
Abstract
Extracts from Holothuria scabra (HS) have been shown to possess anti-inflammation, anti-oxidant and anti-cancer activities. More recently, it was shown to have neuroprotective potential in Caenorhabditis elegans PD model. Here, we assessed whether HS has neuroprotective and neurorestorative effects on dopaminergic neurons in both mouse and cellular models of PD. We found that both pre-treatment and post-treatment with HS improved motor deficits in PD mouse model induced with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) as determined by grid walk test. This was likely mediated by HS protective and restorative effects on maintaining the numbers of dopaminergic neurons and fibers in both substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and striatum. In a cellular model of PD, HS significantly attenuated 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+)-induced apoptosis of DAergic-like neurons differentiated from SH-SY5Y cells by enhancing the expression of Bcl-2, suppressing the expression of cleaved Caspase 3 and preventing depolarization of mitochondrial membrane. In addition, HS could stimulate the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and suppressed the formation of α-synuclein protein. Taken together, our in vivo and in vitro findings suggested that HS is an attractive candidate for the neuroprotection rather than neurorestoration in PD.
KEYWORDS: Holothuria scabra, MPP+, MPTP, tyrosine hydroxylase, α-synuclein, striatal dopamine
Citation: Noonong K, Sobhon P, Sroyraya M and Chaithirayanon K (2020) Neuroprotective and Neurorestorative Effects of Holothuria scabra Extract in the MPTP/MPP+-Induced Mouse and Cellular Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 14:575459. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.575459
https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.575459
RELATED SDGs:
3. GOOD HEALTH AND WELL-BEING

14. LIFE BELOW WATER

ผู้ให้ข้อมูล: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์
ชื่ออาจารย์ที่ทำวิจัย: รองศาสตราจารย์ ดร.กุลธิดา ชัยธีระยานนท์, ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร.มรกต สร้อยระย้า
ชื่อนักศึกษาที่ทำวิจัย: นางสาวกุลวดี หนูหนอง
แหล่งทุนวิจัย: สำนักงานพัฒนาการวิจัยการเกษตร (องค์การมหาชน)
Tags: Holothuria scabra, MPP+, MPTP, striatal dopamine, tyrosine hydroxylase, α-Synuclein
